Holtmeyerhouse
advertisement

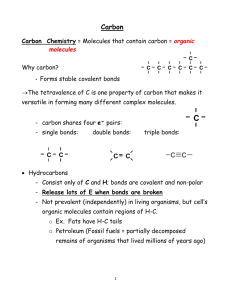
Carbon!!! chapter 25!! why is carbon so cool - it has a lot to do with the valance electrons and their oh so cool arrangement. because there are four, it leaves a lot of room http://www.worldofmolecules.com/interactive_molecules/diamond. for bonding with other elements, in a wide variety of ways. htm organic- means carbon based,used to mean "living " sugars, proteins, fats and DNA are the 4 organic molecules, all carbon based Allotropes of carbon- distinct different forms of the same element. 1st allotrop diamond- all carbons bonded to 4 others, very strong tetrahedral shape, hardest natural substance on earth. used to cut other substances as well as for asthetic purposes 2nd - graphite- carbon in layers or sheets- seperates easily, soft, good for reducing friction ( wheels/tires model cars) or in pencils, loosen locks 3rd amorphous carbon- has no particular shape. this is what happens when carbon based products decompose. charcoal, soot, are types amorphous carbon. 2 other types are bone black, which is the left overs of burned animal bones, which is used to pigment and refine sugars, and coke which is decomposed coal, and is used to convert to graphite and put into batteries etc. 4th fullerenes- buckminster fullerenes or bucky balls. these are spherical carbon structures that occur naturally in soot, and have recently been found to attack enzymes in the AIDS virus. to date we dont' have a lot of actual use for the original fullerene, but the shape 2 has an arcitectual building check out section for become organic/inorganic standard. ( see Epcot) comparisions carbon is one of few elements that can make long chains, it has short, strong covalent bonds bonds easily with many other chemicals required for this kind of building, makes it great at long straight or branched chains!! almost every organic carbon chain- from dna to proteins to hormones can be created synthetically. useful for meds. also create whole tons of inorganic carbons including plastics, styrofoam, DDT, Kevlar, etc!!!! O O N O O H C C H H N H C H H H C N H C O C C C H H O H H charactoricstics organic hydrocarbons inorganic C nonsoluable in water soluable in water low melting and boiling point boiling decompose when heated verysugars. hot fats, grease, kerosene, gasoline etc react with oxygen to combust!!! high melting and have to get very CaCO3, Carbon dioxide don't combust hydrocarbon!!! molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen- these are very nonpolar, strong molecules nonpolar means they don't dissolve in water, they don't conduct electricity , boil and melt at low temps. Examples include all fossil fuels, like oil, gasoline, etc. this is what most hydrocarbons are, as a matter of fact, they are very very common and are even more common on other planets!!! form in many ways, chains, and multiple bonds. we have system for writing them that describes all this and makes it easy to distinguish shape from name! keep in mindmolecular formulathe chem. formula with symbols and numbers C2H6 H H structural formula- all drawn out H - C - C -HEthane H H condensed structural formula, somewhere in the middle with groups put together ! CH3CH3 letal formula- drawing where point represent carbons, great f isomers Ske Hydrocarbons- when talking about them in general, we call them alkanes if they are all single bonded, alkenes if they have double bonds, and alkynes if they have triple bonds. , can be single , double or triple bonded ane endings - single ene endings - double bonds yne are triple bonds. ( saturated means they are all single bonds, saturated with hydrogen, unsaturated means there are dbl or trpl bonds) other than that # of carbons meth-1 hex-6 eth-2 hept-7 prop-3 oct-8 but-4 non-9 pent-5 dec-10 CH32 You try some!!! Take the monomers at the side and create the molecules below! 