Answer key for Ch 14 Zumdahls select prob 1-53 - OPHS
advertisement

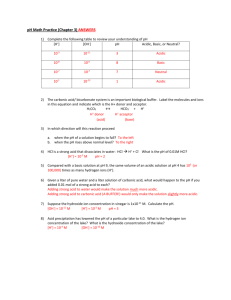
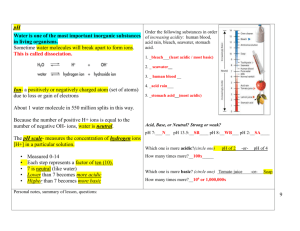
Answer key for Ch 14 Zumdahls 1. @ different temps, H2O has different values for Kw (see problem #47) – Different Kw values will give different [H+], which will in effect change the pH, the higher the temp the lower the pH value drops. ****Keep in mind though that the sample of pure water will still be neutral, the [H+]=[OH-]. 2. Strength refers to the ability of an acid or base to dissociate. Strong acids/bases completely dissociate, while weak acids/bases dissociate less than 5%. Concentration refers to the number of moles per unit of volume. Both strong and weak acids/bases can be concentrated or dilute. HCl is strong because it completely dissociates, it has nothing to do with its concentration. NH3 is weak because it only dissociates a little bit when reacted with water. 4. The major species would be H+, Cl-, H2O, HA, and A-. The strong acid is 100% dissociated, while the weak acid is less than 5% dissociated. The pH would be determined from the strong acid. 7. There is both H+ and OH- present in the solution, using the Kw=[H+][OH-], the amount of H+ can be calculated. 13. pH means to take the –log. True, strong acids completely dissociate which will in general provide more H+. 14. b/c the Kw = 1 .0 x 10-14, so [H+]=[OH-]= 1.0 x 10 -7 15. Yes for example find the pH of 15M HCl. 20. a. acidic b. acidic c. basic d. acidic 21. a. acidic b. basic c. basic d. basic 22. [H+] is the acid component and [OH-] is the base component. 29. a. Kw=[H+][OH-] b. Ka = [H3O+][A-] [HA] c. Kb = [NH4+][OH-] [NH3] 34. Scrubbers prevent the S that is released from burning coal to mix with O2 to form SO2 and SO3. These two gases then mix with water to produce sulfurous and sulfuric acids which are damaging to the environment. CaO mixes with water in the soil to produce calcium hydroxide, which raises the pH of the soil and promotes growth of plants. 36. a Ka = [H+][CN-] [HCN] b. Ka=[H+][OC6H5] [HOC6H5] c. Ka=[H+][C6H5NH2] [C6H5NH3+] 38. in order of the equation a. acid + base conj acid + conj base b. base + acid conj base + conj acid c. acid + base conj base + conj acid 40 a. right, weak b. left, strong c. left, strong d. right, weak e. right, weak 41. HClO4, HClO2, NH4+, H2O 42. NH3, ClO2-, H2O, ClO443. a. HCl b. HNO2 c. HCN 44. a. H2O b. NO2- c. OC6H5- 45. a [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-7M, neutral b. [OH-] = 12.05 M, basic 46. a. [H+] = 6.7 x 10-15M, basic b. [H+]=2.8, acidic 47. T goes up, Kw goes up, more product is formed meaning heat must be on reactant side, which is endothermic b. [H+]=[OH-]= 2.34 x 10-7M 48. a. [H+]=[OH-]=1.71 x 10-7M b. pH = 6.77 c. pH = 12.54 52. Solution A pOH = 4.37, [H+]= 2.3 x 10-10M, [OH-]=4.3 x 10-5M, basic Solution B pOH = 5.40, pH=8.60, [H+]=2.5 x 10-9M, basic Solution C pOH= 12.43, pH=1.57, [OH-]= 3.7 x 10-13 M, acidic Solution D pH=12.78, [H+]=1.7 x 10-13M, [OH-]=0.60M, basic 53. pOH = 11.9, [H+]= .008M, [OH-]=1.2 x 10-12M, acidic