Graham Calladine, David Hoyle
Security Center of Excellence
Microsoft
Session Code: SIA313
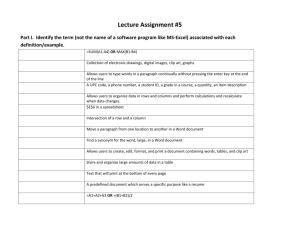
Session Objectives & Takeaways
To learn and understand:
Current Attack Trends that Microsoft is seeing
Attack Vectors
Mitigation Strategies with Windows Products
10 Years…
We have come a long way since Melissa
2003-2004 difficult times
Blaster/Slammer – Was horrible – Hit Home Users hard
Conficker emerged in a different s/w industry – Did not hit
home users hard
Partnerships
MS Response Alliance & Internet Consortium for Advanced Security
on the Internet & CWG
WW Threat Trends
Not a simple trend – Geographically Diverse
Miscellaneous Trojans (inc rouge s/w)
most prevalent
WORMS 2nd most prevalent
Password Stealers & Monitoring tools
Breaches – Data Scarce – (datalossdb.org)
Top is stolen equipment, twice as many incidents
as intrusion
But equipment loss is easily reported!
Data: Microsoft SIR v7 Report
Geographical Trends
8 Locations with most infected machines
USA,UK,France,Italy – Trojans
China, language specific browser threats
Brazil, malware targeting online banking
Spain, Korea, WORMS targeting online gamers
Data Source: SIR V7 Report Pg 40
Threat Landscape is getting better?
Improvement in Software Development Practice
Software Development Lifecycle (SDL)
Geoff 1min Video
Increased Availability of Automatic Patch
Update Process
Patch Tuesday and Auto Updates
However, unpatched client is primary initial infection vector
Social engineering techniques to mislead
Victims
Attacker still finds success with a variety of techniques for
manipulating people
SANS Analysis
The Top Cyber Security Risks” 2009 September
Application Vulnerabilities Exceed
OS Vulnerabilities
Web Application Attacks
Cross Site Scripting, PHP
File Include, and
SQL Injection
Windows:
Conficker/Downadup
Cited from SANS “The Top Cyber Security Risks” 2009 September, http://www.sans.org/top-cyber-security-risks/
Attackers use social engineering
techniques – Human Emotion
FEAR
I want: Protection
Desire
I got: Rogue
Software
I wanWeb
Surfing,
Free Stuff
Trust
Games, etc
want:
Online
Banking,
I Igot:
fake
contents,
Email,
Social Networking
malicious
downloads, etc
etc.
I got: Banking
Malware, Phishing,
Spam, and File Format
Infections, etc.
Microsoft Security Intelligence
Report, 2008 July through
December 2008
Attack Vectors and Trends
Current attacks in the wild
Rogue Security Software and Worm
Browser Based Attacks
Phishing
Cross Site Scripting
Clickjacking
File Format Attacks
Attack Vectors and Trends
Rogue Security Software and
Worms
Browser Based Attacks
File Format Attack
Rogue Unwanted Software
Rank
Family
Most Significant Infected
Category
Machines
Win32/Renos
1
Win32/Renos
2
Win32/Zlob
Trojan Downloaders &
Droppers
Trojan Downloaders &
Droppers
3
Win32/Vundo
Miscellaneous Trojans
3,635,207
4
Win32/ZangoSearchAssistant
Adware
3,326,275
5
Win32/Taterf
Worms
1,916,446
6
Win32/ZangoShoppingreports
Adware
1,752,252
7
Win32/FakeXPA
Miscellaneous Trojans
1,691,393
Win32/FakeSecSen
Miscellaneous Trojans
1,575,648
9
Win32/Hotbar
Adware
1,477,886
10
Win32/Agent
Miscellaneous Trojans
1,289,178
8
Win32/FakeXPA
4,371,508
3,772,217
Rogue Security Software 1
Use Fear to convince victims
Win32/Renos Family
Rogue Security Software 2
Use the same logic
Win32/FakeXPA Family
A Rogue Software Real Sample
http://blogs.technet.com/mmpc/archive/2009/08/20/winwebsec-on-youtube.aspx
Use your Desire
There is no security issue or vulnerability in YouTube.com.
