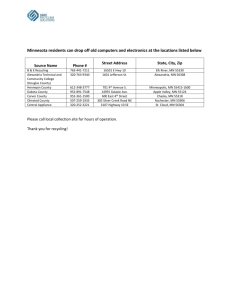
Alexandria Digital Library Project - ERI people pages
advertisement

Alexandria Digital Library Project
ALEXANDRIA DIGITAL LIBRARY
PROJECT
Larry Carver James Frew Greg Janée
Mike Goodchild Linda Hill Terry Smith
www.alexandria.ucsb.edu
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Outline
Alexandria Digital Library Project (ADLP)
History
Goals, activities, partners
Distributed DL supporting georeferenced access
Research and development issues
Operational collections and services
Knowledge organization systems (KOS)
Gazetteers and related KOS
ADEPT learning environment
Concept-based learning spaces
Collections and services
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
2
Alexandria Digital Library Project
ADLP History
Pre-1994: UCSB geo-information and map library
1994-98 DLI-1: georeferenced collections/access
1998-99: Operational ADL (UCSB Library/CDL)
1999-2004 DLI-2: distributed DL
Extension of architecture and access services
Knowledge organization services
Integration of learning services
Geo/GIS-based interfaces
Basic CS research
2004-2008: Large-scale DLs and beyond
NSDL Core Infrastructure and services
Cyber Infrastructure
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
3
Alexandria Digital Library Project
ADLP Goals
Current goals: Distributed DLs and applications
Operational distributed digital library
– services for construction/use of georeferenced collections
– DL federation and interoperation
– scalability over many heterogeneous collections
Development/integration of KOS services
Integration of concept-based learning spaces
– services for creating/using learning environments
Development of geo-based interfaces
Evaluation of services
Basic computational science research
Emerging goals: Large-scale DLs and beyond
Extending NSDL Core Infrastructure and services
Cyber Infrastructure
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
4
Alexandria Digital Library Project
ADLP Major Collaborative Activities
1994-98
4 DLI-1 partners: CMU, Illinois, Stanford, UCB
SDSC, U.Arizona, US Navy, NIMA, LoC, MSFT, ESRI,…
1999-2004
UCSB Library, CDL
DLI-2 partners: UCLA, GT, SDSC/NPACI, Stanford, UCB
DLESE
NSDL CI partners: Cornell, Columbia, U.Mass
NSDL Services partners: IIT Chicago, UCSD
JISC partners: Penn State, Southampton, Leeds
…
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
5
ADLP Activities
Alexandria Digital Library Project
EDUCATIONAL APPLICATIONS
• knowledgebase and lecture composing,
visualization, and presentation tools
• physical geography concept space and
learning object collections
• applications to undergraduate education
• educational evaluation
• learning services and DL integration
• digital classrooms
• metadata content standards
• learning objects
• computational models
USER INTERFACES
• reusable user interface components
• contextual maps, footprint creation
• KOS navigation
• lightweight GIS functionality
• Digital Earth visualization
• image processing
• query-by-content, classification
• spatial extent determination
GEOREFERENCED DIGITAL LIBRARIES
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
distributed georeferenced DL services
NSDL core infrastructure
data environment (e.g., GIS) integration
hardware acceleration for spatial data
collaborative tools
Z39.50 support
ingest and workflow systems
KNOWLEDGE ORGANIZATION
• gazetteers: research and community
• gazetteer content standard
• web service protocols for gazetteers,
thesauri, and other KOS
• ADL gazetteer
• thesauri for feature and object types
• duplicate detection for gazetteers
• textual-geospatial integration services
OPERATIONAL APPLICATIONS
•
•
•
•
georeferenced DL tutorials
distributable software packages
operational libraries: UCSB library, ...
