Environmental economics, politics and worldviews
advertisement

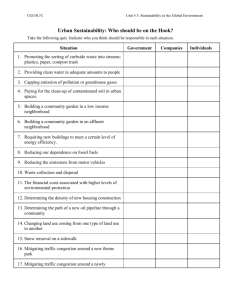
BIOLOGY 1500 OUTLINE FOR CHAPTER 17 Environmental economics, politics and worldviews - - - - - - Resources (aka capital) o Anything obtained from the living and nonliving environment to meet human needs and wants o Can be natural, human, or manufactured resources Natural capital o All the resources that nature provides that can be used to produce goods and services (and to sustain life, which makes human capital possible). o Natural capital=natural resources + natural services o Examples of natural resources: air, soil, ozone layer, biodiversity, mountains, forests…etc o Examples of natural services: air purification, gas balance in air, nutrient cycling, water purification and catchment, control of soil erosion, pest control, filtering of hazardous radiation…etc Human capital o All of the skills, education, and other abilities that humans use to make a living-provide labor, innovation, culture, and organization Manufactured capital o All of the things people have made that contribute to the production of goods and services, such as factories and money In automobile industry, resources used are o Natural resources Metal Energy (coal, petroleum) Water Glass and silicon (sand) Plastic (petroleum) Rubber o Human resources Skilled labor Entrepreneurs Investors Economic systems (supply and demand) o Are means of Using capital Deciding which and how many goods and services are produced Allocating goods and services Economists belong to three schools o Neoclassical: neglect resource depletion and pollution o Ecological: primary focus is resource depletion and pollution o Environmental: natural capital and sustainability are important Sustainability; seven economic strategies to achieve it - - - - - - GDP versus GPI Eight externalities computed in GPI Poverty o Is the inability to meet one’s economic needs o It contributes to….etc o Leads to conflicts and instabilities (riots vs food prices) o Food as an economic system, has inputs and outputs for every step from production to distribution to consumption High- versus Low-throughput economy o High-throughput: high economic growth leads to increased use of natural resources. Neglects pollution. Some recycling and reuse of high quality matter and energy o Low-throughput: reduced inputs and wastes. More recycling and reuse of low-quality and high-quality matter and energy Political systems o Politics is… o Democracy is… o Environmental policy… Principles for environmental policy (list and understand) o Humility o Reversibility o Precaution o Polluter pays o Integration o Public participation o Human rights o Environmental justice Environmental worldviews o Atomistic (individual-centered) Biocentric, aka stewarship (life-centered) Resources are unlimited, but should not be wasted, we should manage earth to support all forms of life Anthropocentric, aka planetary management (humancentered) Resources are unlimited, we are apart of nature, we should manage nature for our needs and wants only o Holistic, aka environmental wisdom (biosphere or ecosystemcentered) Resources are limited, should not be wasted. We are part of nature and depend on it, nature is for all species Environmental literacy o Capacity of an individual to act successfully in daily life on a broad understanding of how people and societies relate to each other and to natural systems, and how to do it sustainably o Requires: awareness, knowledge, skills, and attitudes - End. o In order to: Incorporate appropriate environmental considerations into daily decisions about consumption, lifestyle, career, and civics Engage in individual and collective action Sustainability Dozen o For Energy, Food, Water and generally the reduce reuse recycle Sustainability Principles o Science-based principles: (belongs under planet and implemented through profit) solar energy chemical recycling biodiversity o Social-science principles: (belongs under people and profit) Full-cost pricing (economic) Responsibility to future generations (ethics) Win-win results (politics)