Product Life Cycles
advertisement

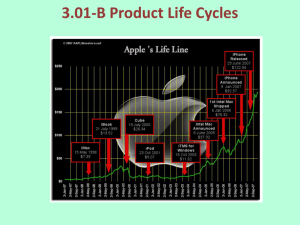
Product Life Cycle Ken Homa © K.E. Homa 2000 Product Life Cycle Maturity Growth Decline Introduction Time Product Life Cycle Maturity Growth Decline Introduction • Typical pattern, highly varied …broadly representative …product, brand, geography …not necessarily predictive …instructive, not definitive …conceptually based: diffusion, tech adoption Diffusion Models Diffusion Models • Innovators (First in) …Motivated by market knowledge • Imitators (Followers) …Motivated by interpersonal influences Simplified Diffusion Model Innovation Rate Initial Innovators Initial Potential Initial Buyers Simplified Diffusion Model Innovation Rate Total Market Potential New Innovators Remaining Potential Already Bought New Buyers Simplified Diffusion Model Innovation Rate Total Market Potential New Innovators Remaining Potential New Buyers Already Bought New Imitators Imitation Rate Simplified Diffusion Model Innovation Rate Total Market Potential New Innovators Remaining Potential New Buyers Already Bought New Imitators Imitation Rate Bass Diffusion Model Total Market Potential Remaining Potential Already Bought Momentum Factor Total Market Potential New Buyers Current Imitation Rate Imitation Rate Innovation Rate New Buyers Rate Bass Diffusion Model Illustrative Penetration Pattern 100.% 90.% 80.% 70.% 60.% ASSUMPTIONS 50.% Market Potential = 1000 40.% Innovation Rate = 10% 30.% Imitation Rate = 33% 20.% 10.% 0.% 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Bass Diffusion Model Illustrative Buying Pattern 150 TOTAL BUYERS ASSUMPTIONS Market Potential = 1000 100 Innovation Rate = 10% IMITATORS Imitation Rate = 33% 50 INNOVATORS 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Technology Adoption Life Cycle 34% 2.5% Innovators 34% 13.5% 16% Early Late Early adopters majority majority Laggards Time of adoption of innovations Adapted from Geoffrey Moore, Crossing the Chasm Product Life Cycle Maturity Growth Decline Introduction • Typical pattern, conceptually based • Cash flow critical …Mature ‘lend’, growing ‘borrow’ …Direct link to portfolio strategy Product Life Cycle Maturity Growth Sales Decline Introduction Profit Loss Loss Product Life Cycle Maturity Growth Sales Decline Introduction Profit Loss Loss Product Life Cycle Cash Flow Summary Net Income Cash Flow from Operations and Investments Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Investment Introduction Growth Maturity Introduction Decline Growth Maturity Decline Business Portfolio => Cash Flow Growth Businesses Intro Businesses External Financing CASH Declining Businesses Mature Businesses High Introduction Growth Develop or Invest/Grow Withdraw Low Market Attractiveness Inflow Outflow Cash Flow Position Linking PLC & Business Portfolio Harvest/ Divest Earn/Protect Decline Mature Low High Relative Business Strength High Cost Low Cost Competitive Cost Position Product Life Cycle Maturity Growth Decline Introduction • Typical pattern, diffusion based • Cash flow critical, portfolio linked • Manageable … PLC Management Maturity Growth Decline Introduction PLC Management Maturity Growth Decline Introduction Faster PLC Management Maturity Growth Higher Introduction Faster Decline PLC Management Maturity Longer Growth Higher Introduction Faster Decline PLC Management Maturity Longer Growth Higher Decline Introduction Faster More profitably … PLC Management Maturity Longer Growth Higher Introduction Faster Tactical differentiation Competitive positioning Strategic regeneration Crossing the Chasm Decline Managing the PLC • Tactical differentiation • Competitive positioning • Strategic regeneration • Crossing the Chasm Differentiated PLC Management Strategy Class Investment Policy Strategic Role Management Focus Introduction Phased/Selective Establish a profitable Market position position or cut losses 1st Mover ? Growth Aggressive Provide future cash flow base Maturity As needed to protect Generate current profits (cost reduction, cash needs line extensions, etc.) Decline Highly Restrictive Sales/Share Installed base Profitable Share Maximize short-term Profits/Cash profits; contain losses Last in ? Product Life Cycle Competitive Positioning Industry Strong Competitor Weak Competitor First Mover, or Predatory Follower Last In … Product Life Cycle Regeneration “Natural” Evolution Product Life Cycle Regeneration “Induced” Regeneration “Natural” Evolution Product Life Cycle Regeneration Mkt A Mkt B Mkt D Mkt C Product Life Cycle Regeneration Mkt A Mkt B Mkt D Mkt C Product Life Cycle Regeneration - Intel 386 Product Life Cycle Regeneration - Intel 486 386 Product Life Cycle Regeneration - Intel Pentium 486 386 Product Life Cycle Regeneration - Intel Pentium 486 386 Innovator’s Dilemma Established Technology Innovator’s Dilemma Disruptive Technology Established Technology Innovator’s Dilemma Disruptive Technology Established Technology Innovator’s Dilemma Disruptive Technology Established Technology Innovator’s Dilemma Disruptive Technology Established Technology Why upstarts and not established players? Innovator’s Dilemma Disruptive Technology Established Technology Why upstarts and not established players? High dependency on existing customers Initial market too small (relative to current) Uncertain potential, certain consequences “Crossing the Chasm” “Immature” solution No “killer application” C h 34% 34% 13.5% a 2.5% 16% Early Late s Innovators Early adopters m majority majority Laggards Time of adoption of innovations Product Life Cycle • Typical pattern, highly varied Maturity Growth Decline … broadly representative … product, brand,geography … not necessarily predictive … instructive, not definitive … conceptually based: diffusion, tech adoption Introduction • Cash flow critical Time … Mature ‘lend’, growing ‘borrow’ … Direct link to portfolio strategy • Manageable … … Differentiated tactics … Competitive positioning … Strategic regeneration … Crossing the Chasm