The Human Body Notes
advertisement

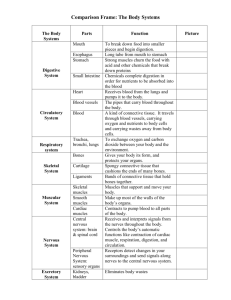
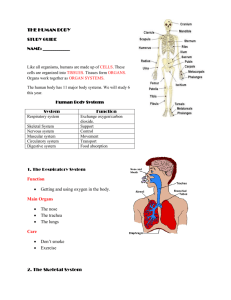
The Human Body Notes Junior 6 Topic 1.1 The two important key words we have encountered in this topic are function and structure. Remember that our body is made up of a structure, that keeps all of our parts together and the way the parts work together is called the function. The body will function well if it is healthy. The human body is made up of many different parts; the external parts – the parts that we can see on the outside such as your hand, nose and leg and the internal parts – the parts which can’t usually see unless under special equipment. It is very important to know and name some internal parts of the body and to also know that each part has its own special job to do but they also have to work closely together with other body parts in order to function well. Topic 1.2 Organs are found inside our body. Each and every organ has a special function inside the body. Some of the main organs include; the eye, the brain, the heart, the liver, the skin, the lungs, the kidneys etc.… Although each organ has a specific function, most organs work together to form an organ system. A group of organs that works together is called an organ system. There are about 10 systems in all. We shall first look at two systems: The skeletal system & the muscular system. The skeletal system At birth the human skeleton is made up of around 300 bones. By adulthood, some bones have fused together to end up with 206 bones. If broken, our bones will re-grow and repair themselves. Often doctors will place a cast on splint to make sure these bones repair straight and true. The three major functions of the skeleton are to protect organs, supports your body and helps you stand upright to be able to produce movement. Your backbone is important for supporting your body. It also allows us to twist and bend. Calcium is very important for our bones and helps keep them strong and healthy. Important facts to know: a) The skull – protects the brain b) The ribcage – protects the heart and lungs c) The spine – also known as the vertebral column (back bone) d) Joints – Our bones in our skeleton are connect to each other by joints. Joints are flexible and we are able to move and bend our bodies. Joints are divided into two; Fixed and movable joints. 1 Our joints are joined together by ligaments. There are four types of joints. 1) ball & socket, 2) hinge, 3) pivot and 4) gliding. (Watch: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z_CObarm8QI) The muscular system We have around 600 muscles in the body. Our muscles cover our skeleton and help us move. Your muscles are like elastic. There are 3 types of muscles in the body: 1) The smooth muscles – These muscles are involuntary as they work on their own. Smooth muscles don’t need any action from your side. They are found in your stomach and bladder. They are normally sandwiched between two organs. The smooth muscles in the wall of the stomach help push food down. 2) Cardiac muscles – These muscles are also involuntary. The heart contracts, relax and sends blood all around the body. 3) Skeletal muscles – These muscles are voluntary (under your control). These muscles are attached to your bones. They tied by small threads called tendons. Skeletal muscles are controlled by our nervous system. Muscles always work in pairs and muscles never push but pull. (Watch: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rGR1eUGV-tA) Musculoskeletal system This is basically both systems working together to produce movement. Without our muscles we cannot move. So both the systems together help us move. Topic 1.3 Organisation of organisms: Cells – tissues – organs – organ systems – organism 2 There about 10 different body systems: 1) The nervous system 2) The circulatory system 3) The respiratory system 4) The digestive system 5) The excretory system 6) The reproductive system 7) The skeletal system 8) The muscular system 9) The immune system 10) The endocrine system This year we shall focus on the first 5 body systems listed on top. It is very important to know the organs needed for each system and the function of each system. (Workbook page 4 – extremely important) Topic 1.4 It is very important that you know were specific organs are located. Look at both your student book (page 8) and workbook (page 6). It is very important to know both the location and label of each organ. Remember which organs belong to the back and which organs are found in the front, 3