Rogue Software
Win32/FakeVimes and Win32/PrivacyCenter
have become more prevalent in the last
2 months
Distributed via fake online scanners
Worms: Win32/Conficker.A to E
Win32/Conficker is a worm that infects other computers across a network by
exploiting a vulnerability in the Windows Server service (SVCHOST.EXE)
On October 23, 2008, Microsoft released critical security update MS08-067
Allow remote code execution if an affected system received a specially crafted
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) request
On November 21, 2008, the first significant worm that exploits MS08-067
was discovered
The first variant discovered, Worm:Win32/Conficker.A, only uses MS08-067
exploits to propagate
On December 29 2008, a significantly more dangerous variant, Win32/Conficker.B,
was discovered
Exploits the MS08-067 vulnerability but uses additional methods to propagate.
It attempts to spread itself to other computers on the network
Combining the vulnerability with social engineering to introduce and spread
the worm in an organization
Continues…
http://www.microsoft.com/security/portal/Threat/Encyclopedia/Entry.aspx?Name=Win32%2fConficker
Social Engineering
by e-mailing infected files
with official-sounding names
to people at a company like
“Corporate Policy.PDF”
Worms: Win32/Conficker.A to E
Release D, monitors 500/50,000 domain
names/day for payloads…
Still is
Conficker Working Group (CWG) formed Jan09
Many people from well know sec groups/researchers
Implemented defense DNS strategy
Kaspersky & OpenDNS – calc’ed 1Y of names
All 110 TLDs involved & signed up
Rapid, effective collaboration – keeps
Conficker constrained
Published Articles for Conficker
Knowledge Base article
KB962007
MMPC blog (http://blogs.technet.com/mmpc)
Get Protected, Now! (October 23, 2008)
A Quick Update About MS08-067 Exploits (November
17, 2008)
Just in Time for New Year’s… (December 31, 2008)
MSRA Released Today Addressing Conficker and
Banload (January 13, 2009)
Centralized Information About the Conficker Worm
(January 22, 2009)
Information about Worm:Win32/Conficker.D (March
27, 2009)
Mitigations
Get the latest computer updates
Install and update anti-malware signatures
Run an up-to-date scanning and removal tool
Use caution with attachments and file transfers
Use caution when clicking on links to web pages
Standard user rights
Protect yourself from social engineering attacks
User Security Best Practices such as strong
Password Policy
Keep eye on vulnerabilities and follow the guideline from
the trusted source
Use recent technologies and systems that can reduce the
risk on exploiting
Attack Vectors and Trends
Rogue Security Software and worms
Browser Based Attacks
File Format Attack
Browser Based Attacks
Phishing
Cross Site Scripting
ClickJacking
Browser Based Attacks
Phishing
Cross Site Scripting
ClickJacking
Phishing: Overview
Phishing is a method of identity theft that tricks
Internet users into revealing personal or
financial information online.
Phishing Scam Samples
Social engineering techniques
“Verify your account”
“If you don't respond within 48 hours,
your account will be closed”
“Dear Valued Customer”
“Click the link below to gain access to
your account”
Spear Phishing and Whaling
Spear phishing - highly targeted phishing
Send email messages that appear genuine to all
employees and members within a community
Whaling - involves targeted attacks on senior
executives and other high ranking people
Phishing Trends in Industry
APWG: Anti Phishing Working Group Report,
2009 1H
http://www.antiphishing.org/reports/apwg_report_h1_2009.pdf
Phish Tank: Current Phish Sites
Live Phish site can be found
http://www.phishtank.com/
Phishing with Hotmail
Illegally acquired by a
phishing scheme and
exposed to a website
Microsoft Recommends:
Renew their passwords for Windows Live IDs
every 90 days
For administrators, make sure you approve and
authenticate only users that you know and can
verify credentials
As phishing sites can also pose additional
threats, install and keep anti-virus software up
to date
Techniques
Man-in-the-middle attacks
Proxies,
DNS Cache Poisoning, etc
URL Obfuscation attacks
Bad Domain Name,
Friendly Login URL’s,
Host Name/URL Obfuscation, etc
Etc…
Anti-Phishing
IE 8 SmartScreen
Mitigations
Use an up-to-date anti-malware product from a
known, trusted source, and keep it updated.