outreach; federated nodes
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
6
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Outline
Alexandria Digital Library Project (ADLP)
History
Goals, activities, partners
Distributed DL supporting georeferenced access
Research and development issues
Operational collections and services
Knowledge organization systems (KOS)
Gazetteers and related KOS
ADEPT learning environment
Concept-based learning spaces
Collections and services
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
7
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Goals
Digital library architecture for
geospatial/georeferenced information
heterogeneous
rich services
scalable
– many providers
– collections, large and small
DL infrastructure, not artifact
standard components and interfaces
distributed participants
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
8
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Issue: discovery
Naïve approach
I want a map of Boulder
“Downtown street map of Boulder, Colorado”
But... remote-sensing imagery is nameless
AVHRR NOAA-13 2002-06-03 14:33 UTC
But... direct placename search is unreliable
I want a map of the Flatirons in the Rocky Mountains just
behind Boulder, Colorado
USGS topographic map “Eldorado Springs”
generally: many names for any given place
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
9
Alexandria Digital Library Project
ADL approach
Coordinate-based
representation and discovery
lat/lon coordinates
rich geometry
client
placenames
– polygons, polylines
spatial operators
gazetteer
– overlaps, contains
Gazetteer
content standard defines
representation
service maps placenames
coordinates
coordinates
library
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
10
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Issue: multiple data types
Geospatial discovery is not amenable to text
treatment
constitutes new data type
Adding notion of different data types has many
implications:
input validation
internal structures, external representations
query language and processing
ranking
user interface components
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
11
Alexandria Digital Library Project
ADL approach
Discovery: “bucket framework”
extensible data type system for metadata
– XML representations, search operations
native metadata is explicitly mapped to buckets
software supports bucket views over arbitrary RDBMSs
9 Dublin Core-like standard buckets
User interface components
background maps, item footprint identification/creation
Spatial ranking
by spatial similarity to query region
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
12
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Bucket mapping
Originator
FGDC
Citation/Originator
U.S. Geological Survey
USGS DOQ
Producer
Photo Science, Inc.
collection
statistics
field-level
searching
bucket-level
searching
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
13
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Collection statistics
Spatial
Temporal
Object Type
Count
cartographic works
324,876
maps
324,876
images
2,014,799
photographs
484,083
aerial photographs 484,083
•
•
•
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
14
Alexandria Digital Library Project
ADL approach
Discovery: “bucket framework”
extensible data type system for metadata
– XML representations, search operations
native metadata is explicitly mapped to buckets
software supports bucket views over arbitrary RDBMSs
9 Dublin Core-like standard buckets
User interface components
background maps, item footprint identification/creation
Spatial ranking
by spatial similarity to query region
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
15
Alexandria Digital Library Project
ADL in context
GIS
affordances
ADL
ODL
OAI
Greenstone
DLs
Web
generality • structure
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
16
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Issue: scalability
Size
easy to accumulate lots of data
– satellites image continuously
geospatial discovery scales... not so well
– indexing unwieldy at 106 items
efficiently joining spatial, other constraint types is difficult
Burden & management
collection building is labor-intensive
providers have differing content, services, IP concerns,
policies, lifetimes
providers already exist
– MS Terraserver: 3 TB, 750 million items
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
17
Alexandria Digital Library Project
ADL approach
Distributed library of peer nodes
library nodes host collections
other nodes host gazetteers, thesauri, other KOS
other components, e.g., map servers
Federated item-level search
over buckets
over individual metadata fields mapped to buckets
Centralized collection-level search/ranking
over collection statistics derived from bucket mappings
– space, time, type, format
any library node can act as collection registry
Collection aggregation
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
18
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Issue: context & use of library items
Context is critical in geospatial DLs
formulating queries
evaluating result sets and individual results
Use of geospatial data
need access descriptions
–
–
–
–
“item content single URL” is insufficient
multiple formats
multiple access methods
multiple components
need integration with common data environments
– ARC/INFO, etc.
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
19
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Geospatial context
Does this answer your question?
Flagstaff Rd.
