IMF's
advertisement

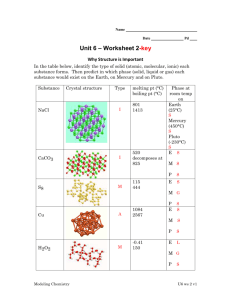
Intermolecular Forces and Physical Properties Chemistry Unit 6 Non-Polar Covalent Compounds Examples: O2, CH4, CO2 Types of particles: 2 or more non-metals IMF’s = Dispersion Physical state – can be s, l, or g – depends on molecular weight (MW) Melting/Boiling Pts. – very low to low Solubility in water – Not soluble Conductivity – poor to non conducting. Polar Covalent Compounds Examples: H2S, HCl, H2O Types of particles: usually 2 or more nonmetals IMF’s = Dipole-Dipole and maybe hydrogen bonds Physical state – can be s, l, or g – depends on molecular weight (MW) Melting/Boiling Pts. – low to medium Solubility in water – most are soluble Conductivity – Do not conduct. Ionic Compounds Examples: NaCl, MgO Types of particles: Metal and Non-metal IMF’s = Ionic bonds Physical state – crystalline solids, brittle Melting/Boiling Pts. – very high Solubility in water – most are soluble Conductivity – conduct as liquids or when dissolved in water.. Metallic Examples: Al, Cu, Fe Types of particles: cations in sea of electrons IMF’s = metallic bonds Physical state – all solids except Hg Melting/Boiling Pts. – variable – depends on charge and size Solubility in water – Not soluble Conductivity – conduct as solids or liquids Covalent Network Compounds Some covalently bonded substances DO NOT form discrete molecules. Diamond, a network of covalently bonded carbon atoms Graphite, a network of covalently bonded carbon atoms Network Covalent Solids Network solids – solids in which all the atoms are covalently bonded to each other Network solids melt at very high temperatures, or not at all (decomposes) – Diamond does not really melt, but vaporizes to a gas at 3500 oC and beyond – SiC, used in grinding, has a melting point of about 2700 oC Network Covalent Examples: Carbon, Silicon, SiO2, C60 Types of particles: usually single atoms IMF’s = covalent bonds Physical state – solids Melting/Boiling Pts. – very high Solubility in water – Not soluble Conductivity – poor to non conducting. Diamond vs. Graphite Different properties due to how it is bonded. Diamond – very hard, high mp- carbons 4 bonds each Graphite – soft solid –carbons have 3 bonds BuckyBalls – C60 Allotropes of Carbon Allotropes of carbon Link Types of Molecular Solids Covalent Molecular Covalent Network (H2O) (SiO2 - quartz) Amorphous (SiO2 - glass)