Use the most recent version of your Web browser,
and keep it up to date by applying security updates
and service packs in a timely fashion.
Use a robust spam filter to guard against fraudulent
and dangerous e-mail.
You can add sites you trust to the Trusted Sites
zone with more than middle security level.
Follow the guidance to take actions
http://www.microsoft.com/mscorp/safety/technologie
s/antiphishing/guidance.mspx
Browser Based Attacks
Phishing
Cross Site Scripting
ClickJacking
Cross Site Scripting: Overview
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Occurs whenever an
application reads user data, and embeds that user data
in Web responses without encoding or validating the
user data
Common vulnerabilities that make Web-based
applications susceptible to cross-site scripting attacks:
Improper input validation
Failing to encode output
Trusting data from shared resources
Cross Site Scripting in News
October 2005
February 2006
June 2008
December 2008
April 2009
MySpace “Samy” worm
Facebook
Yahoo Mail
American Express
Twitter
http://twittercism.com/remove-stalkdaily/
http://xssed.com/ - live XSSed
Types of Cross-Site Scripting
Two major types of cross-site scripting attacks:
Type 1: Non-Persistent
Often referred to as reflected cross-site scripting
Requires some level of social engineering
Type 2: Persistent
Stored cross-site scripting
One attack can affect multiple users
Type 0: DOM-Based
38
Type 1: Non-Persistent
Cross-Site Scripting
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello</title>
Congratulations! You won a prize, </head>
http://www.contoso.com?
<body>
please click here to claim your
id=[malicious
[malicious
code] code]
prize!
</body>
…
Web Server
Malicious User
User
39
Type 2: Persistent
Cross-Site Scripting
Web Server
Malicious User
Blog Comment:
Hello, this article was
helpful! [malicious code]
Thanks,
Kevin
User
Database
Blog Comment:
Hello, this article was
helpful! [malicious code]
Thanks,
Kevin
User
User
40
Mitigation Strategies
Server Sides
Validate all untrusted input
Encode any Web response data that could contain
user or other untrusted input
Use built-in ASP.NET protection via the
ValidateRequest option
Use the System.Web.HttpCookie.HttpOnly property
Use the <frame>, <iframe> IE6 and above security
attribute
Use the Microsoft Anti-Cross Site Scripting Library
(AntiXSS)
Microsoft Anti-Cross Site Scripting
Library V3.1
New features
An expanded white list that supports more
languages
Performance improvements
Performance data sheets (in the online help)
Support for Shift_JIS encoding for mobile browsers
A sample application
Security Runtime Engine (SRE) HTTP module
Security Runtime Engine (SRE) HTTP module
Ideally, you do not need to change your code!
In your your web.config,
<httpModules>
<add name="AntiXssModule"
type="Microsoft.Security.Application.
SecurityRuntimeEngine.AntiXssModule"/>
</httpModules>
In antixssmodule.config,
<ControlEncodingContexts>
<ControlEncodingContext FullClassName="System.Web.UI.Page"
PropertyName="Title" EncodingContext="Html" />
<ControlEncodingContext
FullClassName="System.Web.UI.WebControls.Label"
PropertyName="Text" EncodingContext="Html" />
<ControlEncodingContext
FullClassName="System.Web.UI.WebControls.CheckBox"
PropertyName="Text" EncodingContext="Html" />
</ControlEncodingContexts>
Anti-Cross Site Scripting in Action
Microsoft Anti-Cross Site Scripting Library V3.1
Mitigation Strategies
Client Sides
IE8 XSS Filter
Anti-Cross Site Scripting in Action
IE8 XSS Filter with Microsoft Application Compatibility Tool Kit
Browser Based Attacks
Phishing
Cross Site Scripting
ClickJacking
ClickJacking: Overview
Clickjacking is :
an attack that tricks the victim into initiating
commands on a website that they did not intend.
