Environment and Society

Environment and
Society
Note series for
Environmental Science by
John Wnek
Key Concepts…
Sustainable Systems
Resources
Biological Diversity
The Earth Community
Common Property Resources
Recycling/Reuse
Point and Non-Point Sources of
Pollution
Resources…
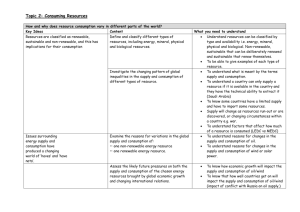
Non-Renewable: Produced over millions of years and are in fixed quantities including: Energy
Resources (fossil fuels); Mineral
Resources (gold, aluminum, zinc);
Non-metallic resources (sand, clay and water
Renewable: Inexhaustible supply of resources including: energy (wind, solar, flowing water nrg); Potentially renewable (air, water, soil and biodiversity)
Pollution…
Point source vs. Non-
Point Source
Classification including
Concentration,
Composition, Persistence
Degradable vs. Non-
Degradable
“The solution to pollution is not dilution”
NJ Department of Environmental Protection, Leading Environmental
Indicators Factsheets. http://www.state.nj.us/dep/indicators/shellfish.pdf
1.
2.
3.
4.
Root Causes of Environmental Problems
Rapid Exponential Growth
Population doubled between 1950 and 1997 (by 2014 should be 7.2 billion people)
A massive degradation of “life support systems”
Poverty – lack of choices and lack of environmental education (this will be discussed more)
Use of “quick fix” methods using non-renewable resources
Root Causes of Environmental Problems
5. Lack of solutions with little emphasis on pollution control and waste reduction
6. Failure to encourage Earthsustaining forms of economic development (recycle and reuse)
7. Urge to dominate and manage
“Approximately ¾ of the Earth has only 15% of the income and uses only 12% of the resources”
Fun Facts
“ In all Lesser Developed Countries
(LDC’s), 1,000,000 people are added to the population count every four days”
“Developed Countries use over 90% of the non-renewable fossil fuel supplies”
Source: Sustainability Initiative, University of Maryland
Sustainability?
Defined (video)
An opposite point of view
Things you can do: World
Change TED talks Alex
Steffen
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Sustainable Societies…
Reduce Waste of Matter & Energy
Emphasize Pollution Prevention
Improve Recycling Efforts & Reuse
Efforts to 60% in Each Community
Longer Lived Products
Increase RENEWABLE ENERGY
SOURCES
Better Protect the Earth’s Habitats and Species
Sustainable Society
7. Establish a RENEWABLE RESOURCE
Balance
8. Value the Importance of Natural
Resources
9. “Slow” Population Growth Rates
10. Reduce Poverty and Improve
Living Conditions in LDC’s
11. Improve Environmental Education
Practices
Population Clock
U.S. 320,499,950
World 7,176,606,100
01:05 GMT (EST+5) Sept. 4, 2013
NOTE: The U.S. POP Clock has been recalibrated to be consistent with
Census 2010 data.
U.S. 305,753,417 Feb. 5, 2009
World 6,758,521,649 Feb. 5, 2009
2013
7.1 billion
Population/Age Pyramids of the Developed and Developing World
From the University of Michigan’s Population Growth Over Human History
The United Nation’s Millennium Goals
eradicating extreme poverty achieving universal primary education promoting gender equality reducing child mortality improving
health combating HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases ensuring environmental sustainability and developing a global partnership for development