Keystone Remediation Course Curriculum - 11th Grade Literature
advertisement
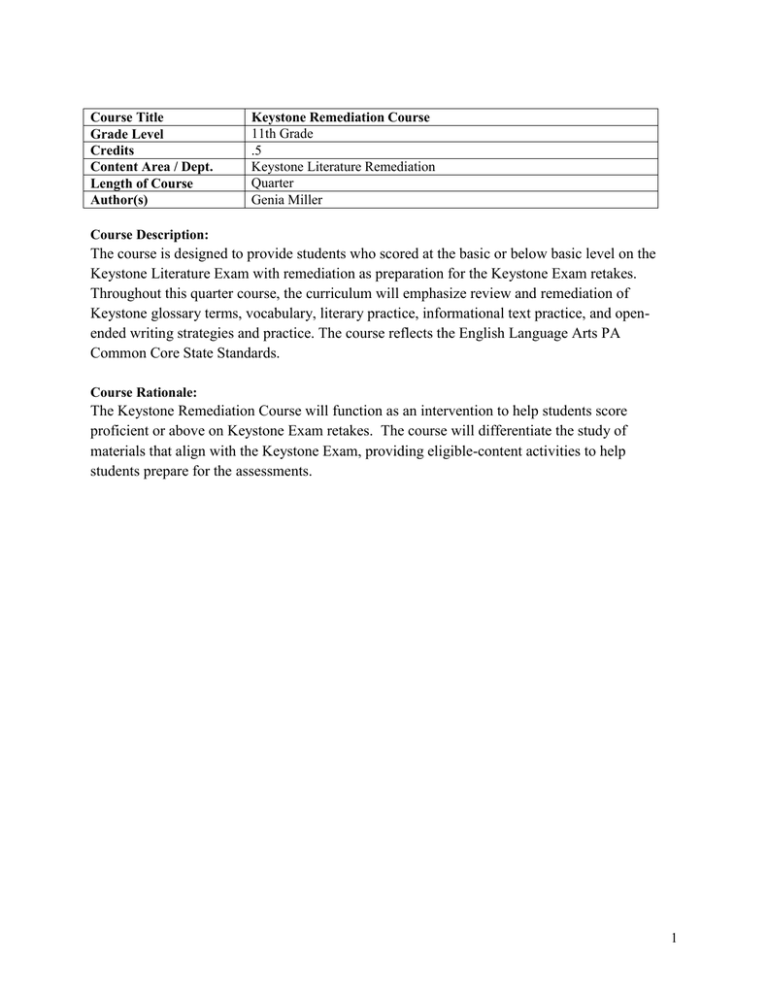
Course Title Grade Level Credits Content Area / Dept. Length of Course Author(s) Keystone Remediation Course 11th Grade .5 Keystone Literature Remediation Quarter Genia Miller Course Description: The course is designed to provide students who scored at the basic or below basic level on the Keystone Literature Exam with remediation as preparation for the Keystone Exam retakes. Throughout this quarter course, the curriculum will emphasize review and remediation of Keystone glossary terms, vocabulary, literary practice, informational text practice, and openended writing strategies and practice. The course reflects the English Language Arts PA Common Core State Standards. Course Rationale: The Keystone Remediation Course will function as an intervention to help students score proficient or above on Keystone Exam retakes. The course will differentiate the study of materials that align with the Keystone Exam, providing eligible-content activities to help students prepare for the assessments. 1 Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Page 8 Page 9 Page 10 Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page 16 Page 17 Page 18 Page 19 Page 20 Page 21-22 Page 23 Table of Contents Course Title: Keystone Remediation Course – Course Description, Course Rationale Table of Contents Curriculum Map Unit Title: Ongoing Vocabulary - Unit Description; Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings; Anchor Descriptor; Eligible Content; PA Common Core Standards; Learning Objectives; Assessment Opportunities; Keystone Glossary Terms & Vocabulary Keystone Glossary Terms & Vocabulary (continued) Sequence of Teaching and Learning; Resources for this Unit; Additional Exam Practice Materials; Remediation Consists Of Study Island – Ongoing Unit Vocabulary Acquisition and Usage; Study Island Remediation; Fictional Texts/Informational Texts Unit 1 – Reading for Meaning – Fiction – Unit Description; Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings; Anchor Descriptor, Eligible Content; PA Common Core Standards; Learning Objectives; Assessment Opportunities Key Unit Vocabulary; Sequence of Teaching and Learning; Resources for this Unit Resources for this Unit (continued); Additional Exam Practice Materials; Remediation Consists Of; Study Island – Unit 1 – Reading for Meaning – Fiction, Study Island Remediation; Fictional Texts Unit 2 – Analyzing and Interpreting Literature – Fiction – Unit Description, Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings; Anchor Descriptor, Eligible Content; PA Common Core Standards; Learning Objective; Assessment Opportunities Learning Objective (continued); Key Unit Vocabulary; Sequence of Teaching and Learning Sequence of Teaching and Learning (continued); Resources for this Unit; Remediation Consist Of, Study Island – Unit 2- Analyzing and Interpreting Literature – Fiction, Study Island Remediation; Fictional Texts Unit 2 – Analyzing and Interpreting Literature – Fiction, Study Island Remediation; Fictional Texts (continued) Unit 3 – Reading for Meaning – Nonfiction – Unit Description; Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings; Anchor Descriptor; Eligible Content; PA Common Core Standards; Learning Objective; Assessment Opportunities Key Unit Vocabulary; Sequence of Teaching and Learning Resources for this Unit; Remediation Consists Of, Study Island – Unit 3 – Reading for Meaning – Nonfiction; Study Island Remediation; Nonfictional Texts Unit 4 – Analyzing and Interpreting Literature – Nonfiction – Unit Description; Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings; Anchor Descriptor; Eligible Content; PA Common Core Standards; Learning Objective; Assessment Opportunities Learning Objectives (continued); Assessment Opportunities (continued); Key Unit Vocabulary; Sequence of Teaching and Learning Sequence of Teaching and Learning (continued); Resources for this Unit Resources (continued); Remediation Consists Of, Study Island – Unit 4 Analyzing & Interpreting Literature – Nonfiction; Study Island Remediation; Nonfictional Texts Appendix 2 Curriculum Map (Quarter Long Course) Quarter Typical # of Weeks Topics 9 weeks Keystone glossary terms, Keystone vocabulary, content vocabulary, literary practice, informational text practice, and open-ended writing strategies and practice 3 Ongoing Vocabulary Unit Title Unit Description Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings Anchor Descriptor L.F.1.2 L.N.1.2 Learning Objectives Determine and clarify meaning of vocabulary in literature. Synthesize glossary terms and vocabulary to demonstrate comprehension of literature during the reading process. Keystone Glossary Terms & Vocabulary Glossary Terms and Vocabulary Analysis & Review-Fiction & Nonfiction This unit will assess student abilities and address student needs to help them develop strategies for analyzing, synthesizing, and employing Keystone glossary terms and vocabulary words on the Keystone Literature Exams. ● Context clues help determine the meanings of words. ● How can recognition of affixes improve vocabulary skills? ● Synthesizing specialized vocabulary is essential to understanding and analysis of fiction and nonfiction. ● What are the specific roles of connotation and denotation when analyzing a piece of