Use iframes and web page layers in DHTML such
that you overlay a potentially malicious button (for
example) on top of an existing legitimate web page.
A ClickJacking Example
Suppose that a hacker site has the following
source code…
Mitigation
Use FrameBreaker Script
<script>if (top!=self)
top.location.href=self.location.href</script>
Use X-Frame-Options Header for IE8
HTTP response header named X-FRAME-OPTIONS with
HTML pages to restrict how the page may be framed
The OPTIONS value contains the token DENY, IE8 will
prevent the page from rendering if it will be contained
within a frame
Add X-FRAME-OPTIONS and Deny to HTTP Response Headers using
IIS Manager,
In html, insert <meta http-equiv="X-FRAME-OPTIONS"
content="DENY" /> in <head> section, or
Using ASP.Net, you can insert Response.AddHeader("X-FrameOptions", "Deny”).
ClickJacking:
FrameBreaker and IE8 Defense
Attack Vectors and Trends
Rogue Unwanted Software
Browser Based Attacks
File Format Attack - Office
File Format Attack: Overview
This class of vulnerability is described as parser
vulnerabilities.
Attacker creates a specially crafted document that
takes advantage of an error in how the code
processes or parses the file format.
Increasingly, attackers are using common file
formats as transmission vectors for exploits.
Office format and PDF format
File Format Attack Trend
Recent (2H08) saw a sharp increase in the
number of file format–based attacks,
Often in the form of spear phishing and whaling
attacks, the victim opens the attachment
Or at a malicious / compromised web site, and the
malicious code forces browsers to a malicious
document, which is opened by victim
Binary Office File Format vs. Open
XML format
Office 2003 (and lower) Binary Format
OLE Structured Storage outer format
File system within a file!
Header
Complex file format
complete with
FAT Table
Sectors
Streams (like files)
Another application
specific inner format
within a stream!
STRM1
STRM2
STRM3
STRM4
Examining The File
Requires a hex editor + expert knowledge
Interesting strings in a stream near the beginning of
the malicious files!
What could possibly go wrong?
Office 2007 Open XML File Format
Safety was a design goal from the beginning
Designed under the SDL
ZIP file container with ‘XML parts’
Also non-XML parts (typically binary data like
embedded images or OLE objects)
Non-XML parts can be disabled by policy
Rename to .zip and open with zip file viewer!
Historical Data
Office Security Bulletin Trend (by quarter)
30
25
Newer is Better
20
% of vulns affecting Office 2007 since Jan 2007
15
10
5
28% Vulnerable
0
1 2 3 4
2004
1 2 3 4
2005
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2
2006
2007
2008
72% Not Vulnerable
Layered Defenses
Harden the Attack Surface
Security Engineering
Security Development Lifecycle
Foundation
Intensive Distributed Fuzzing
Integrate OS Advances
Support for DEP/NX
Leverage WIC Image Parsers
Robust & Agile Cryptography
Reduce the Attack Surface
File Block
Block unused or legacy file formats
Easy policy enforcement
View allows read-only access
Tied in with Protected View for
formats between block and allow
Office File Validation
Binary files
Runs automatically on open
Evaluates file for ‘correctness’
Protects against unknown exploits
Faster updates for changes to rules
Gatekeeper vs MSRC cases
Protected Viewer ‘Sandbox’
Word, Excel, PPT files can run
in the ‘sandbox’
Prevents harmful documents
from damaging user data
and OS
Help users make better
trust decisions
Protected Viewer
Office - FileFormats
Observations on XP
Malicious PPT drops
an EXE and a clean
PPT on users
desktop
Requires
regular
user rights
The EXE creates a
‘.log’ file in users
temp folder and
executes it.