Flatirons #1-5
Green Mountain
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
20
Alexandria Digital Library Project
ADL approach
All library functionality is accessible via...
web service APIs
Java RMI
Content access model
characterizes methods of access
multiple “access points”
– download, service, web interface, offline
– hierarchies of alternatives, decompositions
Context
background maps
library-supplied lightweight GIS functionality
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
21
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Incorporation into NSDL/CI
Geospatial/georeferenced data is an instance of
science data
complex, well-defined structure
rich metadata
large size
poorly served by traditional information retrieval methods
Science data belongs in NSDL
For NSDL: comparable infrastructure enabling...
distributed, content-specific search services
association of DL items and content-specific helper tools
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
22
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Operational status
ADL co-developed with UCSB Library
production-quality software
foundation of operational library since 2000
complete system in 2003
UCSB Library: Map & Imagery Laboratory (MIL)
self-supporting, 5 full-time employees
2.6 million items, 6.5 TB, growing 1.5 TB/year
4.5 million item gazetteer
Remote sites
ESSW, CNR, DLESE, SIO, NTNU, AUT
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
23
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Outline
Alexandria Digital Library Project (ADLP)
History
Goals, activities, partners
Distributed DL supporting georeferenced access
Research and development issues
Operational collections and services
Knowledge organization systems (KOS)
Gazetteers and related KOS
ADEPT learning environment
Concept-based learning spaces
Collections and services
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
24
Alexandria Digital Library Project
KOS activities & contributions
KOS as primary components of DL architecture
Heretofore not acknowledged as a major component
ADL/ADEPT thesaurus and gazetteer service protocols
Gazetteer components of DLs
Growth of a research and development community,
adopting/adapting/sharing our ADL Gazetteer components
Gazetteer research issues
NSDL Textual Geospatial Integration Project
KOS integration into learning environments
Terry Smith will address this in detail
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
25
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Digital Library Components
Libraries
Collections
SERVICES
ACCESSING
ANALYZING
ARCHIVING
CATALOGING
DIGITIZING
RETRIEVING
SEARCHING
VISUALIZING
DATA STORE
CATALOG
OF
OF
OBJECTS
METADATA
KNOWLEDGE ORGANIZATION SYSTEMS
AUTHORITY FILES
CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS
CONCEPT SPACES
DICTIONARIES
GAZETTEERS
GLOSSARIES
ONTOLOGIES
SUBJECT HEADING SETS
THESAURI
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
26
Alexandria Digital Library Project
KOS Generalization
Type
Definition
Label
Relationships
Meaning
Sense-making
Navigation
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
Translation
27
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Digital Gazetteer Essentials
(controlled vocabulary)
•None of these elements are unique identifiers of a particular place
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
28
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Building gazetteer research community
1994-1996: ADL built the first multi-million-entry
international gazetteer and integrated it into the
ADL system
1996-1999: ADL created...
Gazetteer Content Standard
Feature Type Thesaurus (210 preferred terms; 1046 nonpreferred)
rebuilt the ADL Gazetteer (over 4 million entries)
provided web interfaces for searching the ADL Gazetteer
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
29
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Building a research community
1999-present
Digital Gazetteer Information Exchange (DGIE) Workshop,
funded by NSF (66 participants), 1999
JCDL 2002 workshop on Digital Gazetteers – Integration in
Digital Library Services (38 participants; sponsored by NKOS)
NAACL 2003 workshop on Analysis of Geographic References
ADL-hosted discussion list for gazetteer issues; archived by
NSF DLI2 (146 subscribers)
Set of 5.9 million geographic names available for download –
useful for placename recognition in text
Gazetteer Service Protocol and protocol server code
An “external identifier” for ADL Gazetteer records
New gazetteer client that is based on the gazetteer protocol
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
30
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Our network of gazetteer interactions
Electronic Cultural Atlas Initiative (ECAI) gazetteer project
Academia Sinica’s Taiwan Gazetteer
UK Historical Boundaries project
UK Geo-crosswalk project
Digital Library for Earth System (DLESE) Education
Biodiversity research, such as the “Specify” system –
University of Kansas
State projects, such as NY Agricultural History project (in
proposal stage) and Florida statewide gazetteer project
University of Redlands internship proposal (mini-GIS)
Bulgarian Antarctic Place-Names Commission
SRI’s Artificial Intelligence Center (spatial reasoning)
Navy’s SPAWAR Systems Center (natural language process.)