1, Pentene methane 2 nonyne 2,4, octene butane hexene H H H -C-C-C-H H H HH H-C-H H H H-C-H H H H-C-H H H H H -C-C-C-H H HH H H -C- H-C-H H H H H H H-C-H -C- H-C-H H H H H H-C-H H now you can also branch the carbon, they bend and reshape in all sorts of ways, you have to start being careful cause they will bend and can still go from either end and you need to count to see what is your longest chain. The longest chain will get the same name as before- propane, hexene, whatever. the branch gets a prefix that ends yl, with a number telling you where it comes from -c2 methy hexane c-c-c-c-c-c HH H H 3 proply nonane C-H C-CH HCH H H-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C- structural formulas for same look like thisHHHHHH CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2CH2CH3 HHH and CH3CH2CH(CH2CH2CH3)(CH2) 4CH3 Now you try some!!! build a 2 methyl butane or a 4 proply octane cyclopentene 3 methyl 1,4 cyclohexene H H H -C-C-C-H H HH or label these!!! H H H -C-C-C-H H HH H H H -C-C-C-H H HH H -CH isomers have the same molecular formula, different structural formulas, and may have different properties. cyclo compounds are one large example of this butane isobutane C4H10 pentane isopentane Practice Problem 2: The following structures all have the same molecular formula: C8H18. Which 2 of these structures represent the same molecule? where do you see these things? fossil fuels- all the stuff made of the condenced decomposed carbon produc that become petroleum products!! for instance, fossil fuels like gasoline, kerosene, petroleum, natural gas also petroleum jelly, etc these are all very nonpolar, low density, low boiling and melting point, dont' dissolve in water don't conduct electricity. more common on other planets even then on earth!! one to know- benzene!!! a cylco hexene with dbl bonds at 1,3, and 5!!! also good to know that cyclopentanes and hexanes are the basis for sugars your body, as well as fats!! all saccarides, and fatty acids have cyclo hydrocarbons as their base!!! Polymers!!! large organic moleucles with repeating sets. the set itself is called a monomer can be natural like silk, or synthetic like polyester ( hear that, poly means many, the ester is the monomer glucose is a monomer, it makes the polysaccarides in your body! aminoacids are monomers stuck together to make proteins that run your whole system! some important uses of polymers nylon! not just for pantyhose, how about parachutes in WWII silk, cotton, polyester, kevlar, plastic, teflon, lycra halocarbon cl, f, br, I industrial solvents, aerosal propellents antiseptic, groups gasoline chapter 26C-OH functional alcohol additives, antibacterial, polar ether R-O-R used as anesthetic, organic solvent, pollution reducer in gasoline aldehyde C=O on end formaldehyde perservative otherwise good smells of perfumes and candy, vanilla, cinnamon Ketone RC=OR acetone, solvent- hot chocolate other good fragrences carboxylic acid RC=O OH natural acids in walnuts, rasberries, apples, acetic acid, formic acid of ant bites esters COOC smells of fruits, pineapple, banana, oranges, wintergreen amine CNH2 amide CONH2 halocarbons the first functional group you can add to hydrocarbons halogen is F, Cl, Br, I, At on a hydrocarbon ( like a branch) they give the H.C good solvent properties, and they make great proppellents name them like we name branches. Ch3Ch2ChFCh2Ch2Ch3 3 flouro hexane alcohols have an OH. can be on end, in middle, or part of a branch alcohols have lower boiling point than water, higher than hydrocarbons. great solvents, disinfectants, gasoline additives ( combustible) naming- methanol, ethanol if on end - called primary 2 propanol or 3 hexanol if in middle, name like a branch- secondary 3 methyl 3 heptanol, would be tertiary. ( not as common) amines and amides both contain nitrogen! amines are a NH2 group on the end, name by adding "amine" CH3CH2CH2NH2 propanamine charactoristics of amines- these nitrogen based compounds are found in polymers like nylon as well amino acids and DNA. lots of vitamins and anesthetic drugs. also nicotine, cocaine and methanphedimines are all amines. also because amines are amino acids that make up proteins also provide the smell of rotting flesh ( yuck) called ptomaine, cause food poisioning. amides these are NH2 and a double bonded Oxygen . name root carbon group and add the word amide to it. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CONH2 make the peptide bonds of proteins, hexanamide