Mutations that happen during Transcription and Translation
advertisement

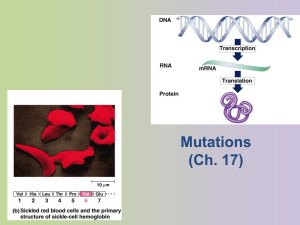
Mutations that happen during Transcription and Translation What happens if there is a mistake (mutation) in the DNA code? • Possibly proteins won’t be made or are made improperly. • If the mutations occur in the gametes, the offspring’s DNA will be affected positively, negatively, or neutrally. • What can cause a mutation? – – – – – Replication error Transcription/translation error Cell division error Chemical agents (mutagens) Spontaneous changes Point mutation • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. Point mutations • May change the amino acid code if the mutations occurs in the right place in the code. mRNA Normal Protein Stop Replace G with A mRNA Point mutation Protein Stop Frameshift mutations • Losing or gaining a single nucleotide base • This mutation would cause nearly every amino acid in the protein after the deletion to be changed Deletion of U mRNA Protein Chromosomal mutations • When a part of a chromosome is left out, a deletion occurs A B C D E F G H A B C E F G H Deletion • When part of a chromatid breaks off and attaches to its sister chromatid, an insertion occurs. A B C D E F G H A B C B C D E Insertion F G H Changes to the chromosome • When part of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches backwards, an inversion occurs. A B C D E F G H A D C B E FGH Inversion • When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome, a translocation occurs. AB C D E F GH WX Y Z W X AB C DE F GH Translocation Y Z nondisjunction failure either of two homologous chromosomes to pass to separate cells during the first meiotic division Repairing DNA • Enzymes proofread the DNA and replace incorrect nucleotides with correct nucleotides. • The greater the exposure to a mutagen such as UV light, the more likely is the chance that a mistake will not be corrected.