Reflex Action & Senses: Biology Explained
advertisement

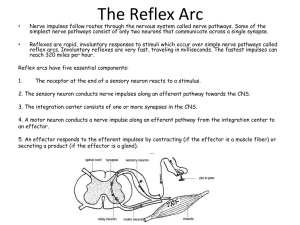
REFLEX ACTION MECHANISM, for instance, patellar reflex = knee-jerk Striking the patellar tendon with a reflex hammer [4] just below the patella [11] stretches [1] the quadriceps muscle. This produces a signal (an afferent [9] impulse) which travels back, through a sensory neuron, to the spinal cord [3] and synapses [5] in the spinal cord, completely independent of any higher centre [10]. From there, a motor neuron [6] conducts an efferent [8] impulse back to the quadriceps muscle, triggering [7] contraction. This contraction, coordinated with the relaxation of the flexor hamstring [2] muscle causes the leg to kick. This reflex is a reflex of proprioception [12] which helps maintain posture and balance, allowing to keep one's balance with little effort or conscious thought. The patellar reflex is a clinical and classic example of the monosynaptic reflex arc. The bipolar sensory neuron synapses directly on a motor neuron in the spinal cord. 1.- To pull something so that it becomes longer 7.- To make something function 2.- A muscle at the back of the upper part of your leg 8.- An impulse that comes 3.- A set of nerves that connect the brain to other nerves in the body (it's made of gray and white matter) 4.- A tool with a rubber part at the top that a doctor uses to hit a tendon and test a reflex 5.- To establish a connection between nerve cells 6.- A nerve cell that conducts an impulse 9.- An impulse that goes 10.- The brain, for instance 11.- The kneecap or knee bone 12.- Perception of your own position or movement THE FIVE SENSES STIMULUS Receptor Type Organ Sense Light Cones and rodes in the retina. Photoreceptors Eye Sight or vision Sound vibrations Receptor cells in cochlea. Inner ear Hearing or audition Contact, pressure or puncture Receptors and nerve endings of the dermis. Skin Touch Changes of temperature Specific receptors in the dermis. Skin Touch Substances dispersed in the air Receptor cells in the olfactory epithelium Olfactory epithelium Smell Tongue Taste Mechanoreceptors Thermoreceptors Chemoreceptors Molecules dissolved in water or saliva Receptor cells in taste buds