literature? Eligible Content L.F.1.2.1 L.F.1.2.2 L.F.1.2.3 L.F.1.2.4 L.N.1.2.1 L.N.1.2.2 L.N.1.2.3 L.N.1.2.4 PA Common Core Standards CC.1.3.9--10.I CC.1.3.9--10.J CC.1.2.9--10.J CC.1.2.9--10.K Assessment Opportunities Teachers will employ a number of assessment strategies in order to evaluate individual student understanding and requirements. SAS Assessment Creator provides examples of Keystone Benchmark, Diagnostic, Formative, and Summative Assessments: http://www.pdesas.org/module/assessment/ Search.aspx In addition, formative assessments will encompass a variety of strategies both formal and informal. They will include, but are not restricted to question-answer, interactive engagement check-ins (think-pair-share, splashes, partner finds, student-authored assessments, appointment clock activities), guided practice, presentations, short answer writing, class work, homework, and quizzes. Summative assessments will include, but are not limited to, objective test including a cold read and a short written response, a Keystone Constructed Response to reflect cumulative knowledge, and/or a presentation reflecting essential terms and concepts. A: Affix, Allegory, Alliteration, Allusion, Analysis, Antonym, Argument/Position, Author’s Purpose B: Bias, Biography C: Character, Characterization, Climax, Compare/Contrast, Conflict/Problem, Connotation, Context Clues, Controlling Idea, Cultural Significance 4 (addressed in context in all units throughout the quarter) D: Defense of a Claim, Dialect, Dialogue, Diction, Differentiate, Drama, Dramatic Script, Draw Conclusion E: Elements of Fiction, Elements of Nonfiction, Evaluate, Explain, Explicit, Exposition F: Fact, Falling Action, Fiction, Figurative Language, Flashback, Focus, Foreshadowing G: Generalization, Genre H: Headings, Graphics and Charts: (Headings, Graphics, Charts), Hyperbole I: Imagery, Implicit, Inference, Informational Text, Interpret, Irony K: Key/Supporting Details, Key Words L: Literary Device, Literary Element, Literary Form, Literary Movement. Literary Nonfiction M: Main Idea, Metaphor, Monologue, Mood, Motif, Multiple‐ meaning Words N: Narrative, Narrator, Nonfiction O: Opinion P: Personification Plot rising action, climax, falling action, resolution, antagonist, protagonist, conflict Poetry meter, imagery, connotative words, denotative words, concrete words, rhyme scheme, rhythmic patterns, figurative language Point of View: first person, third person limited, third person omniscient Prefix Propaganda: Propaganda Techniques: Name‐ calling, Bandwagon, Red herring, Emotional appeal, Testimonial, Repetition, Sweeping generalization (stereotyping), Circular argument, Appeal to numbers, facts, or statistics R: Resolution, Rising Action S: Satire Sentence Variety: simple, complex, compound, compound‐ complex Various Sentence Beginnings: dependent clauses, independent clauses, phrases Sequence of Steps, Setting, Simile, Soliloquy Sound Devices: assonance, consonance, alliteration, rhyme, onomatopoeia Speaker, Stage Direction, Structure of Poem, Style, Suffix, Summarize, Symbolism, Synonym, Syntax T: Text Organization/Structure Sequence: question‐ answer cause‐ effect Theme, Tone U: Universal Character, Universal Significance V: Voice 5 Sequence of Teaching and Learning Number of Lessons / Blocks Lesson Topic 1 Block Ongoing throughout Ongoing throughout Why Vocab? Glossary Terms & Vocabulary Introduction, Review & Assessment Context Clues/ Affixes Ongoing throughout Reinforcement & Modeling Ongoing throughout Real-life Application Ongoing throughout Critical reading for vocabulary recognition Ongoing throughout Ongoing throughout 1 Block Constructed Response Extended comprehension Review Ongoing throughout Course Lesson Activities “Get to Know You” vocab handout and snowball fight activity to demonstrate prior knowledge of Glossary Terms and Vocabulary. Teacher directed learning (direct instruction, board activities, guided practices, PowerPoint presentations) to address vocabulary words relevant to unit lesson understanding. Daily checks and reminders during vocabulary lessons and reading of literature to reinforce deciphering skills with context clues and affixes identification. Games, group activities, and partner activities to reinforce term concepts Small group search for Keystone terms and vocabulary in popular media (internet, tv, books, magazines, movies, etc.) Students work in groups to identify modern references to and applications of Keystone concepts and present their findings to the class using a multimedia format. Close read excerpts of unit literature and participation in teacherfacilitated activities and discussions. Introduction of reading skill, guided practices, and “It’s Your Turn” independent multiple choice and constructive response activities will help to extend the learning. Constructed responses to literature using detailed glossary terms and vocabulary. Teacher-facilitated reminders of the importance of increasing vocabulary to enhance reading and writing skills. Complete review activities to tie up each unit including glossary terms and vocabulary to prepare for summative assessments. Resources for this Unit Keystone Finish Line: Literature Study Island Common Core Coach (for American Literature and Informational Texts I) Currents in Literature: Genre Volume Keystone Item and Scoring Sampler Supplemental Literary Materials