Period 1 (Pre-history to 600 BCE)

Technological and Environmental
Transformations to 600 BCE
Big Geography and the Peopling of the Earth
Early human development occurred during the
Paleolithic Period
Origins in Africa
Hominids
Anatomically modern humans (homo sapiens sapiens) develop about 150,000 years ago
Begin migrations
http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evosite/evo101/IIE2cHuma nevop2.sht
ml
Lucy http://www.answersingenesis.org/articles/am/v2/n2/they-lovelucy
Settlement of Australia: Approximately 60,000 BCE
Settlement of Eurasia: Approximately 50,000 BCE
Settlement of Americas: Approximately 14,000 BCE
Hunting-foraging
Nomadic
Small groups based on bonds of kinship
Relatively Egalitarian
Adaptation to local environment
Development of stone tools
Use of fire for cooking, warmth, and deterring predators
No written language
Evidence of culture seen in cave paintings, artifacts, and human remains
Evidence of primitive, simple religion
Lack of developed material culture
Although groups were adapted to their specific environment, hunter-foragers did interact with each other and engage in exchange of ideas and goods
The Neolithic Revolution and Early Agricultural Societies
Neolithic: New Stone Age
Began approx. 10,000 years ago
Use of stone tools for agricultural production
Most likely the result of climate change
Domestication of plant and animal species
See map on page 9 in textbook
First began in the Eastern Mediterranean
http://huberb.people.cofc.edu/ANTH%20101%20Huber's%20Introduction%20to%20Anthropology.html
Gradual process and dependent upon the geography
Not all societies develop agriculture
See map on page 9 of textbook.
Agricultural centers emerged in:
Mesopotamia, the Nile River Valley, Sub-Saharan Africa, the Indus River Valley, the Yellow River, Papua New
Guinea, Mesoamerica, and the Andes
Emerged in grasslands (steppes)
Central Eurasia and parts of Africa
Animal husbandry
Mobile lifestyle
Wealth measured in livestock
Greater degree of complexity and cooperation
More reliable food sources
Population densities increase
Permanent settlements
Religion becomes more complex
Some matrilineal, others patrilineal
Trade developed between and among early agricultural settlements
http://www.americanneopaganism.com/ancientp agantimeline.htm
http://howardbloom.net/reinventing_capitalism/ http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/en try/Catal_Huyuk http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Image:CatalHoyukSouthArea.JPG
Dramatic impact on the environment
Erosion
Clearing of forests for farmland
Desertification
Overgrazing of pastureland
Increase in human population
Increase in disease
Craft specialization
Social Stratification
Patriarchy
Technological innovations were developed to improve agricultural production, trade, and transportation
Key examples:
Pottery
Plows
Woven textiles
Metallurgy
Wheels and wheeled vehicles http://www.historiasiglo20.org/prehistory/po ttery.htm
The Development and Interactions of Early Agricultural,
Pastoral, and Urban Societies
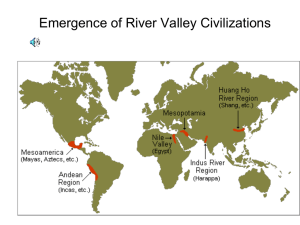
Core and foundational civilizations emerged in the following:
Mesopotamia
Egypt
Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa
Shang China
Olmec
Chavin
Map quiz: Students will take a quiz to identify the core and foundational civilizations.
http://www.unionparishschools.org/rivervalleyciv/interest.htm
Mesopotamia
http://www.utexas.edu/courses/classicalarch/images2/mapane.jpg
Egypt
http://www.iziko.org.za/sh/resources/egypt/images/map_e1
_l.gif
Indus River Valley Civilization
http://www.rivervalleycivilizations.com/indus.php
The Yellow River Valley Civilization
Shang Dynasty
http://www.chinahighlights.com/image/map/ancient/shang-dynasty-map1.gif
http://theresaclarkintdis4.blogspot.com/2009/09/week-
6.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Chavin-small.png
State: a sovereign political entity which contains a stable population, defined territory, and established government
Control over larger territory, population, and resources
Divine Right
Military
Competition for land and resources
Geography
Bronze
Iron
Horses
Chariots
Composite bows http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/Hyksos.aspx
Architecture and Urban Planning
Arts and Artisanship
Systems of Record Keeping
Law Codes
Religion
Polytheism: Belief in many gods
Most common
Vedic Religion becomes basis of Hinduism
Monotheism: Belief in one god
Hebrews
Zoroastrianism (Persian Empire)
Trade
Local, regional, and transregional trade
Exchange of goods, cultural ideas, and technology
Examples:
Egypt and Nubia
Mesopotamia and Indus River Valley