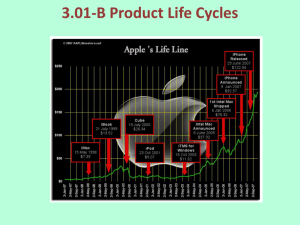
product life cycle - the Arden Business Department
advertisement

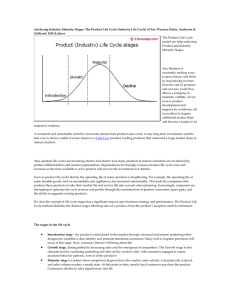
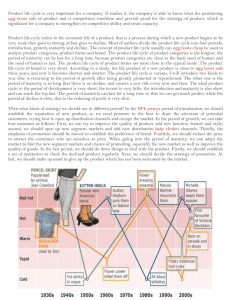
3.1 - MARKETING Lesson 7 – Product Life Cycle Starter Activity You are about to watch a short video about Fab lollies – listen out for how long the product has been on the market and what changes have been made in that time Learning Outcomes All All • Understand the • Apply real-life four phases of the products to the product life cycle life cycle model • Understand what is meant by an ‘extension strategy’ • Describe various extension strategy techniques that have been adopted by reallife businesses Most • Explain the link between cash flow and the product life cycle What is the ‘Product Life Cycle’? • Businesses cannot expect a product to sell forever • Just like human life, products progress through a life cycle from introduction (birth) to withdrawal (death) • The product life cycle shows the stages through which, it is argued, a product passes over time 1959 - 2000 What is the ‘Product Life Cycle’? • A product’s life cycle is the amount of time a business expects the product to sell for • Some products can have a short life cycle i.e. technology or fashion items. • Some products have had a long life cycle – Cadbury Dairy Milk has been on sale in the UK since 1905 and Kellogg’s Cornflakes since 1924 SALES REVENUE What is the ‘Product Life Cycle’? INTRODUCTION 0 GROWTH MATURITY TIME DECLINE Activity You are going to be given a card that describes a feature of one of the stages of the product life cycle. You need to decide which stage that your feature is referring to. When you have decided, you need to come up to the front and blu-tak your card onto the product life cycle diagram that is on the next slide… SALES REVENUE INTRODUCTION 0 GROWTH MATURITY TIME DECLINE Task 1. Copy down the features of each stage of the product life cycle onto your product life cycle. 2. Think of a product which is in each stage of the product life cycle. 3. Extension task – for each product you have thought of how can the business manipulate the marketing mix to maximise sales during that stage of the product life cycle? What might an ‘Extension Strategy’ be? • Manufacturers are likely to try to extend the maturity stage of the product life cycle for as long as possible, since this is usually the most profitable stage • So they develop an extension strategy - a method used to increase the life of a product and prevent it falling into decline • This involves slightly changing the product to give it a fresh appeal to its target market, or changing it in such a way that it appeals to a new segment of the market i.e. changing the design or use of the product SALES REVENUE What is an ‘Extension Strategy’? INTRODUCTION 0 GROWTH MATURITY TIME DECLINE What is an ‘Extension Strategy’? • A good example of an extension strategy in use is the Sony Playstation: Think, Pair Share Take timed turns listening, sharing and responding 1. Using the list of extension strategies shown on page 236 of the course textbook, can you think of some examples of real-life products that have had their life cycles extended? How were the extensions achieved? 2. Think time – 30 seconds 3. Who goes first - wait for start 4. In pairs, Partner A shares, Partner B listens 5. Time up 6. Class discussion What is an ‘Extension Strategy’? Write a paragraph in your book explaining one way that one of the following businesses might extend it’s product life cycle: • • • • Cadbury Playstation Lego Audi Activity Working as a pair, complete the table you have been given. You need to consider what the cash flow situation might be at each stage of the product life cycle. For example, is cash flow positive (more money coming in than going out) or negative (more money going out than coming in) and by how much? You will also need to consider the reason for the cash flow situation. You should use the text book to to help you with this. Cash Flow and the Product Life Cycle LIFE CYCLE STAGE CASH FLOW SITUATION REASON DEVELOPMENT OF THE PRODUCT Negative – much more Money is being spent on research and money going out than is development, materials and paying workers. No coming in. money coming in from sales. INTRODUCTION Negative – money starting Money is being spent on launching the product to come in but still more i.e. advertising and other promotion costs. Not going out. much money coming in from sales. GROWTH Sales are growing so money coming in is Positive – but only by a increasing. However, promotion and production small amount. costs are high as the business produces more. MATURITY Positive – much more All of the start-up and development costs have money coming in than is been paid. The value of sales is much higher than going out. the costs of production. DECLINE Sales are declining and selling prices have to be Negative – but only by a reduced. If an extension strategy is used, this will small amount. cost money to put in place. Learning Outcomes All All • Understand the • Apply real-life four phases of the products to the product life cycle life cycle model • Understand what is meant by an ‘extension strategy’ • Describe various extension strategy techniques that have been adopted by reallife businesses Most • Explain the link between cash flow and the product life cycle Rally Robin In pairs, take turns to give your answers 1. In pairs, take it in turns to suggest an example of a product that fits into one of the stages of the product life cycle 2. You should aim to think up 4 or 5 products for each stage of the life cycle 3. Go on until the time is up