Additional Exam Practice Materials: Measuring Up Diagnostic Practice Tests 4Sight Practice Tests PSSA Reading Coach, Performance Indicator, Jumpstart & Reading Coach (Grade 11) Remediation consists of the following: Additional teacher generated practice exercises & activities Period 12 remediation 6 After school tutoring with English tutor Study Island: Ongoing Unit Vocabulary Acquisition and Usage Study Island Remediation Fictional Texts/ Informational Texts Eligible Content Eligible Content Study Island - Keystone English Literature L.F.1.2.2, L.N.1.2.2 Identify how the meaning of a word is changed when an affix is added; identify the meaning of a word with an affix from a text. Use context clues to determine or clarify the meaning of unfamiliar, multiple-meaning, or ambiguous words. Identify and/or apply a synonym or antonym of a word used in a text. Affixes and Roots Draw conclusions about connotations of words. Connotation and Denotation L.F.1.2.3, L.N.1.2.3 L.F.1.2.1, L.N.1.2.1 L.F.1.2.4, L.N.1.2.4 Context Clues, Multiple Meaning Words Synonyms and Antonyms 7 Unit 1 Title Unit Description Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings Anchor Descriptor L.F.1.1 L.F.1.2 L.F.1.3 Learning Objectives Analyze an author’s purpose and techniques in literature. . Determine and clarify meaning of vocabulary in literature. Reading for Meaning--Fiction This unit will assess student abilities and address student needs to help them develop strategies for reading fiction proficiently for meaning. ● Why do author choices and techniques determine the effects of a piece of fiction? ● An author’s word choice influences all other components of fiction. ● How do literary themes relate to societal issues, transcending time and culture? ● Author perspective creates literary tone to influence audience mood. ● All fictional texts should speak explicitly as well as implicitly to readers.. ● How does an author use a fictional work to imply his/her beliefs. Eligible Content L.F.1.1.1 L.F.1.1.2 L.F.1.1.3 L.F.1.2.1 L.F.1.2.2 L.F.1.2.3 L.F.1.2.4 L.F.1.3.1 L.F.1.3.2 PA Common Core Standards CC.1.3.9--10.A CC.1.3.9--10.B CC.1.3.9--10.C CC.1.3.9--10.E CC.1.3.9--10.I CC.1.3.9--10.J Assessment Opportunities Teachers will employ a number of assessment strategies in order to evaluate individual student understanding and requirements. SAS Assessment Creator provides examples of Keystone Benchmark, Diagnostic, Formative, and Summative Assessments: http://www.pdesas.org/module/assessment/ Search.aspx In addition, formative assessments will encompass a variety of strategies both formal and informal. They will include, but are not restricted to question-answer, interactive engagement check-ins (think-pair-share, splashes, partner finds, student-authored assessments, appointment clock activities), guided practice, presentations, short answer writing, class work, homework, and quizzes. Summative assessments will include, but are not limited to, objective test including a cold read and a short written response, a Keystone Constructed Response to reflect cumulative knowledge, and/or a presentation reflecting essential terms and concepts. Synthesize literary terms and vocabulary to demonstrate comprehension of literature during the reading process. 8 Key Unit Vocabulary fiction, main ideas, supporting details, author’s purpose Sequence of Teaching and Learning (2.5 weeks) Number of Lesson Topic Lesson Activities Lessons / Blocks ½ Block Intro to Fiction ½ Block Benchmark Ongoing throughout Ongoing throughout Vocabulary Ongoing throughout Background Investigation: Extended Comprehension Skill Reinforcement Ongoing throughout Prevalent Themes & Concepts 1 Block Increments Critical reading of Fiction 1 Block Increments Extension Activities ½ Block Increments 1 Block Exam Practice 1 Block Summative Assessment 1 Block Summative Assessment Review Character Chum activity to demonstrate prior knowledge of literary fiction authors and terms. “It’s Your Turn” reading activity to assess skills for the following: (Multiple Choice: main ideas and author’s purpose Constructed Response: summarizing) Students receive vocabulary words relevant to unit. Teacher directed learning to address words as needed. Small group search for background information (biographies, reviews, articles…) about authors and literature. Study Island lessons: teacher facilitated review of Study Island lessons with differentiated instruction as needed (See Study Island chart below.) Teacher-led discussions throughout the readings on the relevant themes & concepts developed in fictional literature and how they are relevant to modern issues. Close read excerpts of Keystone Finish Line: Literature-Fiction and participation in teacher-facilitated activities and discussions: Introduction of reading skill, guided practices, and “It’s Your Turn” independent multiple choice and constructive response activities will help to complement the learning. Students read supplementary fictional literature and participate in teacher-facilitated activities & assessments. Various exercises including Keystone Constructed Responses will reflect and support Keystone Literature Exam requirements. Diagnostic, Formative & Summative practice exams to check individual requirements and accomplishments Complete review activities to tie up unit and prepare for summative assessment. Summative Assessment from one