Chapter 26 Urinary system infections
advertisement

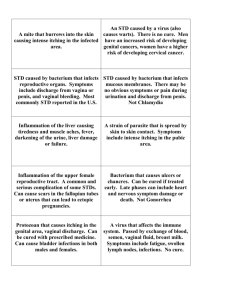
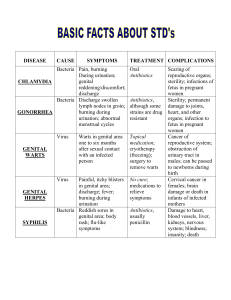
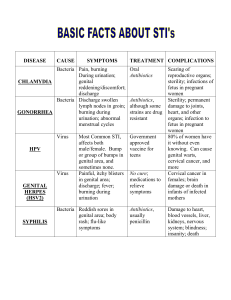
Chapter 26 Urinary system infections Medgar Evers College Bio 261 Prof. Santos Anatomy of Female Urinary system Normal Microbiota • The upper urinary tract is void of normal microbiota. • The lower urethra is inhabited by certain microorganisms such as species of Lactobacillus, Staphylococcus, Corynebacterium, Haemophilus, Streptococcus, and Bacteroides. Women • Microbiota is influenced by estrogen level. • After puberty, the level of estrogen increases. This increase causes an increase in Lactobacillus that produces acid by products that lower the pH of the vagina. • This low pH keeps other pathogens away. Urinary system Infections • Microbes usually enter the reproductive system through the: • • Vagina (females) or urethra (males) Bacterial Disease Cause Sympto ms Pathoge treatmen nesis t Bacterial Cystitis Cystitis usually caused by E. coli & S. saprophyticus • May also be caused by Proteus, Klebsiella, Enterococcus, Pseudomonas Burning, Bacterial painful, frequent ascends the urination, foul urethra. smell and red colored urine, fever, chills, back pain, vomiting Antimicrobial medication, hygiene, and drinking fluids. Leptospirosis Disease Cause Sympto ms Pathoge Treatme nesis nt Leptospirosis Leptospira interrogans Chills, fever, headache, muscle aches Penetration of mucous membrane, travels via bloodstream, and colonization throughout body. Avoid contact with animal urine, An antibiotics such as tetracycline. Genital system diseases • Sexually transmitted vs. non sexually transmitted. Bacterial vaginosis Disease Cause Symptoms Pathogenesis treatment Bacterial vaginosis Gardnerella Vaginalis A small aerotolerant, gram positive bacteria Infection without inflammation; thin white grayish bubbly vaginal discharge, fishy odor, Diagnosis by clue cells, higher vaginal pH Treatment: metronidazole Normal clue cell of Human Vagina Infected clue cells Vulvovaginal Candidiasis Disease Cause Sympto ms Pathoge Treatme nesis nt Vulvovaginal Candidiasis Candida albicans Itching, burning, thick white vaginal discharge, redness and swelling An inflammatory response to the overgrowth of the yeast An antifungal medication such as clotrimazole. Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome Disease Cause Symptoms Pathogenesis treatment Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome S. aureus fever, diarrhea, vomiting, muscle aches, low blood pressure, and a rash. Toxin (TSST-1) A superantigen Antimicrobial agents, frequent change of tampons by menstruating women Bacterial sexually transmitted diseases • Most of these are STD’s (sexually transmitted diseases) • Prevented by condoms • Treated with antibiotics Bacterial infections include • • • • Gonorrhea Chlamydial Genital System infections Syphilis Chancroid Gonorrhea- most common reported STD in the United States Incidence of Gonorrhea on the USA USA Distribution of Gonorrhea Gonorrhea • agent of infection =Neisseria gonorrhoeae • Attaches to oral or urogenital mucosa by fimbriae • Females may be asymptomatic; males have painful urination and pus discharge • Treatment with antibiotics • Untreated may result in endocarditis, meningitis, and arthritis and ophthalmia neonatorum – infant eye infections Gonorrhea – gram-negative, pairs of cocci Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) • Polymicrobic, usually – N. gonorrhoeae – C. trachomatis • Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs. It usually occurs when sexually transmitted bacteria spread from your vagina to your uterus and upper genital tract. Signs and symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease may include: • • • • • • • • Pain in your lower abdomen and pelvis Heavy vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor Irregular menstrual bleeding Pain during intercourse Low back pain Fever, fatigue, diarrhea or vomiting Painful or difficult urination PID may cause only minor signs and symptoms or none at all. Asymptomatic PID is especially common when the infection is due to chlamydia. Chlamydial genital system infections Disease Cause Sympto ms Pathoge treatmen nesis t Chlamydial genital system infections Chlamydia trachomatis Men; whitegray penile discharge, pain in the testes Women; vaginal discharge and bleeding and lower and upper abdominal pain Bacteria attaches to specific receptors on the epithelial cells, inflammatory response and massive cellular immune response causes damage Azithromycin and other antimicrobial medications. The U.S. Incidence of Syphilis Geographical Distribution of Syphilis Syphilis •Caused by Treponema pallidum •Invades mucosa or through skin breaks Syphilis • Primary stage: Chancre at site of infection • Secondary stage: Skin and mucosal rashes • Latent period: No symptoms • Tertiary stage: Gummas on many organs • Treatment: Benzathine penicillin • Congenital: Neurological damage Lesions of Primary Stage Syphilis Lesions of Secondary Stage Syphilis Lesions of Tertiary Stage Syphilis Chancroid (Soft Chancre) • Causative agent: Haemophilus ducreyi • Symptoms: Painful ulcers of genitals swollen lymph nodes in groin • Diagnosis: Culture • Treatment: Erythromycin; cetriaxone Viral STD’S Genital Herpes • Caused by herpes simplex virus 2 (human herpesvirus 2, or HSV–2) • Painful vesicles on genitals • Neonatal herpes transmitted to fetus or newborns • Recurrences from viruses latent in nerves • Suppression: Acyclovir Genital Warts • Human papillomaviruses • Warts in genital area • HPV 16 causes cervical cancer and cancer of the penis • Treatment: Podofilox; imiquimod • Prevention: Vaccination against HPV strains Male genital warts AIDS Disease Cause Symptoms Pathogenesis treatment AIDS Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 No symptoms or flu like symptoms, latent period followed by other infections that are opportunistic HIV-1 infects CD+4 t cells and macrophages and destroys them and thus weakening the immune system Abstinence from sex, protection, antiviral medications such as reverse transcriptase and protease inhibitors, and good life style Protozoal STD Trichomoniasis • Causative agent: Trichomonas vaginalis • Found in semen or urine of male carriers • Vaginal infection causes irritation and profuse foul, greenish yellow frothy discharge • pH: 5–8 • Diagnosis: Microscopic identification, DNA probe • Treatment: Metronidazole