MITOSIS
advertisement

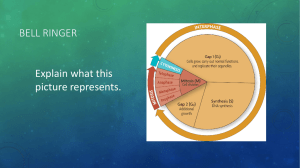
MITOSIS Think About This… What is this? What IS cancer?? What are some causes? What are some reasons for cell division? How do you think a cell would accomplish this task? SO WHY LEARN ABOUT CELL DIVISION?? Growth Cancer- uncontrolled growth Cells have given life spans; need to replace! Lining of esophagus 2-3 days Lining of small intestine 1-2 days Skin 2-4 weeks Stem Cells All Cells Come From Cells One concept of the cell theory we just learned about! All organisms reproduce their own kind… Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Types of Cell Division We Will Learn About Mitosis- Division of somatic cells (body cells) Meiosis- Creation of gametes (sex cells) Lab- You Are a 19th Century Cell Biologist In this lab, you will assume the role of a biologist in the mid-1890s. You are fascinated by the power of the microscope to reveal the inner workings of living cells. The invention of the compound microscope, along with new stains, make it possible for you to see cell structures that no one has ever seen before. You plan to collaborate with your colleagues to discover the events of cell division. Lab- You Are a 19th Century Cell Biologist Things you know right now: 1) The cell has many organelles. 2) The nucleus seems to be pretty important. 3) There seem to be “structures” inside the nucleus that undergo changes during cell division (chromosomes). Lab- You Are a 19th Century Cell Biologist 1) Obtain a microscope and a slide of onion root tip. 2) Focus under low power. MITOSIS-ONION ROOT TIP 3) Move to high power; only adjust here with the fine focus. Lab- You Are a 19th Century Cell Biologist 4) Select one cell whose chromosomes are clearly visible & sketch in the box. 5) Look around and select 4 other cells whose internal appearances are different and sketch them as well. 6) Try and place your sketches in order from 15. 7) Check your answers with Mrs. Romano… how many did you get right?? Lab- You Are a 19th Century Cell Biologist 8) Identify the phases of cell division. 9) Count the number of cells in your slide in each stage of cell division. 10) Answer the analysis questions. MITOSIS Review- Cell Parts TERMS TO KNOW: Nucleus Nuclear envelope Centriole Spindle Fiber Chromatin Chromatid Chromosome Centromere Chromatin vs. Chromosomes Do All Cells Divide?? NO!! Muscles, neurons, red blood cells, white blood cells generally DO NOT go through mitosis. Cell Cycle Orderly sequence of cell division INTERPHASE- Cell grows, DNA replicates, gets ready to divide; LONG MITOSIS (cell divides) 4 parts Chromosome duplication MITOSIS- Step 1 of 4 Prophase- chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane disappears, spindle forms MITOSIS- Step 2 of 4 Metaphase- chromosomes move to center of the cell and attach to spindle fibers MITOSIS- Step 3 of 4 Anaphase- Chromosome strands move towards opposite ends MIATOSIS- Step 4 of 4 Telophase- Chromosomes reach ends; nuclear envelope reforms; cytoplasm divides (CYTOKINESIS) Plant vs. Animal Cell Mitosis ANIMALS- cleavage furrow PLANTS- cell plate Stages in an onion root tip Movie Mitosis Video Review- Mitosis Animation Mitosis Movie!! Cancer Out-of-control cell reproduction TUMOR- mass of cells Benign Malignant Breast Cancer cells Metastasis Most dangerous property of cancer cells is their ability to spread beyond their original site Detection Detection Visual Radiation Imaging (spot glows under UV light) Biological or chemical test (spot changes color when exposed to a chemical) Treatment Radiation Therapy Chemotherapy Causes Getting older Genetics Tobacco UV radiation (sunlight) X-rays Certain chemicals (asbestos, vinyl chloride, nickel) Certain viruses/ bacteria (HPV, Hepatitis C, HIV) Certain hormones (excess estrogen) Alcohol Poor diet/ lack of exercise Melanoma- One Type of Skin Cancer Breast Cancer Lung Cancer Prostate Cancer Leukemia Colon Cancer Video The Genetics of Cancer