Mesopotamia, Egypt, Indus Valley Study Guide
advertisement

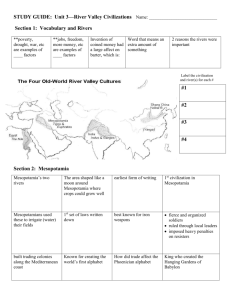
Unit 2 – Mesopotamia/Egypt study guide Mesopotamia 1. What does Mesopotamia mean? 2. What are the 2 rivers of Mesopotamia? 3. What is a city-state? How were they defended? 4. What were several geographic conditions of Mesopotamia? 5. Why is Mesopotamia called the Fertile Crescent or “the cradle of life” 6. How old is the Mesopotamian’s form of writing & why did they create it? 7. Gilgamesh – ancient Mesopotamian story, about a great king that journeyed the world & fought gods & monsters. This story make references to a great flood destroying cities 8. Each city-state was protected by a different god, where would you find the temple for that god & what was it known as? Would you be able to find similar things today? Explain your answer. 9. Why was cuneiform created & where did they write this language? 10. What inventions come out of Mesopotamia? How do we use them today? 11. Define the following: division of labor, irrigation, barter, surplus, polytheism, monotheism, ziggurat, Hammurabi’s Code, Cuneiform a. Irrigation – way of supplying water to an area of land b. Division of labor – a system in which members of a group perform different tasks based on their abilities and the needs of the group. c. Barter – trading between two groups of resources or products d. Surplus – the amount of something that is more then what is needed. e. Polytheism – belief in multiple gods f. Monotheism – belief in one god g. Ziggurat - a huge mud-brick temple built by the ancient Sumerians to worship their gods & goddesses h. Code of Hammurabi- the world's first system of laws, recorded by Hammurabi, king of Babylonia, about 1780 B.C. “An Eye for an Eye”. i. People would find these laws inscribed on to a stone pillar that would be placed in the center of town ii. The laws were both religious based & society based. Egypt: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. What is the difference between Upper & Lower Egypt? How does this relate with the Nile river? What are the significant events found in each Egyptian Kingdom? The Old Kingdom had a strong government because it was ruled by a theocracy. What is a theocracy? Who was the Great Pyramid of Giza built for? Who in Egyptian society were normally mummified? Why were they put through this procedure? List at least 2 things that were done during the mummification process. Why is Pharaoh Hatshepsut different from other Egyptian pharaohs? King Tutankhamen “King Tut” ruled from about 1333 BC – 1323 BC. He is often known as the boy king since he ruled from 8 – 18. We know the most about him & Egyptian burial tombs through the founding of his tomb. Ramses II was the last powerful Pharaohs that created a strong kingdom through conquering Egypt’s neighboring countries. How were women treated in Egypt? How many gods & goddesses could be found in Egypt? What is papyrus? How are hieroglyphics different from modern languages? How were archeologists able to translate hieroglyphics? What 2 objects were normally found in front of temples? Describe them. Define the following: delta, pharaoh, afterlife, mummies, engineering, trade route Indus Valley: 16. Which modern country would you find both the Indus valley & the Harappa civilization? 17. Why would this valley that led to the development of India be in another country? 18. The first Indus Valley civilization had 2 major cities – Harappa & Mohenjo Daro. This civilization focused on culture & the arts. They were able to create ordered cities in a grid pattern. 19. The Aryan civilization the entered the Indus Valley around 1700 BC helped develop the oldest Indian language. Archeologists have been unable to translate it. It is often called a dead language. Why do you think they call it a dead language? What other language have we looked at might once have been called a dead language & how did we eventually learn to read it? 20. Who were the 3 main gods of Hinduism? What is an easy way to describe what they represent? 21. Caste system: 22. 23. Untouchables – foreigners, criminals, people with diseases. They were seen as “outcastes”, not allowed in certain areas, & often given polluting jobs ex. burying the dead, disposing of dead animals, any job that no one else would be willing to do. 24. Explain how the concept or reincarnation & karma are linked together. 25. Castes are social classes into which a person is born & lives their entire life. If a person has a good karma they may be reincarnated into a higher caste. 26. Monsoon – seasonal storms that cause wet & dry seasons, very wet or very dry 27. Subcontinent – large landmass that is part of a continent but considered a separate region. 28. Himalayas – highest mountains in the world, northern border of India 29. Hindu Kush – mountain rang to the northwest of India 30. What are the Indian contributions? 31. What are the four principles of Jainism? 32. Who used this main belief of Jainism to enact change through their individual causes? How were these beliefs used & why do you think they worked so well? 33. What are the 4 noble truths of Buddhism? 34. What do Siddharta Gautama & Mahavira have in common? Extra: 35. What do Mesopotamia, Egypt, & China all have in common?