or more of the following: Objective questions and written response/Keystone constructed response /cummulative hands-on project Examples from SAS: http://www.pdesas.org/module/assessment/Search.aspx#assessmentsea rch Resources for this Unit Keystone Finish Line: Literature Study Island Common Core Coach (for American Literature and Informational Texts I) Currents in Literature: Genre Volume Keystone Item and Scoring Sampler 9 Supplemental Literary Materials Additional Exam Practice Materials: Measuring Up Diagnostic Practice Tests 4Sight Practice Tests PSSA Reading Coach, Performance Indicator, Jumpstart & Reading Coach (Grade 11) Remediation consists of the following: Additional teacher generated practice exercises & activities Period 12 remediation After school tutoring with English tutor Study Island: Unit 1 Reading for Meaning-Fiction Study Island Remediation Fictional Texts Eligible Content Eligible Content Study Island - Keystone English Literature L.F.1.1.1 Identify and/or analyze the author’s intended purpose of a text. Explain, describe, and/or analyze examples of a text that support the author’s intended purpose. Analyze, interpret, and evaluate how authors use techniques and elements of fiction to effectively communicate an idea or concept. Identify and/or explain stated or implied main ideas and relevant supporting details from a text. Note: Items may target specific paragraphs. Summarize the key details and events of a fictional text, in part or as a whole. Author's Purpose L.F.1.1.2 L.F.1.1.3 L.F.1.3.1 L.F.1.3.2 Author's Purpose Author's Technique Main Idea and Supporting Details Summarization 10 Unit 2 Title Unit Description Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings Anchor Descriptor L.F.2.1 L.F.2.2 L.F.2.3 L.F.2.4 L.F.2.5 Learning Objective Make and support interpretations of literature. Compare, analyze, and evaluate literary forms. Compare, analyze, and evaluate literary elements. Interpret and analyze the universal significance of literary fiction. Analyzing and Interpreting Literature--Fiction This unit encourages students to employ background knowledge of literary concepts and vocabulary to help them analyze, interpret, and compare fictional genres. ● How do author assumptions and beliefs influence textual analyses? ● How do varied artistic mediums differ in their approach to a subject? ● From what sources do authors draw to create a fictional work? ● Author experience and personality couples with audience perspective in analyses and interpretations of literature. Eligible Content L.F.2.1.1 L.F.2.1.2 L.F.2.2.1 L.F.2.2.2 L.F.2.2.3 L.F.2.2.4 L.F.2.3.1 L.F.2.3.2 L.F.2.3.3 L.F.2.3.4 L.F.2.3.5 L.F.2.3.6 L.F.2.4.1 L.F.2.5.1 L.F.2.5.2 L.F.2.5.3 PA Common Core Standards CC.1.3.9--10.B CC.1.3.9--10.G CC.1.3.9--10.H CC.1.3.9--10.A CC.1.3.9--10.C CC.1.3.9--10.D CC.1.3.9--10.E CC.1.3.9--10.F CC.1.3.9--10.H Assessment Opportunities Teachers will employ a number of assessment strategies in order to evaluate individual student understanding and requirements. SAS Assessment Creator provides examples of Keystone Benchmark, Diagnostic, Formative, and Summative Assessments: http://www.pdesas.org/module/assessment/ Search.aspx In addition, formative assessments will encompass a variety of strategies both formal and informal. They will include, but are not restricted to question-answer, interactive engagement check-ins (think-pair-share, splashes, partner finds, studentauthored assessments, appointment clock activities), guided practice, presentations, short answer writing, class work, homework, and quizzes. Summative assessments will include, but are not limited to, objective test including a cold read and a short written response, a Keystone Constructed Response to reflect cumulative knowledge, and/or a presentation reflecting essential terms and concepts. 11 Identify and analyze devices and patterns in literary fiction. Key Unit Vocabulary making inferences, drawing conclusions, literary form, character, setting, plot, narrative, figurative language, literary devices Sequence of Teaching and Learning (2.5 weeks) Number of Lessons / Blocks 2 Blocks Ongoing throughout ½ Block 15 minute increments throughout unit Ongoing throughout Lesson Topic Background Discovery Students investigate authors and literature appropriate to fiction unit. In small groups, students use Pages Application to create brochures to highlight literary trends, noted writers, styles and devices. Present to class. Vocabulary Students receive vocabulary words relevant to unit. Teacher directed learning to address words as needed. Writing Techniques Teacher-directed character development exploration. Exercise & Devices culminates into pair/share student-authored monologs defining modernday character/situation. Peer assessment for unit terms (plot line, character, lit devices…) Skill Reinforcement Study Island lessons: teacher facilitated review of Study Island lessons with differentiated instruction as needed (See Study Island chart below.) Prevalent Themes and Concepts Ongoing throughout Ongoing throughout Devices and Patterns Ongoing throughout Comparing Literature ½ Block Increments 1 Block Increments Exam Practice 1 Block Review: Fiction Units Summative 1 Block Lesson Activities Critical Reading Extension Activities Teacher-led discussions throughout the reading on the relevant themes & concepts developed in literature