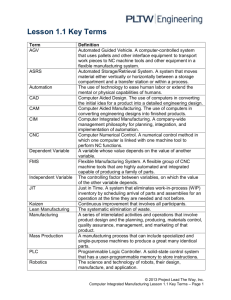
A2_manufacturing Systems
advertisement
Systems & Control Edexcel Product Design - Graphics Today: Systems & Control • • • • Manufacturing Systems Computer Integrated Manufacture (CIM) Robotics & Artificial Intelligence Flow Charts Reminders • QA – Quality Assurance – Monitors the quality of a product through its design and development stages through to manufacture – QA is an assurance that the end product has quality • QC – Quality Control – Is the achievement of QA – Uses inspection and testing • TQM – Total quality management – – – – Also called TQC – Total quality control Integrated into the manufacturing system QA at every stage of the production process Eg production team must produce a high quality component that the assembly team know is quality assured and will fit perfectly Reminders • JIT – just-in-time – Everything is made just-in-time – A pull system • QFD – Quality function deployment – Creating successful products – Incorporates consumer satisfaction – Advantages: • • • • • Reduced time to market Less design modifications Less design and manufacturing costs Better quality Enhanced customer satisfaction Lines and cells • Production lines – Fixed – Single task • Cells – Flexible – Various required skills, techniques, machinery etc Manufacturing Systems • Advanced manufacturing technology – When computers are used at every stage of the manufacturing process – Ensures fast, efficient, high quality production 1 of 4 Manufacturing Systems • Quick response manufacturing (QRM) – – – – – – – – – Makes companies more efficient and profitable Instead of batch production, ‘flow’ production Respond to demand, instead of planning for expected demand Uses TQM, JIT and manufacturing cells (teams) It’s main aim is to increase flexibility and responsiveness Teams have specific tasks, but can alter if needed No excess products are manufactured Suppliers deliver raw materials directly to the production line Products are finished and flow directly to a waiting truck for delivery – Pull system according to markets demands 2 of 4 QRM Manufacturing Systems • Concurrent Manufacturing – – – – – – All stages of the manufacturing process working together Does change to one part mean changes to another? Designs become ‘right first time’ Reduces product development time Earlier release of products Brings together design, manufacturing, project management, technical support, marketing – Communication is vital – Internationally computer networks are essential – Uses QFD – quality function deployment 3 of 4 Manufacturing Systems • Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) – Several machines linked together by a material handling system (robot or conveyor) – Uses CNC – Can produce different products at the same time – High flexibility 4 of 4 FMS continued • Two main features: – Machine flexibility • Whole system produces a different product • Can change the order of the machines – Routing flexibility • Same machine for different products Computer Integrated Manufacture (CIM) • One step further than FMS • All aspects of the company’s operations (not just manufacture) • Uses computer networks – Business information – Production information – Manufacturing operations • Tasks: – – – – Uses CAD Planning cost effective workflow Controlling machines Business operations – ordering stock, materials and invoicing customers • Relies on computers and data (sometime incompatible) CIM Systems • Data integration – Product data management (PDM) – Lean manufacturing (including JIT) – CAM, CNC, computer aided quality (CAQ) – Material handling systems • Automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) • Automatic guided vehicles (AGVs) Product data management systems (PDM) • Passes data from design to manufacture • Data: – 3D models – CAD drawings – CNC programs • Advantages: – Reduced time to market – Improved productivity – Improved control Lean manufacturing & JIT • Manufacturing has no “fat” in the process • Same idea as JIT – No warehouses, materials arrive just when needed • Right materials, components and products arrive at the right time • Reduces waste and overstocking • Manufacture must predict the market CAM, CNC, computer aided quality (CAQ) • CAM – computer aided manufacture • CNC – computer numerical control • CAQ – Computer aided quality – Coordinate measuring systems – Uses a probe – Finds “zero” Material handling systems • Automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) – Robotic system for sorting, storage and retreival – Uses racking systems – Conveyor belt or truck • Automatic guided vehicles (AGVs) – Uses radio frequency wires in the floor – Or use optical sensors – Computer controlled Robotics & Artificial Intelligence • Robots on fully automated production and assembly lines/cells – Manipulate and transport parts, tools or implements Flow Charts • Start/stop • Processes • Decisions • Arrows Flow Charts • Open loop Start Process Process • Closed loop Start Process Decision Yes Process Stop Stop No Task • Produce a sheet (title: Manufacturing) with the following information on: – – – – • • • • Manufacturing Systems Computer Integrated Manufacture (CIM) Robotics & Artificial Intelligence Flow Charts Use key points (in YOUR OWN words) Thin columns with information Advantages and disadvantages where relevant Try include images / colours to ease its use