THREDDS project at UCAR (event gazetteers)
Illinois Institute of Technology (geoparsing research)
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
31
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Advancing and extending gazetteers
Named Time Periods
World War I ___|_____|___
1914 1918
Named Spatiotemporal Events
Such as Hurricane Hugo
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
32
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Advancing and extending gazetteers
What happens when we extend the
digital gazetteer model to anatomy:
named structures in the brain, for
example?
http://www.ohiou.edu/~linguist/l550ex/brainpic.htm
Or to celestial space
and 3-d features?
Credit & Copyright: Sherry Buttnor
http://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/ap011120.html
Anticline Famennian sandstone, Hastière
http://www.nitg.tno.nl/eng/iccp_tripj.shtml
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
33
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Advancing and extending gazetteers
Obtaining extents from image analysis
Santa Barbara Municipal Airport
• Recognizing
patterns
• Identifying features
from gazetteers
• Deriving the extent
of the features from
feature analysis
• Adding bounding
box footprints to
gazetteer entries
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
34
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Advancing and extending gazetteers
Lake Bigler, thru 1920s
Lake Bonpland (also Bondland),
thru 1890s
Da-ow-a-ga, thru 1850s
The duplicate detection
problem.
Given variant names and
variant footprints, how
do we determine that
two pieces of information
are about the same
place?
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
35
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Advancing and extending gazetteers
Effective and efficient database indexing
techniques for large spatial + text data
collections
From Michael Freeston, New Generic
Indexing Technology
Test database of 2-d shapes in a
geographic area to test the “sufficiency”
of spatial generalizations (e.g., bounding
boxes) for information retrieval based on
spatial similarity (e.g., degree of overlap
or containment)
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
36
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Gazetteer ITR Proposal
Advancing and Extending Georeferencing
Interoperability and Services (AEGIS)
Medium ITR proposal for 2003
Michael Goodchild, UCSB, PI
Lewis Lancaster, Berkeley/ECAI, co-PI
Formalization and extension
Performance and scalability
Cross-cultural issues
Cognitive and behavior issues
Extents: representation of a feature’s geometry
Integration of locator services
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
37
Alexandria Digital Library Project
NSDL Textual Geospatial Integration
2001 - 2003
Goals
Participants
Extend NSDL infrastructure by
enabling
geographic queries
across heterogeneous,
text and non-text
resources
spatial georeferencing
of arbitrary texts without
explicit geographic
cataloging
University of California, Santa
Barbara
James Frew, PI
Terence Smith
Michael Bueno
Linda Hill
Information Retrieval Lab,
Illinois Institute of Technology
Ophir Frieder
David Grossman
Eric Jensen
Steve Beitzel
The American Geological Institute (AGI) has permitted us to use a set
of their GeoRef records for system training.