and how they relate to time periods and issues. Teacher-facilitated activities identifying literary devices & patterns in unit readings. Close read excerpts of unit literature ( excerpts, poetry & drama) and participation in teacher-facilitated activities and discussions. Introduction of reading skill, guided practices, and “It’s Your Turn” independent multiple choice and constructive response activities will help to extend the learning. Teacher-directed literature comparison. Pair/share and small group activities researching, analyzing & sharing various forms of literature. Practice assessments for recognition of structure and components of short story excerpts, poetry & drama. Diagnostic, Formative & Summative practice exams to check individual requirements and accomplishments Students read supplementary fictional literature and participate in teacher-facilitated activities & assessments. Various exercises including Keystone Constructed Responses will reflect and support Keystone Literature Exam requirements. Complete review activities to tie up unit and prepare for summative assessment of fiction Units. Summative Assessment from one or more of the following: Objective 12 Assessment 1 Block Summative Assessment questions and written response/Keystone constructed response /cummulative hands-on project Examples from SAS: http://www.pdesas.org/module/assessment/Search.aspx#assessmentsearc h Resources for this Unit Keystone Finish Line: Literature Study Island Common Core Coach (for American Literature and Informational Texts I) Currents in Literature: Genre Volume Keystone Item and Scoring Sampler Supplemental Literary Materials Additional Exam Practice Materials: Measuring Up Diagnostic Practice Tests 4Sight Practice Tests PSSA Reading Coach, Performance Indicator, Jumpstart & Reading Coach (Grade 11) Remediation consists of the following: Additional teacher generated practice exercises & activities Period 12 remediation After school tutoring with English tutor Study Island: Unit 2 Analyzing and Interpreting Literature-Fiction Study Island Remediation Fictional Texts Eligible Content Eligible Content Study Island - Keystone English Literature L.F.2.1.1 Make inferences and/or draw conclusions based on analysis of a text. Cite evidence from a text to support generalizations. Analyze how literary form relates to and/or influences meaning of a text. Compare and evaluate the characteristics that distinguish fiction from literary nonfiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate connections between texts. Compare and evaluate the characteristics that distinguish narrative, poetry, and drama. Conclusions, Inferences, and Generalizations Conclusions, Inferences, and Generalizations Genres L.F.2.1.2 L.F.2.2.1 L.F.2.2.2 L.F.2.2.3 L.F.2.2.4 Genres Connections Between Texts Structure and Elements of Poetry, Structure and Elements of Drama, Genres 13 L.F.2.3.1 L.F.2.3.2 L.F.2.3.3 L.F.2.3.4 L.F.2.3.5 L.F.2.3.6 L.F.2.4.1 L.F.2.5.1 L.F.2.5.2 L.F.2.5.3 Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate character in a variety of fiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate setting in a variety of fiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate plot in a variety of fiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate theme in a variety of fiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate tone, style, and/or mood in a variety of fiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate point of view in a variety of fiction. Interpret and analyze works from a variety of genres for literary, historical, and/or cultural significance. Identify, explain, interpret, describe, and/or analyze the effects of personification, simile, metaphor, hyperbole, satire, foreshadowing, flashback, imagery, allegory, symbolism, dialect, allusion, and irony in a text. Identify, explain, and analyze the structure of poems and sound devices. Identify and analyze how stage directions, monologue, dialogue, soliloquy, and dialect support dramatic script. Characters Setting Plot Theme Tone, Style, and Mood Point of View Cultural and Historical Significance Literary Devices Structure and Elements of Poetry Structure and Elements of Drama 14 Unit 3 Title Unit Description Reading for Meaning--Nonfiction This unit will assess student abilities and address student needs to help them develop strategies for reading nonfiction proficiently for meaning. Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings ● ● ● ● Anchor Descriptor L.N.1.1 L.N.1.2 L.N.1.3 Learning Objective Analyze a literary author’s purpose and techniques. Determine and clarify definitions of vocabulary in literature. Synthesize understanding of main ideas and supporting details to demonstrate comprehension of literature during the reading process. How do specific author techniques influence the development of a work of nonfiction? What tools does an author employ to communicate his ideas and claims. How does word choice determine meaning and tone in nonfictional texts? Authors use context clues to help the reader discover implied meanings of words and phrases. Eligible Content L.N.1.1.1 L.N.1.1.2 L.N.1.1.3 L.N.1.1.4 L.N.1.2.1 L.N.1.2.2 L.N.1.2.3 L.N.1.2.4 L.N.1.3.1 L.N.1.3.2 L.N.1.3.3 PA Common Core Standards CC.1.2.9--10.C CC.1.2.9--10.E CC.1.2.9--10.F CC.1.2.9--10.J CC.1.2.9--10.K CC.1.2.9--10.A CC.1.2.9--10.B CC.1.2.9--10.C