DIFFERENT KINDS OF JOINTS
advertisement

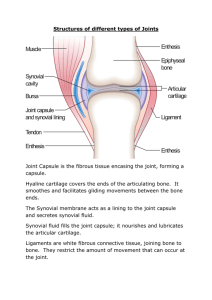
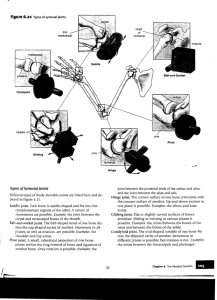
DIFFERENT KINDS OF JOINTS 5.4 Joints are where two or more bones meet. They are divided into three types depending on how freely the bones can move. Movement would not be possible without the three joint types. 1. Fixed or immovable joints Eg. Joints between cranium plates. 2. Slightly moveable joints Eg. Between vertebrae and ribs 3. Freely moveable (synovial) joints Eg. Knee, shoulder and elbow joints Fixed or immovable joints • Bones cannot move at all. • They interlock/overlap-held together by tough fibre. • Present in areas requiring great strength. The joints in the cranium and sacrum (base of the spine) are good examples. Sacrum Slightly moveable joints • Limited movement. • Held together by strong, white straps called ligaments and joined by cartilage. This acts as a cushion and stops bones rubbing together. • Eg. Joints between your vertebrae and ribs. In the vertebrae the cartilage acts as shock absorbers when running and jumping. • The joints between your ribs and sternum move slightly when you breath in and out. Remember- Ligaments: Join bone to bone Tendons: Join muscle to bone Freely moveable joints Also called synovial joints. They all have these parts: Joint capsule: Holds together and protects Synovial membrane: Lines the capsule and contains synovial fluid Joint cavity: Small gap between the bones Cartilage: Covers end of bones Ligaments: Holds bones together and keeps them in place Eg. Freely moveable joints (cont) Divided into four types: 1) Ball/socket, 2) Hinge, 3) Pivot 4) Gliding Ball and Socket Joint • Most moveable joint • One bone has a ball that fits into a socket on the Hip joint other one. • Can turn in many directions. • Eg. Hip and shoulder joint. Shoulder joint The hinge joint • Works like a hinge on a door. • The bone can swing backwards and forwards. • Cotton reel shaped bone fits into a hollow on the other. • The joint will open until it is straight, but no further. • Eg. The elbow and knee joints The pivot joint One bone has a bit that juts out, like a peg. This fits into a ring or notch on the other bone. • Limited movement (Only rotation). • Eg. Joint between atlas and axisThe top two bones of your vertebrae. • The joint between the radius and the ulna (Bones in your lower elbow) The gliding joint • The ends of the bone are flat enough to glide over each other. • There is a little movement in all directions. • Least movement of all synovial joints. • Eg. Joints between carpals (hand) and tarsals (foot). carpals