Impact of Product Life Cycle on Marketing Decisions - HSB-LHS
advertisement

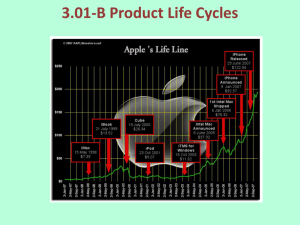
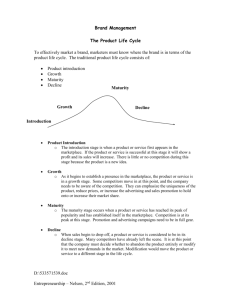
Impact of Product Life Cycle on Marketing Decisions Project #3 :: She Sells Cell Phones at the Cell Store Product Life Cycle The marketing theory that a product moves through different stages of life from its birth to its death Stages: introduction, growth, maturity, decline Marketing decisions impact each stage of the product life cycle Introduction A product is introduced to the market, and usually, sales growth is slow Early adopters, or innovators, are the primary buyers of the product or brand Growth The product is growing up, and sales are quickly increasing Copycat products are hitting the market, so competition is building Early adopters continue to buy the product and are joined by followers Maturity The product can be compared to adulthood Sales are steady Competition is probably the fiercest It’s becoming difficult to tell the differences among competing products The supply of the product now exceeds demand Decline This stage could be considered its golden years Product sales decrease due to shifts in consumer preference or technological innovations The only way to make money on the product is to sell large volumes since prices have been cut so much Eventually, the product may need to be removed from the market Pricing Decisions What price will we charge? Introductory stage: prices are set high to recover investment in the product; there are few to no competitors Growth stage: prices are lowered to attract customers and compete with copycat products Maturity stage: prices are stabilized to maintain market share Decline: prices are lowered to get rid of stock on hand Promotion Decisions Introductory stage: the level of promotion is high with the intent being to “get the word out” about the product so that customers know about its existence and features; the business promotes the product to its channel members to get them to carry the product Growth stage: the level of promotion remains high or increases, but its focus shifts to persuading customers of its benefits over those of the competition Maturity stage: the level of promotion is steady with funds directed to advertising and sales promotion to remind customers about the product or brand Decline: the level of promotion is reduced and eventually trails off Place Decisions Where will the product be offered? Introductory stage: efforts are made to get good channel members to offer the product; the business may offer exclusive distribution rights Growth stage: the business increases the number of distribution outlets Maturity stage: the business works on building intensive distribution – getting the product in as many outlets as possible Decline: the business alters or gets rid of the product; manufacturers drop the product from their offerings Product Decisions What assortment of products will be offered? Introductory stage: the business offers a basic product Growth stage: the business increases its assortment of products and offers new features and models Maturity stage: the business modifies the product to appeal to new customers Decline: the business alters or gets rid of the product; manufacturers drop the product from their offerings Extend a Product’s Life Cycle Product modifications are used to extend the life of the products This entails changing product quality or packaging Modify the Market Businesses also modify their markets by increasing the frequency with which present customers use the product, by finding new customers, or by creating new uses for the product