Assessment Opportunities Teachers will employ a number of assessment strategies in order to evaluate individual student understanding and requirements. SAS Assessment Creator provides examples of Keystone Benchmark, Diagnostic, Formative, and Summative Assessments: http://www.pdesas.org/module/assessment/ Search.aspx In addition, formative assessments will encompass a variety of strategies both formal and informal. They will include, but are not restricted to question-answer, interactive engagement check-ins (think-pair-share, splashes, partner finds, studentauthored assessments, appointment clock activities), guided practice, presentations, short answer writing, class work, homework, and quizzes. Summative assessments will include, but are not limited to, objective test including a cold read and a short written response, a Keystone Constructed Response to reflect cumulative knowledge, and/or a presentation reflecting essential terms and concepts. 15 Key Unit Vocabulary nonfiction, author’s purpose, informational texts Sequence of Teaching and Learning (2 weeks) Number of Lesson Topic Lesson Activities Lessons / Blocks ½ Block Intro to Nonfiction Teacher-facilitated Walk Around Survey to assess prior knowledge of nonfiction writing ½ Block Benchmark “It’s Your Turn” reading activity to assess skills for the following: (Multiple Choice: main ideas with details and author’s purpose Constructed Response: summarizing) 2 Blocks Background Teacher-facilitated investigation of authors and literature Investigation: appropriate to nonfiction unit. In small groups, students use web Extended tools to research noted writers and their literary trends, styles and Comprehension devices. Present web-based projects to large group. Ongoing Vocabulary Students receive vocabulary words relevant to unit. Teacher throughout directed learning to address words as needed. Ongoing Prevalent Themes Teacher-led discussions throughout the readings on the relevant throughout & Concepts themes & concepts developed in nonfiction literature and how they reflect modern issues. Close read excerpts of Keystone Finish Line: Literature1 Block Critical Reading of Nonfiction and participation in teacher-facilitated activities and Increments Nonfiction discussions: Introduction of reading skill, guided practices, and “It’s Your Turn” independent multiple choice and constructive response activities will help to complement the learning. Ongoing Skill Reinforcement Study Island lessons: teacher facilitated review of Study Island throughout lessons with differentiated instruction as needed (See Study Island chart below.) 1 Block Extension Activities Students read supplementary fictional literature and participate in Increments teacher-facilitated activities & assessments. Various exercises including Keystone Constructed Responses will reflect and support Keystone Literature Exam requirements. Ongoing Friday Nonfiction Friday individual close read of Critical Reading Series: throughout all Experience Disasters, Apparitions, Eccentrics & Heroes with small group literature units activities: Finding Main Ideas, Recalling Facts, Making Inferences, Using Words Precisely, Author’s Approach, Summarizing & Paraphrasing, Critical Thinking, and Writing Responses ½ Block Exam Practice Diagnostic, Formative & Summative practice exams to check Increments individual requirements and accomplishments 1 Block Review Complete review activities to tie up unit and prepare for summative assessment. 1 Block Summative Summative Assessment from one or more of the following: Assessment Objective questions and written response/Keystone constructed response /cummulative hands-on project 1 Block Summative Examples from SAS: Assessment http://www.pdesas.org/module/assessment/Search.aspx#assessme ntsearch 16 Resources for this Unit Keystone Item and Scoring Sampler Study Island Common Core Coach (for American Literature and Informational Texts I) Critical Reading Series: Disasters, Apparitions, Eccentrics & Heroes National & local newspaper & magazine articles Short Takes (Informational & Persuasive Essays) Supplemental Historical Documents Supplemental Technical Texts Additional Exam Practice Materials: Measuring Up Diagnostic Practice Tests 4Sight Practice Tests PSSA Reading Coach, Performance Indicator, Jumpstart & Reading Coach (Grade 11) Remediation consists of the following: Additional teacher generated practice exercises & activities Period 12 remediation After school tutoring with English tutor Study Island: Unit 3 Reading for Meaning-Nonfiction Study Island Remediation Nonfictional Texts Eligible Content Eligible Content Study Island - Keystone English Literature L.N.1.1.1 Identify and/or analyze the author’s intended purpose of a text. Explain, describe, and/or analyze examples of a text that support the author’s intended purpose. Analyze, interpret, and evaluate how authors use techniques and elements of nonfiction to effectively communicate an idea or concept. Explain how an author’s use of key words or phrases in text informs and influences the reader. Identify and/or explain stated or implied main ideas and relevant supporting details from a text. Note: Items may target specific paragraphs. Summarize the key details and events of a nonfictional text, in part or as a whole. Analyze the interrelationships of ideas and events in text to determine how one idea or event