AP Chemistry
advertisement
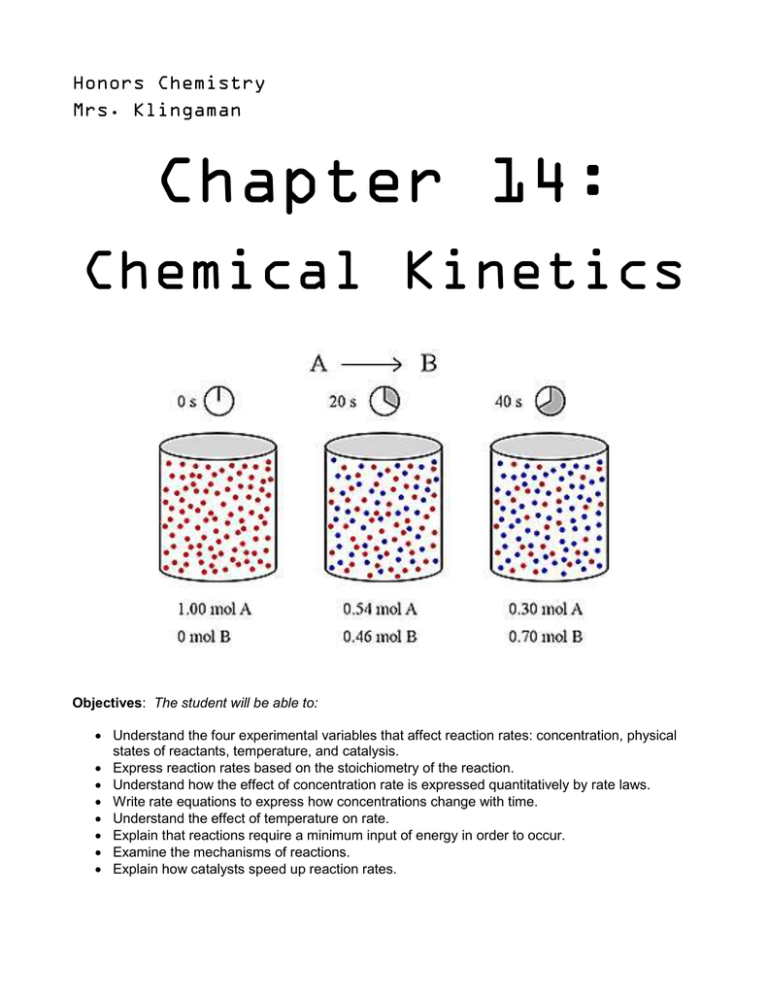
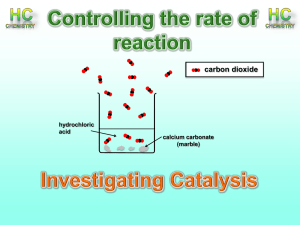
Honors Chemistry Mrs. Klingaman Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics Objectives: The student will be able to: Understand the four experimental variables that affect reaction rates: concentration, physical states of reactants, temperature, and catalysis. Express reaction rates based on the stoichiometry of the reaction. Understand how the effect of concentration rate is expressed quantitatively by rate laws. Write rate equations to express how concentrations change with time. Understand the effect of temperature on rate. Explain that reactions require a minimum input of energy in order to occur. Examine the mechanisms of reactions. Explain how catalysts speed up reaction rates. 14.1 - Factors that Affect Reaction Rates (pgs. 575-577) 1. The area of chemistry that is concerned with the speeds, or rates, of reactions is called 2. Identify and briefly explain the four factors that affect the rate at which a reaction occurs. 14.3 -14.4– Concentration and Rate (pgs. 582-592) 3. Define the term rate law: 4. For the general reaction aA + bB cC + dD, the rate law generally has the form: 5. Exponents in the Rate Law are called reaction ____________. Although the exponents in the rate law are sometimes the same as the coefficients in the balanced equation, this is not necessarily the case. The values of these exponents must be determined _______________. a) Definition: First order (pg. 587) – b) Definition: Second order (pg. 589) - 14.5 – Temperature and Rate (pgs. 593-595) 6. The rates of most chemical reactions ___________________ as the temperature rises. 7. Briefly explain the main ideas of the collision model. 8. Briefly explain the orientation factor with respect to the collision model. 9. Define activation energy. Copy the curve in figure 14.15 and label the Ea, ∆E, and activated complex) 14.7 – Catalysis (pgs. 607-613) 10. Define catalyst, homogenous catalyst, and heterogeneous catalyst. 11. As a general rule, a catalyst _______________ the overall activation energy for a chemical reaction by providing a completely different mechanism for the reaction. 12. What do we call the biological catalysts involved in reactions within living systems like the human body? 13. What are some properties of enzymes?