Genital Tract Infections MLAB 2434 – Microbiology Keri Brophy-Martinez
advertisement

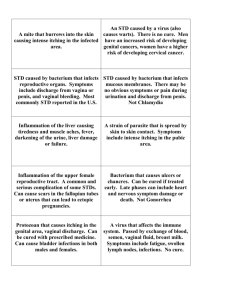
Genital Tract Infections MLAB 2434 – Microbiology Keri Brophy-Martinez Definitions STI = Sexually Transmitted Infection STD = Sexually Transmitted Disease VD = Venereal Disease After Venus, goddess of love Modes of Transmission Intimate person-person sexual contact Vaginal intercourse Oral sex Anal sex Mother to child Pregnancy Childbirth Blood products/ tissue transplant Sexually Transmitted Infections Genital Chlamydiosis Chlamydia trachomatis • Obligate intracellular bacterium Most common bacterial STD Symptoms • Male: urethritis, discharge • Female: Usually asymptomatic; can progress to PID Chlamydia trachomatis Lab Diagnosis Not culturable Identified by nucleic acid probes Sexually Transmitted Infections Neisseria gonorrhoeae Infects columnar epithelial cells of the GU tract Incubation period 2-7 days Can spread in blood, producing rash on extremities and arthritis in joints Neisseria gonorrhoeae Symptoms Male: urethral inflammation with dysuria, pyuria, urethral discharge Female: asymptomatic; can lead to PID Treatment Cephalosporin antibiotic class • Cefixime or ceftriaxone with doxycycline Neisseria gonorrhoeae Laboratory Diagnosis Typical GN dc, kidney- bean shape Gram stain significant in males, not in females( due to other GN normal flora) Identify via CTA sugars or other rapid kits Market using DNA probes instead of culture Sexually Transmitted Infections (cont’d) Ulcerative STI’s Syphilis – Treponema pallidum • Incubation period of 1-90 days • Chancre development at site of inoculation, full-body rash, potential to affect the CNS • Can not be cultured; DFA or serology testing (RPR) used Sexually Transmitted Infections (cont’d) Chancroid – Haemophilus ducreyi • Seen in underdeveloped countries • Incubation period 4-7 days after exposure • Erythematous papule develops into a pustule which ruptures to form an ulcer. Ulcer usually found on external genitalia • Lab diagnosis • Direct smear (school of fish) and culture of ulcer • Oxidase positive; catalase negative Sexually Transmitted Infections (cont’d) Genital Herpes- Herpes Simplex Virus • • • • HSV-1: fever blisters/ cold sores HSV-2: genital herpes Virus is shed in the absence of symptoms Transmitted by sexual contact with secretions from infected sites • Incubation period 1-26 days after exposure • Lab diagnosis • Viral isolation-cheap • Molecular testing- improved sensitivity & TAT Sexually Transmitted Infections (cont’d) Bacterial vaginitis Signs • Discharge • Vaginal itching • Odor STD’s • Bacterial vaginosis • Trichomoniasis Bacterial vaginosis Loss of normal vaginal flora Mobiluncus, Mycoplasma hominis, and Gardnerella vaginalis take over pH increases causing a fish-like odor Bedside diagnosis pH- greater than 4.5 Whiff test-addition of KOH, smell for a fishy odor Bacterial Vaginosis Lab diagnosis • Wet Prep • Clue cells: exfoliated vaginal epithelial cells covered with GVR and curved GNR’s • Lack of PMN’s • Presence of odor, pH >4.5 • Culture • No growth on BAP • V agar: shows as beta hemolytic colonies • Catalase/Oxidase negative Trichomonas vaginalis Flagellated, urogential parasite Symptoms Itching Burning Yellow-green frothy discharge Foul-smelling odor Lab Diagnosis Wet Prep • Observance of moving parasites in vaginal discharge Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Common STD in individuals under 24 Skin- skin transmission Asymptomatic Self-limiting Associated with genital warts and cervical cell dysplasias and cancers Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Systemic illness Transmission via sexual contact, exposure to blood or body fluids Virus attacks the CD4 helper T-cells Increased potential for opportunistic pathogens Symptoms include: fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy, skin rash Lab Diagnosis HIV-1 antibody test- screen Western blot/immunofluorescence- confirmatory Genital Bacterial Cultures: Specimen Collection, Transport and Handling Specimen types Urethral discharge Cervical/ vaginal Throat Anus Specimen collection, transport and handling Cotton, rayon or dacron swabs Isolation of gonococci • Place in modified Stuart’s or Amie’s (with charcoal) • prevents drying • Culture within 6 hours of collection Viral culture • Place swab in viral transport media. Genital Cultures Direct Examination Gram stain • Performed on male urethral discharge • Examine for bacteria (intra & extracellular), PMN’s and other cells Wet mount • Performed on vaginal discharge • Examine for clue cells, yeast, Trichomonas vaginalis • Examine for PMN’s Genital Bacterial Cultures: Culture Set-Up Examples of media to inoculate Incubate media • • • • • • BAP MAC Chocolate CNA V- agar Thayer-martin, Modified Thayer-Martin, GCLect • Lim broth Temperature: 35OC Atmosphere: CO2 Time: 18-24 hours Genital Bacterial Cultures: Culture Interpretation Quantitate and identify all potential pathogens Preliminary report sent out at 24 hours Hold all plates 72 hours Genital Tract: Pathogens Neisseria gonorrhoeae Hemophilus ducreyi Gardnerella vaginalis Trichomonas vaginalis Beta-hemolytic Streptococci Groups A and B Listeria species Staphylococcus aureus Candida/yeast species Gram negative rods • In predominant numbers • In predominant numbers • Accompanied by an absence of normal flora Genital Tract: Normal Flora Lactobacillus sp. Coagulase negative Staphylococcus species Diptheroids Anaerobic cocci and gram negative rods Enterococcus species References Hook, E. W. (2012, July). A new look at genital herpes: the critical role of the laboratory in diagnosis and management. Medical Laboratory Observer, 44(7), 8-12. http://www.atsu.edu/faculty/chamberlain/golden2000/cas e5.htm http://tiny.cc/kcpyhw Kiser, K. M., Payne, W. C., & Taff, T. A. (2011). Clinical Laboratory Microbiology: A Practical Approach . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. Mahon, C. R., Lehman, D. C., & Manuselis, G. (2011). Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology (4th ed.). Maryland Heights, MO: Saunders.