Chapter 2
advertisement

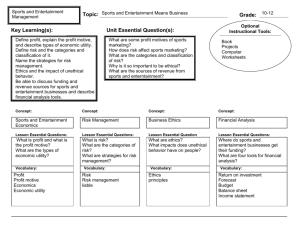
Chapter 2 Sports and Entertainment Means Business 2.1 Sports and Entertainment Economics 2.2 Risk Management Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Lesson 2.1 Sports and Entertainment Economics Goals Define profit and explain profit motive Describe types of economic utility Chapter 2 Slide 2 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Do Now Discuss with the person next to you the reasons to run a business (this includes sports teams and concerts). Chapter 2 Slide 3 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western THE PROFIT MAKERS profit the amount of money remaining from revenues after all expenses are paid revenue the money a business receives from the sales of goods and services profit motive making decisions to use resources in ways that result in the greatest profit Chapter 2 Slide 4 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Cultural Opportunities for Profits Worldwide distribution revenue is critical for movie profits. China has a tremendous movie market. The government censors movies for content Pirated movies diminish theater sales Chapter 2 Slide 5 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western ECONOMICS economics the study of how goods and services are produced, distributed, and consumed - Chapter 2 Slide 6 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western macroeconomics the study of the economics of the entire society microeconomics the study of the relationships between individual consumers and producers Sports and entertainment marketers are focused on microeconomics. relationships with consumers Chapter 2 Slide 7 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Sports and Entertainment Economics economic utility the amount of satisfaction a person receives from the consumption of a particular product or service Chapter 2 Slide 8 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Types of Utility form utility when the physical characteristics of a product or service are improved time utility making the product or service available when the customer wants it place utility the product is available where it is wanted possession utility the product or service is available at an affordable price Chapter 2 Slide 9 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western List the four types of economic utility Chapter 2 Slide 10 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Do Now What is risk? What does Turner Field or Phillips Arena do to reduces the risk of injury to an attendee during a concert or game? Chapter 2 Slide 11 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Lesson 2.2 Risk Management Goals Define risk and describe the categories and classifications of risk. Name and describe four strategies for risk management. Chapter 2 Slide 12 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western RISKING IT ALL risk the possibility of financial gain or loss or personal injury Chapter 2 Slide 13 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Three Categories of Risk 1. Natural risk occurs from unavoidable weather conditions 2. Human risk dishonest customers and employees inadequately trained employees 3. Economic risk occurs due to changes in the economy Chapter 2 Slide 14 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Three Additional Classification of Risk 1. gain or loss risk speculative risk either a gain or loss could result pure risk a chance of an event occurring that could only result in a loss Chapter 2 Slide 15 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Three Additional Classification of Risk 2. controllable or uncontrollable risk controllable risk if a loss can be prevented or the likelihood of its occurrence reduced uncontrollable risk nothing can be done to prevent the risk Chapter 2 Slide 16 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Three Additional Classification of Risk 3. Insurable or Uninsurable risk insurable risk a pure risk for which the chances of loss are predictable and the amount of the loss can be estimated uninsurable risk the chance that a dollar loss could occur the amount of the loss cannot be estimated Chapter 2 Slide 17 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western What are four steps a sports venue could take to avoid risk of injury to fans attending games? Chapter 2 Slide 18 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western MANAGING RISK risk management preventing, reducing, or lessening the negative impacts of risk by using the strategies of risk avoidance, risk insurance, risk transfer, and/or risk retention Chapter 2 Slide 19 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Strategies to Manage Risk 1. Risk Avoidance – precautions to avoid risky situations 2. Risk Insurance – buy insurance for predictable risk 3. Risk Transfer – put the liability on another company or even the customer 4. Risk Retention – retain money to cover the cost of a given risk Chapter 2 Slide 20 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Chapter 2 Sports and Entertainment Means Business 2.3 Business Ethics 2.4 Financial Analysis Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Lesson 2.3 Business Ethics Goals Define ethics. Discuss the impacts of unethical behavior. Chapter 2 Slide 22 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western DO ETHICS COUNT? ethics a system of deciding what is right or wrong in a reasoned and impartial manner Business should be conducted with integrity, trust, and fairness. Chapter 2 Slide 23 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Ethics and Character Matter principles high standards of rules and guidelines character development a progression in behavior where people advance from childish behavior to mature behavior based on principles Young people need good role models. Chapter 2 Slide 24 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Prepare a 3 minute skit to show what ethics is. be sure you can explain the relevance make sure it is appropriate Chapter 2 Slide 25 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western BUSINESS BEHAVIOR People and businesses should act ethically while pursuing a profit. Chapter 2 Slide 26 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Seeking an Advantage Sometimes it is hard to continue to act ethically when you observe people who receive a benefit from acting unethically. Chapter 2 Slide 27 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western When Being Bad Profits Only fans can really influence the behavior of ethically challenged athletes and celebrities. Chapter 2 Slide 28 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Effective and Ethical Good decisions are both ethical and effective. Good decisions are the right choices for the long term. Chapter 2 Slide 29 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Bell Ringer: October 12, 2015 Start a new bell ringer document for this week! How can the bad behavior of celebrities be controlled? Chapter 2 Slide 30 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Lesson 2.4 Financial Analysis Goals Discuss sources of funding and revenue for sports and entertainment businesses. Describe four tools for financial analysis. Chapter 2 Slide 31 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western IT TAKES MONEY Profit is the primary purpose of sports and entertainment marketing. Chapter 2 Slide 32 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Finding Funding Investors generally provide the funding for an event to cover all the costs that must be incurred before tickets are ever sold. Would you be willing to provide funding to boost someone’s career? Why or Why not? Chapter 2 Slide 33 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western return on investment the income from a venture that is distributed to investors Chapter 2 Slide 34 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Money Sources Funds to repay investors are raised through ticket sales broadcast rights licensing facilities Chapter 2 Slide 35 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Name three sources of revenue from sports and entertainment. Chapter 2 Slide 36 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western WHERE IS THE MONEY? forecast a plan that predicts the expenses to be incurred and the revenues to be received Chapter 2 Slide 37 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western BUDGETS budget a plan for how available funds will be spent The purpose of a budget is to control costs so they do not exceed the funds available. Chapter 2 Slide 38 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Financial Statements balance sheet net worth = assets – liabilities shows net worth at a specific point in time income statement shows revenues and expenses for a specific period of time reveals company’s profit or loss Chapter 2 Slide 39 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western What is the purpose of a forecast? Chapter 2 Slide 40 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Bell Ringer October 13, 2015 What types of documents does an investor want to see before making an investment? Chapter 2 Slide 41 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Bell Ringer October 14, 2015 Name 3 sources of revenue from sports and entertainment. Chapter 2 Slide 42 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Bell Ringer October 15, 2015 What are the four strategies for managing risk? Chapter 2 Slide 43 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western Bell Ringer October 16, 2015 Review for test. Chapter 2 Slide 44 Sports and Entertainment Marketing © Thomson/South-Western