may interact and influence another. Author's Purpose L.N.1.1.2 L.N.1.1.3 L.N.1.1.4 L.N.1.3.1 L.N.1.3.2 L.N.1.3.3 Author's Purpose Author's Technique, Informational Documents Author's Technique Main Idea and Supporting Details Summarization Connections Between Texts, Main Idea and Supporting Details, Text Organization and Graphics 17 Unit 4 Title Unit Description Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings Anchor Descriptor L.N.2.1 L.N.2.2 L.N.2.3 L.N.2.4 L.N.2.5 Learning Objective Make and support interpretations of literature. Analyzing and Interpreting Literature--Nonfiction This unit encourages students to employ background knowledge of literary concepts and vocabulary to help them analyze, interpret, and compare nonfictional genres. ● How do author assumptions and beliefs influence textual analyses? ● How do varied artistic mediums differ in their approach to a subject? ● How do nonfiction author style and techniques compare to those in literary fiction? ● Literary development of devices (character, setting, plot, theme, tone/style/mood, and point of view) determine analyses of nonfiction. ● The order in which points are made, how they are introduced and developed, and the connections drawn between them reveal author technique for creating informational texts. ● How does an author use relevant evidence to make valid claims in argumentative texts? Eligible Content L.N.2.1.1 L.N.2.1.2 L.N.2.2.1 L.N.2.2.2 L.N.2.2.3 L.N.2.3.1 L.N.2.3.2 L.N.2.3.3 L.N.2.3.4 L.N.2.3.5 L.N.2.3.6 L.N.2.4.1 L.N.2.4.2 L.N.2.4.3 L.N.2.4.4 L.N.2.4.5 L.N.2.5.1 L.N.2.5.2 L.N.2.5.3 L.N.2.5.4 L.N.2.5.5 L.N.2.5.6 PA Common Core Standards CC.1.2.9--10.B CC.1.2.9--10.G CC.1.2.9--10.A CC.1.2.9--10.C CC.1.2.9--10.D CC.1.2.9--10.E CC.1.2.9--10.H Assessment Opportunities Teachers will employ a number of assessment strategies in order to evaluate individual student understanding and requirements. SAS Assessment Creator provides examples of Keystone Benchmark, Diagnostic, Formative, and Summative Assessments: http://www.pdesas.org/module/assessment/ Search.aspx 18 Compare, analyze, and evaluate literary forms. In addition, formative assessments will encompass a variety of strategies both formal and informal. They will include, but are not restricted to question-answer, interactive engagement check-ins (think-pair-share, splashes, partner finds, student-authored assessments, appointment clock activities), guided practice, presentations, short answer writing, class work, homework, and quizzes. Summative assessments will include, but are not limited to, objective test including a cold read and a short written response, a Keystone Constructed Response to reflect cumulative knowledge, and/or a presentation reflecting essential terms and concepts. Compare, analyze, and evaluate literary elements. Identify and analyze text organization and structure in literary nonfiction. Identify and analyze essential and nonessential information in literary nonfiction. Key Unit Vocabulary inferences, conclusions, generalizations, varieties of nonfiction, elements of nonfiction, text structure, organizational features, fact & opinion Sequence of Teaching and Learning (2 weeks) Number of Lessons / Lesson Topic Lesson Activities Blocks Ongoing Vocabulary Students receive vocabulary words relevant to unit. Teacher directed throughout learning to address words as needed. Ongoing Author Purpose Small group research author information (biographies, reviews, throughout Interviews articles…) and literature relative to non-fiction unit. Students interview “authors” with questions about style, purpose & technique. 15 minute Skill Reinforcement Study Island lessons: teacher facilitated review of Study Island increments lessons with differentiated throughout instruction as needed (See Study Island chart below.) unit Introductory Students choose topic with which they have background knowledge. 1 Block Informative Text Write a short informative article answering Who? What? When? Activity Where? Why? How? Present to large group. Close read excerpts of unit literature ( informational texts) and 1 Block Critical Reading: participation in teacher-facilitated activities and discussions. Increments Informational Texts Introduction of reading skill, guided practices, and “It’s Your Turn” independent multiple choice and constructive response activities will help to extend the learning. Ongoing Prevalent Themes Teacher-led discussions throughout the readings on the relevant throughout and Concepts themes & concepts developed in nonfiction literature and how they 19 Ongoing throughout 1 ½ Blocks ½-1 Block 1 Block Increments Ongoing throughout ½ Block Increments 1 Block Increments Ongoing throughout all lit units 1 Block 1 Block 1 Block reflect issues. Teacher-facilitated activities identifying literary devices & patterns in unit readings. Students analyze propaganda. Small groups create political cartoons and present to class. Large group identifies and evaluates persuasive devices and techniques. The claim: What do I think? Argumentative Text The reasons: Why do I think this? Connection The evidence: How do I know this is the case? And I quote! from expert Close read excerpts of unit literature ( argumentative texts) and Critical Reading: participation in teacher-facilitated activities and discussions. Argumentative Introduction of reading skill, guided practices, and “It’s