Muscular System Study Guide: Key Terms & Concepts
advertisement

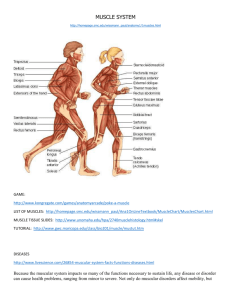
Muscular System Study Guide TEST on Thursday January 29 Key Terms- Be able to define and describe the structure/function/location of the following terms: Flexion Extension Tendon Ligament Fascicle Muscle Fiber Myofibril Myofilament Concepts- Actin Mysosin Thick/Dark Filament Thin/Light Filament Sliding Filament Theory Sarcolemma Sarcoplasm Neuromuscular Junction. Troponin/Tropomyosin Smooth Muscle Cardiac Muscle Skeletal Muscle Striated Involuntary/Voluntary Sarcomere 1. Functions of the Muscular System 2. Sliding Filament Theory- Understand the basic steps described in class and be able to explain how the nervous system, Calcium, ATP/ADP, myosin heads, actin, power stroke, etc all contribute to a muscle contraction. 3. Muscle Fatigue 4. Clinical Applications of Muscular System- Be prepared to answer questions regarding each topic. Specific information was presented on Thursday and can be located on class resource page. Muscular Atrophy & Muscular Hypertrophy p 279 Exercise Induced Muscle Damage p 279 Rigor Mortis p 285 Pharmacology of the NMJ p 286 Creatine Supplementation p 290 Aerobic Training vs Strength Training p 293 Anabolic Steroids p 297 5. Structure of the Muscle-how is it arranged? 6. Identification-You will be responsible for the knowing location and function of all the muscles we noted/starred on the coloring page.(Frontal, Orbicularis Oculi, Orbicularis Oris, Masseter, Temporal, Sternocleidomastoid, Trapezius, Pectoralis Major, Latissus Dorsi, Deltoid, Biceps Brachii, Triceps Brachii, External Obliques, Rectus Abdominus, Sartorius, Gluteus Maximus, Quadriceps Group, Hamstring Group, gastrocnemius, ) 7. Three Types of Muscle- How they look, where they’re located, whether they are voluntary or involuntary. Be able to identify them based on their visual appearance. 8. Muscular Diseases/Disorders-Muscular Dystrophy, Fibromyalgia, Cerebral Palsy, Distonia and Spinal Muscle Atrophy. Review Muscular System Intro Packet and notes from Monday’s video. 9. Understand how muscles can only contract and relax and they work in pairs to create smooth movement. 10. Review all Analysis & Review Questions from the Stations Lab