Scientists, Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
advertisement
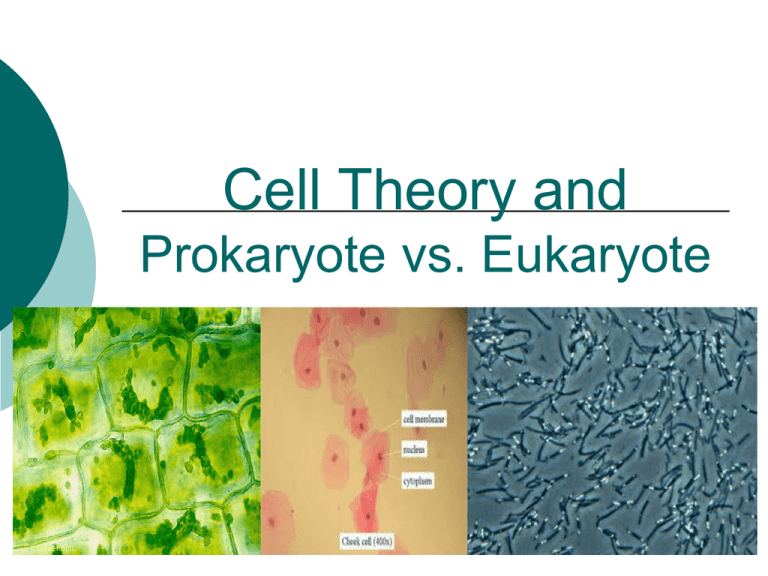
Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote What is a Cell? Cell – Basic unit of living things. Organisms are either: Unicellular – made of one cell such as bacteria and amoebas. Multicellular – made of many cells such as plants and animals. Scientists to Remember Robert Hooke (1665) – Observed “cells” in cork Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1674) Father of Microscopy Saw tiny living things in pond water. What is a Theory An accepted principle or statement based on natural and physical phenomena that is supported by data from a collection of repeated tests by independent researchers. Cell Theory Confirmed discoveries that all scientists believe to be true about cells: 1. Cells are the basic unit of life. 2. All living things are made of cells. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. The Discovery of Cells before nucleus true nucleus Eukaryotes Has a nucleus Bigger Have membrane bound Organelles (golgi, ER, lysosomes…etc) DNA inside nucleus Can be uni- OR multicellular organisms 4 Types:animals, plants, fungi, protist Eukaryotes Prokaryotes NO nucleus NO membrane bound organelles - just ribosomes ALL are unicellular Smaller DNA – single strand and circular ALL Bacteria Prokaryotes Similarities 1. 2. 3. Can be unicellular Contain all four biomolecules Have organelles in common - Plasma membrane, Cytoplasm, DNA, Ribosomes The Endosymbiotic Theory The endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time ago, prokaryotic cells engulfed other prokaryotic cells by endocytosis. This resulted in the first eukaryotic cells. Explains the origin of eukaryotic cells Explains the origin of certain membrane-bound organelles What Exactly Happened? Evidence in support of the endosymbiotic theory: Similarities between mitochondria, chloroplasts, & prokaryotes: Circular DNA Ribosomes Binary fission - division in half











