Chapter 1

What Is an Information System?
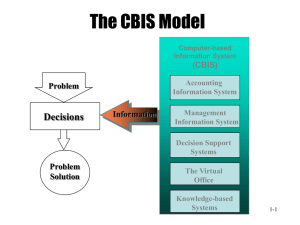
The Components of an Information System
1
Computer-Based Information Systems
(continued)
• CBIS components
– Hardware: computer equipment used to perform input, processing, and output activities
– Software: computer programs that govern the operation of the computer
– Database: organized collection of facts and information
– Telecommunications: electronic transmission of signals for communications
– Networks: connect computers and equipment in a building, around the country, and around the world
2
Computer-Based Information Systems
(continued)
• CBIS components (continued)
– Internet: world’s largest computer network
– People: manage, run, program, and maintain the system
– Procedures: strategies, policies, methods, and rules for using a CBIS
3
Business Information Systems
• Most common types of information systems used in business organizations
– Electronic and mobile commerce systems
– Transaction processing systems
– Management information systems
– Decision support systems
– Specialized business information systems
4
Business Information Systems
(continued)
Business Information Systems
5
Information and Decision Support
Systems
• An effective TPS provides a number of benefits to a company
• A TPS can speed business activities and reduce clerical costs
• Data stored in TPSs is used to help managers make better decisions
6
Management Information Systems
• Management information system (MIS)
– Organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases, and devices
– Provides routine information to managers/decision makers
• Primary focus is operational efficiency
7
Management Information Systems
(continued)
Management Information System
8
Decision Support Systems
• Decision support system (DSS)
– Organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases, and devices
– Supports problem-specific decision making
• Focus is on decision-making effectiveness
9
Decision Support Systems (continued)
Essential DSS Elements
10
Specialized Business Information
Systems: Knowledge Management,
Artificial Intelligence, Expert Systems, and Virtual Reality
• Knowledge management systems (KMSs): an organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases, and devices to create, store, share, and use the organization ’s knowledge and experience
• Artificial intelligence (AI): field in which the computer system takes on the characteristics of human intelligence
11
Artificial Intelligence
The Major Elements of Artificial Intelligence
12
Expert Systems
• Give the computer the ability to make suggestions and act like an expert in a particular field
• Allow organizations to capture and use the wisdom of experts and specialists
• The knowledge base contains the collection of data, rules, procedures, and relationships that must be followed to achieve value or the proper outcome
13
Systems Development
• Systems development: creating or modifying existing business systems
• Systems development can be:
– Performed in-house
– Outsourced
• To improve results of a systems development project, it is divided into several steps
14
Systems Development (continued)
An Overview of Systems Development
15
Organizations and Information
Systems
• Organization: collection of people and other resources established to accomplish a set of goals
• An organization is a system
– Inputs: resources (materials, people, money)
– Outputs: goods or services
16
User Satisfaction and Technology
Acceptance
• Technology Acceptance Model (TAM): specifies factors that can lead to higher acceptance and usage of technology
• Technology diffusion: measure of widespread use of technology
• Technology infusion: extent to which technology permeates a department
17
User Satisfaction and Technology
Acceptance (continued)
• Competitive advantage: significant, long-term benefit to a company over its competition
– Ability to establish and maintain a competitive advantage is vital to the company ’s success
18
Risk
• Managers must consider the risks of designing, developing, and implementing new or modified information systems
• Information system may be a failure
• Costs of development and implementation can be greater than the returns from the new system
19