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
38
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Example text -> Estimated footprint
Structure and petrography of the schist of Skookum Gulch, Callahan-Yreka
area, eastern Klamath Mountains, Northern California
<key>blueschist | California | Callahan California | foliation | Klamath Mountains |
melange | metamorphic rocks | Ordovician | Paleozoic | petrology | schists | Silurian |
Siskiyou County California | Skookum Gulch | United States | Yreka California</key>
<ab>The schist of Skookum Gulch (SSG) is an informal name applied to a fault-bounded
melange composed mainly of schistose metamorphic rocks and less abundant sedimentary and
igneous rocks located in the eastern Klamath Mountains of Northern California. The SSG
features outcrops of lawsonite+sodic amphibole blueschist and epidote+sodic amphibole
rocks transitional to the greenschist facies. Isotopic dating indicates that the schist
was metamorphosed during the Ordovician. The SSG is the oldest known Paleozoic
blueschist-bearing melange in California and one of the oldest preserved blueschist
terranes in North America. Tonalitic rocks associated with the schist have Early Cambrian
ages and are among the oldest rocks yet dated within the Klamath Mountains. Field
relations indicate that the schist of Skookum Gulch is a complex tectonic melange
composed of metavolcanic, ...</ab>
<coord>N410000N420000W1220000W1230000</coord>
• Derived footprint - small
• Blue: derived footprint – large
• Red: GeoRef footprint
Alexandria Digital Library Project
KOS activities & contributions
KOS as primary components of DL architecture
Heretofore not acknowledged as a major component
ADL/ADEPT thesaurus and gazetteer service protocols
Gazetteer components of DLs
Growth of a research and development community,
adopting/adapting/sharing our ADL Gazetteer components
Research issues
NSDL Textual Geospatial Integration Project
KOS integration into learning environments
Terry Smith will address this in detail
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
40
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Outline
Alexandria Digital Library Project (ADLP)
History
Goals, activities, partners
Distributed DL supporting georeferenced access
Research and development issues
Operational collections and services
Knowledge organization systems (KOS)
Gazetteers and related KOS
ADEPT learning environment
Concept-based learning spaces
Collections and services
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
41
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Applications services based on DLs
Integrate applications with DL infrastructure
Important applications include
Web portals lack library organization
“packages” not integrated with DLs
Services/collections supporting learning environments
Services/collection supporting research
Apply domain-specific KOS principles for organizing
collections/services for given application
Geospatial applications: use georeference
Science learning environments: use concept spaces
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
42
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Science learning spaces: Concept KOS
Concepts of science as basic knowledge granules
Sets of concepts form bases for scientific representation
DL and KOS technology can support organization of science
learning materials in terms of concepts
– Collections of models of science concepts (knowledge base)
– Collections of learning objects (LO) cataloged with concepts
– Collections of instructional materials organized by concepts
Organize learning materials as “trajectory through
concept space”
Lecture, lab, self-paced materials
Services for creating/editing/displaying such materials
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
43
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Learning environment components/services
Input/Edit Services
Search Services
Concept
Knowledge
Bases
Display Services
Input/Edit Services
Search Services
Input/Edit Services
Search Services
Lecture
Collections
ADEPT
Object
Collections
Display Services
Display Services
ADEPT Search Services
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
44
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Application to learning environments
Application
Collections created
Introductory physical geography (F2002, S2003)
Knowledge base (KB) of strongly structured concepts
Structured lectures and labs
Learning objects cataloged by ADN metadata (+ concepts)
Services created
For concepts
–
–
For instructional materials
–
–
Web-based concept input tool
Graphic and text-based display tools
Web-based “lecture composer”
“Conceptualization” graphing tool
For learning objects
–
Metadata input tool
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
45
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Learning environment display (lecture mode)
The lecture is presented on three projection screens,
showing the
Concept window (left)
Lecture window (center)
Object window (right)
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
46
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Model of science concepts
Representing a concept involves more than terms
Objective, information-rich, scientific representations
– e.g., for concepts of heat diffusion, DNA, drainage basin, …
Associated semantics
– e.g., relating to measurement, recognition,…
Many interrelationships
– e.g., hierarchical, causative, property,…
Models of science concepts