Requires
regular
user rights
The malware creates
2 binaries in
system32 and
modifies HKLM
registry keys
Requires
admin
rights
The binaries are
injected into SYSTEM
processes like
winlogon.exe
Requires
admin
rights
Observations on Vista
Malicious PPT drops
an EXE and a clean
PPT on users
desktop
Requires
regular
user rights
The EXE creates a
‘.log’ file in users
temp folder and
executes it.
Requires
regular
user rights
The malware creates
2 binaries in
system32 and
modifies HKLM
registry keys
Requires
admin
rights
The binaries are
injected into SYSTEM
processes like
winlogon.exe
Requires
admin
rights
Better Together
File Block
GateKeeper
Standard User
/ UAC
UAC “Dark
Roast”
Mitigations
Configure your computer to use Microsoft Update
Ensure that Microsoft security update MS06-027 has been applied to any
affected software in your environment:
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/bulletin/ MS06-027.mspx.
Keep your third-party software up to date. Updates for Adobe products can
be downloaded from http://www.adobe.com/downloads/updates/.
If possible, upgrade your software applications to the most recent versions,
since these demonstrate lower rates of attack.
Avoid opening attachments or clicking links to documents in e-mail or instant
messages that are received unexpectedly or from an unknown source.
Use up-to-date antivirus software from a known, trusted source that offers
real-time protection and continually updated definition files to detect and
block exploits.
Summary
Trends are WORMS, Rogue, FileFormat
Varies world wide
Security Community effort in industry to keep
on top
Technology evolving fast to solve root cause
(GateKeeper)
Updates, Virus Checkers, Good Risk
Management are key, Security Standards
Lockdowns go a long way
Quick Case Study
AppLocker + Windows only rules + App rules
No execute for standard users for writable areas
Bitlocker
Lockdown to reduce attack surface
Virus checker/Updates etc…
Gives a solid defense in-depth client build!
Summary
Both security vendors and IT professionals should
Adjust their risk management processes appropriately to
help ensure that all operating systems and applications are
protected (ISO 27000, COBIT, MS Sec Risk Guide)
Keep updating wide range of potential security issues
Take appropriate actions based on your risk assessment
As individual to protect against malicious code
Keep update the security patches and anti-virus signatures,
and if possible upgrade to newer software
Educate themselves for potential security risks
IT professionals and consumers should take advantage of
the defense-in-depth technologies, such as firewalls,
antivirus programs, and antispyware programs available
from trusted sources…
Summary
Most important of all…
Stay informed & up to date
Microsoft Malware Protection Center
Microsoft Security Update Guide
Microsoft Security Engineering Center
Microsoft Security Response Center
Microsoft SIR v7 Report
Microsoft AV
Security Essentials
End to End trust
Microsoft Security Development Lifecycle
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures :
http://cve.mitre.org
Track Resources
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures : http://cve.mitre.org
Nation Vulnerability Database : http://nvdnist.gov
www.securityfocus.com, www.secunia.com, www.securitytracker.com
Microsoft Malware Protection Center, Microsoft Security Update Guide, Microsoft
Security Engineering Center, Microsoft Security Response Center, Microsoft SIR v7
Report, Microsoft AV, Security Essentials, End to End trust, Microsoft Security
Development Lifecycle
Resources
www.microsoft.com/teched
www.microsoft.com/learning
Sessions On-Demand & Community
Microsoft Certification & Training Resources
http://microsoft.com/technet
http://microsoft.com/msdn
Resources for IT Professionals
Resources for Developers
Related Content
SIA-205: SDL-Agile: Microsoft’s Approach to Security for Agile Projects
Complete an evaluation
on CommNet and enter to
win an Xbox 360 Elite!
© 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft, Windows, Windows Vista and other product names are or may be registered trademarks and/or trademarks in the U.S. and/or other countries.
The information herein is for informational purposes only and represents the current view of Microsoft Corporation as of the date of this presentation. Because Microsoft must respond to changing market conditions, it should
not be interpreted to be a commitment on the part of Microsoft, and Microsoft cannot guarantee the accuracy of any information provided after the date of this presentation. MICROSOFT MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS,
IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, AS TO THE INFORMATION IN THIS PRESENTATION.