Your Turn” Texts independent multiple choice and constructive response activities will help to extend the learning. Teacher-directed literature comparison. Pair/share and small group Comparing activities researching, analyzing and sharing various forms of Literature nonfiction literature. Practice assessments for recognition of structure and components of informational and argumentative texts. Exam Practice Diagnostic, Formative & Summative practice exams to check individual requirements and accomplishments Extension Students read supplementary fictional literature and participate in Activities teacher-facilitated activities & assessments. Various exercises including Keystone Constructed Responses will reflect and support Keystone Literature Exam requirements. Friday Nonfiction Friday individual close read of Critical Reading Series: Disasters, Experience Apparitions, Eccentrics & Heroes with small group activities: Finding Main Ideas, Recalling Facts, Making Inferences, Using Words Precisely, Author’s Approach, Summarizing & Paraphrasing, Critical Thinking, and Writing Responses Review: Fiction Complete review activities to tie up unit and prepare for summative Units assessment of fiction Units. Summative Summative Assessment from one or more of the following: Assessment Objective questions and written response/Keystone constructed response /cummulative hands-on project Summative Examples from SAS: Assessment http://www.pdesas.org/module/assessment/Search.aspx#assessments earch Devices and Patterns Introductory Argumentative Text Activity Resources for this Unit Keystone Item and Scoring Sampler Study Island Common Core Coach (for American Literature and Informational Texts I) Critical Reading Series: Disasters, Apparitions, Eccentrics & Heroes National & local newspaper & magazine articles Short Takes (Informational & Persuasive Essays) Supplemental Historical Documents 20 Supplemental Technical Texts Additional Exam Practice Materials: Measuring Up Diagnostic Practice Tests 4Sight Practice Tests PSSA Reading Coach, Performance Indicator, Jumpstart & Reading Coach (Grade 11) Remediation consists of the following: Additional teacher generated practice exercises & activities Period 12 remediation After school tutoring with English tutor Study Island: Unit 4 Analyzing & Interpreting Literature— Nonfiction Study Island Remediation Nonfictional Texts Eligible Content Eligible Content Study Island - Keystone English Literature L.N.2.1.1 Make inferences and/or draw conclusions based on analysis of a text. Cite evidence from a text to support generalizations. Analyze how literary form relates to and/or influences meaning of a text. Compare and evaluate the characteristics that distinguish fiction from literary nonfiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate connections between texts. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate character in a variety of nonfiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate setting in a variety of nonfiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate plot in a variety of nonfiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate theme in a variety of nonfiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate tone, style, and/or mood in a variety of nonfiction. Explain, interpret, compare, describe, analyze, and/or evaluate point of view in a variety of nonfiction. Identify, analyze, and evaluate the Conclusions, Inferences, and Generalizations Conclusions, Inferences, and Generalizations Genres L.N.2.1.2 L.N.2.2.1 L.N.2.2.2 L.N.2.2.3 L.N.2.3.1 L.N.2.3.2 L.N.2.3.3 L.N.2.3.4 L.N.2.3.5 L.N.2.3.6 L.N.2.4.1 Genres, Informational Documents Connections Between Texts Characters Setting Plot Theme Tone, Style, and Mood Point of View Informational Documents 21 L.N.2.4.2 L.N.2.4.3 L.N.2.4.4 L.N.2.4.5 L.N.2.5.1 L.N.2.5.2 L.N.2.5.3 L.N.2.5.4 L.N.2.5.5 L.N.2.5.6 structure and format of complex informational texts. Identify, explain, compare, interpret, describe, and/or analyze the sequence of steps in a list of directions. Explain, interpret, and/or analyze the effect of text organization, including headings, graphics, and charts. Make connections between the text and the content of graphics and charts. Analyze and evaluate how graphics and charts clarify, simplify, and organize complex informational texts. Differentiate between fact and opinion. Explain, interpret, describe, and/or analyze the use of facts and opinions in the text. Distinguish essential from nonessential information. Identify, explain, and/or interpret bias and propaganda techniques in nonfictional text. Explain, describe, and/or analyze the effectiveness of bias (explicit and implicit) and propaganda techniques in nonfictional text. Explain, interpret, describe, and/or analyze the author’s defense of a claim to make a point or construct an argument in nonfictional text. Directions Text Organization and Graphics Text Organization and Graphics Text Organization and Graphics Fact and Opinion Fact and Opinion Fact and Opinion, Main Idea and Supporting Details Bias and Propaganda Techniques Bias and Propaganda Techniques Author's Argument 22 Appendix See Common Core Standards for English Language Arts See Keystone exams: Literature--Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content See PA Writing Rubrics See PA Department of Education Standards Aligned Systems 23









