Product and Branding Concepts
advertisement

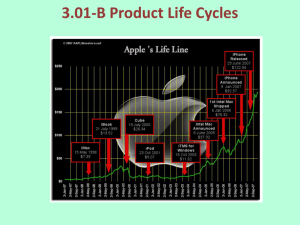
Product, PLC and Services Chapters 10 - 12 What is a Product? • Anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a want or need. It is usually judged on (1) product features (2) services mix & quality and (3) price appropriateness • Core benefit, Basic product, Expected product, Augmented product, Potential product Augmented Product Installation Packaging Brand Name Delivery & Credit Quality Level Core Benefit or Service Warranty Features AfterSale Service Design Product Classifications PRODUCTS Consumer Products Convenience Products Shopping Products Business Products Specialty Products Unsought Products Some Product Definitions • Product line – a group of closely related product items. • Product mix – all products that a firm sells. • Width – refers to how many different product lines the firm carries • Depth – refers to how many variants of each product are offered Depth of the product lines Gillette’s Product Lines & Mix Width of the product mix Blades and razors Toiletries Mach 3 Sensor Trac II Atra Swivel Double-Edge Lady Gillette Super Speed Twin Injector Techmatic Series Adorn Toni Right Guard Silkience Soft and Dri Foamy Dry Look Dry Idea Brush Plus Writing instruments Lighters Paper Mate Flair Cricket S.T. Dupont Product Line Strategies • Extensions: Adding additional products to an existing product line in order to compete more broadly in the industry. • Contractions: deleting products from product lines if there are low sales, cannibalization, obsolesce or few resources. What is the Product Life Cycle (PLC)? • A concept that provides a way to trace the stages of a product’s acceptance, from its introduction (birth) to its decline (death). • It is based on the product category. The Product Life Cycle Introductory Growth Stage Stage Maturity Stage Decline Stage Product Dollars Category Sales Product Category Profits 0 Time Introduction Stage • • • • • • • High failure rates Little competition Frequent product modification Limited distribution High marketing and production costs Negative profits Promotion focuses on awareness and information • Intensive personal selling to channels Growth Stage • • • • • • • • Increasing rate of sales Entrance of competitors Market consolidation Initial healthy profits Promotion emphasizes brand ads Goal is wider distribution Prices normally fall Development costs are recovered Maturity Stage • • • • • • • • Declining sales growth Saturated markets Extending product line Stylistic product changes Heavy promotions to dealers and consumers Marginal competitors drop out Prices and profits fall Niche marketers emerge Decline Stage • Long-run drop in sales • Large inventories of unsold items • Elimination of all nonessential marketing expenses • Options for Deleting Products: • • • • Maintaining Deletion Harvesting Contracting Marketing Strategies for PLC INTRODUCTION Product Strategy Distribution Strategy Promotion Strategy Pricing Strategy Limited models Frequent changes GROWTH More models Frequent changes. Limited Expanded Wholesale/ dealers. Longretail distributors term relations MATURITY DECLINE Large number Eliminate of models. unprofitable models Extensive. Margins drop. Shelf space Awareness. Aggressive ads. Advertise. Stimulate Stimulate Promote heavily demand.Sampling demand Higher/recoup Fall as result of Prices fall competition & development (usually). efficient produccosts tion. Phase out unprofitable outlets Phase out promotion Prices stabilize at low level. Percentage of Adopters Categories of Product Adopters Early Innovators Adopters 2.5% 13.5% Early Majority 34% Time Late Majority 34% Laggards 16% Diffusion Process and PLC Curve Introduction Growth Decline Maturity Sales Product life cycle curve Early majority Late majority Early adopters Innovators Laggards Diffusion curve What is a Service? • Any act or performance that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything • Medical, utilities, entertainment, professional (law, medical), transportation, financial Characteristics of Services • Intangibility – cannot be touched, seen, tasted, heard or felt in the same manner as goods. • Inseparability –services are produced and consumed simultaneously • Heterogeneity – services are less standardized and uniform than goods. • Perishability – services cannot be stored, warehoused or inventoried. Managing Services • Managing differentiation – Can’t live by price alone – Reliability, innovativeness and resilience • Managing service quality – Service gaps – Common practices • Managing productivity – Seven approaches