Review Sheet – Chemistry – Ch
advertisement

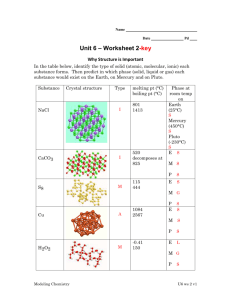
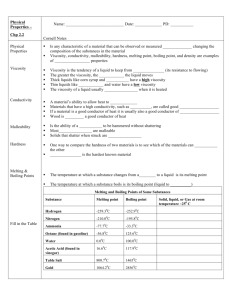
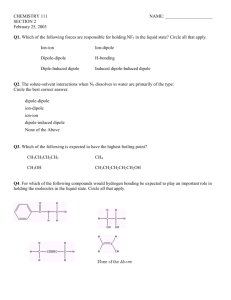
Review Sheet – Chemistry, Level 3 – Ch. 14: Liquids & Solids Name: ____________________ Date:___________ Period:___ This test covers materials in the textbook in Chapters 14 (pp. 456-491). You are always responsible for the topics on the previous tests. Test Expectations The student should be able: Describe how the Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Matter predicts the properties of substances Analyze the forces and relative strengths of the forces between particles in a solid, liquid or gas and compare the substances in terms of basic properties such as melting point, boiling point, viscosity, surface tension, or vapor pressure Describe the type and properties of one of the four solids Draw or use phase diagrams or heating curves to describe phase changes 1. Define each of the following terms clearly and completely. (a) condensed state of matter – (s) amorphous solid (b) phase – (t) adhesion – (c) phase diagram – (u) cohesion – (d) heating curve – (v) covalent-network solid – (e) intramolecular force – (w) phase change – (f) intermolecular force – (x) vapor pressure – (g) metallic bond – (y) heat of fusion – (h) hydrogen bond – (z) heat of vaporization – (i) dipole-dipole force – (aa) sublimation – (j) dispersion force – (bb) deposition – (k) permanent dipole – (cc) vaporization – (l) temporary dipole – (dd) condensation – (m) induced dipole – (ee) phase change – (n) viscosity – (ff) freezing – (o) surface tension – (gg) melting – (p) water – (r) crystalline solid – (hh) Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Matter – 2. Explain the following in one to three sentences. (a) Water’s boiling point is higher in Denver than in Southington. (b) Graphite is a conductor, but diamond is an insulator. (c) C5H12 has a higher boiling point than C3H8. 3. For each of the solids listed, give I. the type of solid (ionic, molecular, metallic, or network) II. the particles that occupy the corners of the crystal lattice III. the bond or force that holds the solid together. (a) NH3 (b) Ag (c) Ge (d) Sn (e) KBr 4. Which type are each of the solids described below? (a) crystalline solid with slight odor that melts at 78◦C (b) solid that conducts in the solid phase (c) solid with a very high melting point that does not conduct (d) solid that does not conduct but dissolves in water to make a conducting solution 5. For the phase diagram at the right, name the phase or phases that exist at each of the lettered points. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 6. Referring to the phase diagram in # 5, what change or changes would occur if (a) one started at point A and raised the pressure? (b) one started at point B and raised the temperature? 7. Referring to the phase diagram in # 4, which is more dense, the solid or the liquid? How do you know? 8. Explain the following in one to three sentences. (a) Which liquid, Hg or H2O, has a greater surface tension? (b) Which liquid, H2O or C5H12, has greater viscosity? (c) Which liquid, HCl or HF, has a higher boiling point? (d) Which liquid, C5H12 or C8H18, has a higher vapor pressure? 9. Draw a phase diagram for the substance with the following properties. I. normal melting point: -17◦C II. normal boiling point: 57◦C III. triple point: -22◦C and 200 mmHg IV. critical point: 220◦C and 1400 mmHg 10. Draw a heating curve for the substance in # 9 at 1 atm of pressure.