Notes: The Water Cycle and Unique Properties of Water
advertisement

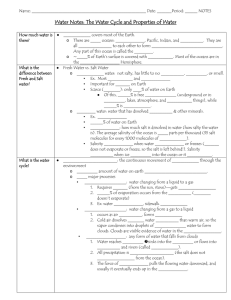
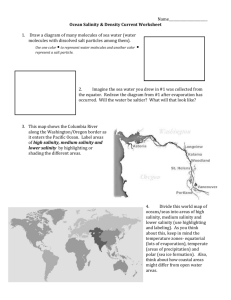
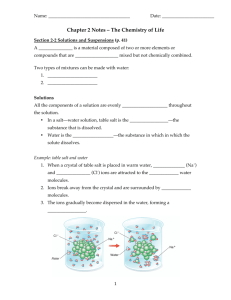
Notes: The Water Cycle and Unique Properties of Water 1/13/15 How much water is there? • Water covers most of the Earth. – There are 4 oceans: Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic. They are all connected to each other to form one huge ocean. Any part of this ocean is called the sea. • ~71% of Earth’s surface is covered with water. Most of the oceans are in the Southern Hemisphere. What is the difference between salt and fresh water? • Fresh Water vs. Salt Water – Fresh water: not salty, has little to no taste, color, or smell. • Ex. Most rivers and lakes • Important for life on Earth • Scarce (rare): only 3% of water on Earth – Of this, 30% is free flowing (underground or in rivers, lakes, atmosphere, and living things), while 70% is frozen. Fresh water vs. Saltwater (cont.) • Salt water: water that has dissolved salts & other minerals. – Ex. Oceans – 97% of water on Earth – Salinity: how much salt is dissolved in water (how salty the water is). The average salinity of the ocean is 35 parts per thousand (35 salt molecules for every 1000 molecules of water). – Salinity increases when water evaporates or freezes (salt does not evaporate or freeze, so the salt is left behind!). Salinity decreases when ice melts into the ocean or it rains. What is the Water Cycle? • The water cycle: the continuous movement of water through the environment – Total amount of water on earth does not change. – 3 major processes: •Evaporation •Condensation •Precipitation Evaporation • Evaporation: water changing from a liquid to a gas – Requires heat (from the sun, stove)—gets WARMER – 85% of evaporation occurs from the ocean (salt doesn’t evaporate) – Ex: water boiling, sidewalk drying Condensation • Condensation: water changing from a gas to a liquid – occurs as air cools, forms clouds – Cold air dissolves less water vapor than warm air, so the vapor condenses into droplets of liquid water to form clouds. Clouds are visible evidence of water in the atmosphere. Precipitation • Precipitation: any form of water that falls from clouds – Water reaches land →sinks into the soil or flows into streams and rivers (called runoff). – All precipitation is fresh water (the salt does not evaporate from the ocean). – The force of gravity pulls the flowing water downward, and usually it eventually ends up in the ocean. Draw the Water Cycle Draw the Water Cycle How is water unique? • Water is a unique substance. – allows life to live on Earth • exists in three phases: –solid –liquid –gas on Earth What is polarity? • Polarity: A polar molecule is a molecule that has positive (+) and negative (-) regions. – These regions allow it to become attracted to many other types of molecules. • In polar molecules, electrons are not distributed equally, which causes the molecule to bend and makes water polar. Polarity What is the difference between cohesion and adhesion? • Cohesion: ability of water molecules to stick to each other. – Water molecules want to “stick together” like magnets because of its positive (+) and negative (-) regions (opposite charges attract). – Polarity causes attraction between molecules – Causes surface tension—attraction between molecules at the surface; makes water bead up into drops and allows light objects to sit on top of the water. Water has high surface tension. • Adhesion: The ability of water to stick to other substances What is the density of water? • Density = mass/volume (g/mL or g/cm3) • Objects sink or float in water because of density • Density of water = 1 g/mL • Density less than water (1) = floats (less dense) • Density greater than water (1) = sinks (more dense) What is buoyancy? • Buoyancy: Force that pushes up on an object in fluid • Related to density: the lower the density = the more buoyant the object What is turbidity? • Turbidity is the measure of the clarity of the water (how clear the water is). – More solids in water = high turbidity = murky or muddy water – Less solids in water = low turbidity = clear water • To increase turbidity: add lots of fine sediments (silt, clay, etc) Turbidity What is specific heat? • Specific Heat: the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1g of any substance 1ºC – Water has a HIGH specific heat • Takes A LOT of energy to heat water • When water cools off, A LOT of heat is released • Oceans/Lakes stay warmer longer in winter, even if temperature decreases; it takes longer to heat them up in summer Why is water called the universal solvent? 1.A solvent is a liquid capable of dissolving another substance. 2.Water is capable of dissolving a lot of different substances, which is why it is called the universal solvent. 3.Water dissolves more substances than any other liquid! 4.Water’s polarity is one of its characteristics that makes it the universal solvent.