Chapter 6 Review Answers
advertisement
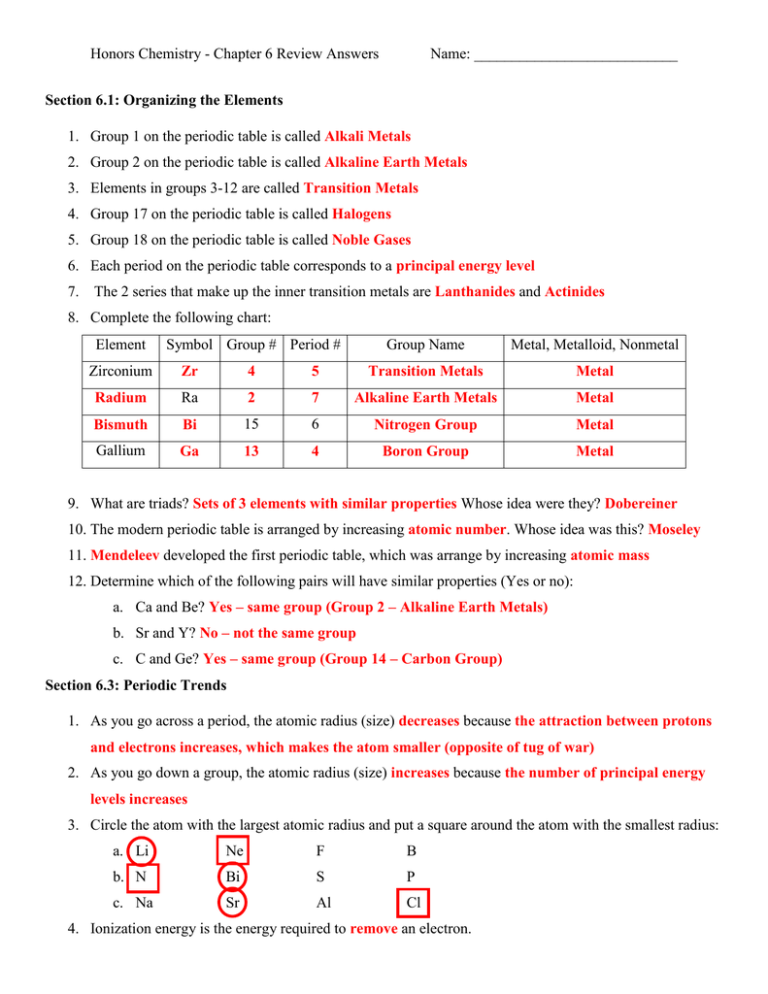
Honors Chemistry - Chapter 6 Review Answers Name: ___________________________ Section 6.1: Organizing the Elements 1. Group 1 on the periodic table is called Alkali Metals 2. Group 2 on the periodic table is called Alkaline Earth Metals 3. Elements in groups 3-12 are called Transition Metals 4. Group 17 on the periodic table is called Halogens 5. Group 18 on the periodic table is called Noble Gases 6. Each period on the periodic table corresponds to a principal energy level 7. The 2 series that make up the inner transition metals are Lanthanides and Actinides 8. Complete the following chart: Element Symbol Group # Period # Group Name Metal, Metalloid, Nonmetal Zirconium Zr 4 5 Transition Metals Metal Radium Ra 2 7 Alkaline Earth Metals Metal Bismuth Bi 15 6 Nitrogen Group Metal Gallium Ga 13 4 Boron Group Metal 9. What are triads? Sets of 3 elements with similar properties Whose idea were they? Dobereiner 10. The modern periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number. Whose idea was this? Moseley 11. Mendeleev developed the first periodic table, which was arrange by increasing atomic mass 12. Determine which of the following pairs will have similar properties (Yes or no): a. Ca and Be? Yes – same group (Group 2 – Alkaline Earth Metals) b. Sr and Y? No – not the same group c. C and Ge? Yes – same group (Group 14 – Carbon Group) Section 6.3: Periodic Trends 1. As you go across a period, the atomic radius (size) decreases because the attraction between protons and electrons increases, which makes the atom smaller (opposite of tug of war) 2. As you go down a group, the atomic radius (size) increases because the number of principal energy levels increases 3. Circle the atom with the largest atomic radius and put a square around the atom with the smallest radius: a. Li Ne F B b. N Bi S P c. Na Sr Al Cl 4. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron. Honors Chemistry - Chapter 6 Review Answers Name: ___________________________ 5. As you go across a period, ionization energy increases because the atom becomes more stable with more valence electrons, thus the atom does not want to lose any electrons (it would take a lot of energy to remove one) 6. As you go down a group, ionization energy decreases because the valence electrons are farther away from the nucleus and more shielded (see question 8 for more detail). 7. Why do you think second ionization energy is higher than first ionization energy? Second ionization energy is the energy required to remove a second electron. It is more difficult to remove a second electron (because the attraction between protons and electrons increases). 8. Explain how the shielding effect determines the trend in ionization energy: Ionization energy decreases as you go down a group because the atom increases in size, which means that there are more shielding electrons between the valence electrons and the nucleus. The shielding electrons “absorb” most of the attraction from the nucleus, so the valence electrons are not held as tightly. It is easier to remove one of the valence electrons (lower ionization energy) because they are not held as tightly by the nucleus. 9. Circle the atom with the highest ionization energy and put a square around the atom with the lowest ionization energy: a. Rb Ru Tc b. Cu Au Ag c. Cs Fr At Sb Rn 10. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract an electron. 11. As you go across a period, electronegativity increases because the atoms have more valence electrons, and want to attract electrons to obtain stability. 12. As you go down a group, electronegativity decreases because the valence electrons are farther away from the nucleus (more shielded) and there is not a strong attraction from the nucleus to pull an electron in. 13. Circle the atom with the highest electronegativity and put a square around the atom with the lowest electronegativity: a. B Ga Tl In b. Li Ne Be C c. Mg Cd As Kr 14. Metals form ions called cations that have a positive charge (lose electrons). Nonmetals form ions called anions that have a negative charge (gains electrons). 15. A negative ion is larger than its parent atom because it gained electrons. 16. A positive ion is smaller than its parent atom because it lost electrons. Honors Chemistry - Chapter 6 Review Answers Name: ___________________________ 17. Circle the smallest atom/ion. Put a square around the largest atom/ion. a. Cu Cu+ Cu2+ b. N N- N3- c. C4- C2- C 18. What is the most active metal? Francium (Fr) 19. What is the most active nonmetal? Fluorine (F) C2+ C4+







