Integration of Geriatric Curriculum Content into a Synergy
advertisement

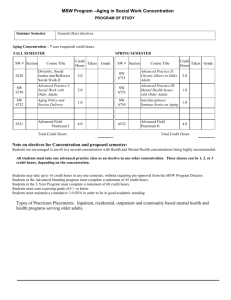
Integration of Geriatric Curriculum Content into a Synergy Model Driven Acute Care NP Program BM CL EA R , DN P, F N P - C, ACN P - BC G EORGIA R EG ENTS UN I V ERSITY COL L EG E OF N URSING GRU Acute Care Nurse Practitioner Program History 2010-HRSA grant awarded First DNP ACNP program in the Southeast 2011 Program for Accelerated Certification Education (PACE-ACNP) Mastering Essentials by Gaining Awareness during immersion days (MEGA i days) The APRN Consensus Model •Licensure -granting of authority to practice. •Accreditation -formal review and approval by a recognized agency of educational degree or certification programs in nursing or nursingrelated programs. •Certification - formal recognition of the knowledge, skills, and experience demonstrated by the achievement of standards identified by the profession. •Education -formal preparation of APRNs in graduate degree-granting or post-graduate certificate programs NCSBN, 2008 Primary Care NP roles Primary Care Education: Focus on comprehensive chronic, continuous care characterized by a long term relationship between the patient and NP. Cares for patients with a focus on disease prevention, assessment and management of common acute and chronic illnesses. Populations: Pediatric Adult Gerontological Family NONPF, 2011 Acute Care NP roles Acute Care Education: Focus on restorative care that is characterized by rapidly changing clinical conditions. Care for patients with unstable chronic conditions, complex acute illnesses, and critical illnesses Populations: Pediatric Adult Gerontological NONPF, 2011 AACN Synergy Model AACN,2015 Patient Characteristics Outcomes Nurse Competencies Patient Characteristic Stability Level 5 Highly stable Nurse Competency Course Clinical Judgement Constant Responsive to therapies Low risk of death Level 1 Collects basic-level data Follows protocols Questions the limits of one's ability Delegates the decision-making AGACNP I AGACNP II Level 3 Moderately stable Maintains steady state for limited time Some responsiveness to therapies Level 1 Minimally stable Labile Unstable Unresponsive to therapies High risk of death Level 3 Collects and interprets complex patient data Makes clinical judgments based on an immediate grasp of the whole picture Recognizes patterns and trends Recognizes limits and seeks appropriate help Level 5 Synthesizes and interprets multiple sources of data Uses past experiences to anticipate problems Helps patient and family see the "big picture“ Recognizes the limits of clinical judgement Seeks multidisciplinary collaboration AGACNP III & AGACNP practicum Why a geriatric focus? Inpatients over the age of 65 years of age 38.7%(2010) Average length of stay 5.5-5.7 days Percent of adult day services center participants: 63.5% (2012) Percent of home health agency patients: 82.4% (2011) Percent of hospice patients: 94.5% (2011) Percent of nursing home residents : 85.1% (2012) Percent of residential care community residents: 93.3% (2012) CDC, 2010 CDC, 2013 UAB Faculty Scholars Program Offered by UAB Geriatric Education Center 1) advanced illness and palliative care 2) transitions in care 3) family systems and self/caregiver management 4) communication skills addressing the cultural aspects of aging and health literacy UAB Faculty Scholars Program 160 hours of training 5 in person sessions 2 day Interdisciplinary geriatric education conference 12 Continuing education modules 1 Scholarly activity-publishable article or grant 1 Curriculum enhancement activity Vulnerability • Overview of Aging • Low vision and aging: an interdisciplinary approach • Incontinence Resource Availability • SNF, ALF, SCALF, IL, LTC – What Does It All Mean • Preventing Elder Investment Fraud • Medicare Overview Complexity • Complex Decision Making • Advanced Care Planning • Family systems • Medication Management • Health Disparities and Aging • Ethics and Aging Advocacy Moral agency • Developing Empathy • Geriatrics for Hospice and Palliative Care Workers Caring Practices • Geriatric Interdisciplinary Team Training • Inter-professional Competencies Collaboration Gerontology Day “Unless someone like you cares a whole awful lot, Nothing is going to get better. It's not.” An Aging Society For the first time in history, people aged 65 and over will soon outnumber children under the age of 5. Throughout the world today, there are more people aged 65 and older than the entire populations of Russia, Japan, France, Germany and Australia— combined. By 2050, the U.N. estimates that the proportion of the world's population age 65 and over will more than double, from 7.6% today to 16.2%. The United States contains more people age 65 and older than the total population of Canada. Americans aged 65 and older outnumber the combined populations of New York, London, and Moscow. http://transgenerational.org/aging/demographics.htm#ixzz2YBlYejb0 Objective Structured Clinical Exam (OSCE) Focus on: Uncommon presentations of common illness Polypharmacy Mobility Geriatric Immersion Experience References Center for Disease Control(CDC),2010. Older Adult Health,National Hospital Discharge Survey. Accessed http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/older-american-health.htm Center for Disease Control(CDC),2013. Older Adult Health,Long term health services overview. Accessed http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/older-american-health.htm National Council for State Boards of Nursing(NCSBN),2008.Consensus Model for APRN Regulation: Licensure, Accreditation, Certification and Education. Accessed http://www.aacn.nche.edu/educationresources/APRNReport.pdf National Organization of Nurse Practitioner Faculties(NONPF), 2011. Statement on Acute Care and Primary Care Nurse Practitioner Practice. Accessed http://c.ymcdn.com/sites/www.nonpf.org/resource/resmgr/imported/NPPrimaryCareAcuteCarePracticeFINAL.pdf