Already exist for chemistry (ASA), materials (NIST),…
Generalize such models for this application
Structure items in concept KB using model
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
47
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Model of science concepts
ID
TYPE and FACET
CONTEXT (KNOWLEDGE DOMAIN)
TERM(S) (P/NP)
DESCRIPTION(S)
HISTORICAL ORIGIN(S)
EXAMPLE(S)
HIERARCHICAL RELATIONS
DEFINING OPERATIONS
SCIENTIFIC REPRESENTATION(S)
– Scientific classifications
– Data/Graphical/Mathematical/Computational reps
PROPERTIES
CAUSAL RELATIONS
CO-RELATIONS
APPLICATION(S)
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
48
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Item in concept knowledge base
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
49
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Concept input tool
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
50
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Collections of learning materials
Lecture/lab composer
Creates learning materials with
– Tailorable structure
– Underlying organization as “forest of trees” of concepts
Small reusable granules for
– Easy creation/edit/access/re-use
Can link in
– Concepts from concept KB
– Items from learning object collections
– Items from lecture collection
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
51
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Current instructional material window
The left-hand
frame displays
the structure of
the lecture
The righthand frame
displays the
content of the
lecture
ADL icons
(globe image)
attached to a
concept link to
a display of
concept
properties in
the concept
window
Other icons attached to a concept link to a display of concept
examples in the illustration window
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
52
Alexandria Digital Library Project
View of learning material by concepts
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
53
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Lecture/lab/… composer tool
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
54
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Learning object collections
Cataloged with tool for metadata creation
ADN metadata content standard with concept fields
Use of ADL/ADEPT middleware search services
E.g., in creation of lecture/lab presentation materials
Display of collection items in collection window
Photos, images, maps, text, videos,…
Support in display window for ADL browser
Allows dynamic search of collection holdings
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
55
Alexandria Digital Library Project
The illustrations window
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
56
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Evaluation of concept-based approach
Evaluation of efficacy for student learning
Do students attain “deeper levels” of understanding?
Comparison approach to evaluation
Evaluation of value to instructors/TAs
UCLA evaluation team
Evaluation issues
Instrumenting students’ use of course materials
Time to assess pedagogic value of approach
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
57
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Example of lessons learned
Importance of “conceptualizations” of concept
e.g., characterize concept of Fluvial Landscape with
concepts of {River, Watershed}
Embed conceptualizations in lecture/labs (not in KB)
Idea of learning materials as trees in concept space
Construct labs using analogous “lab” composer
Tailored for lab presentations/work
Supports of logic of using concepts as framework
Can import material from lecture/other collections
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
58
Alexandria Digital Library Project
Summary
DL infrastructure as basis for Learning Environments
Collections
– Concept KBs, Lectures, DL objects
Services
– Creation/Search/Display
Evaluation of efficacy of approach
Community-based development of KBs, Learning
Materials, Collections
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
59
ADLP Activities
Alexandria Digital Library Project
EDUCATIONAL APPLICATIONS
• knowledgebase and lecture composing,
visualization, and presentation tools
• physical geography concept space and
learning object collections
• applications to undergraduate education
• educational evaluation
• learning services and DL integration
• digital classrooms
• metadata content standards
• learning objects
• computational models
USER INTERFACES
• reusable user interface components
• contextual maps, footprint creation
• KOS navigation
• lightweight GIS functionality
• Digital Earth visualization
• image processing
• query-by-content, classification
• spatial extent determination
GEOREFERENCED DIGITAL LIBRARIES
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
distributed georeferenced DL services
NSDL core infrastructure
data environment (e.g., GIS) integration
hardware acceleration for spatial data
collaborative tools
Z39.50 support
ingest and workflow systems
KNOWLEDGE ORGANIZATION
• gazetteers: research and community
• gazetteer content standard
• web service protocols for gazetteers,
thesauri, and other KOS
• ADL gazetteer
• thesauri for feature and object types
• duplicate detection for gazetteers
• textual-geospatial integration services
OPERATIONAL APPLICATIONS
•
•
•
•
georeferenced DL tutorials
distributable software packages
operational libraries: UCSB library, ...
outreach; federated nodes
Smith et al • NSF • April 3, 2003
60