Introduction to Plants: Evolution, Characteristics and Life Cycle
advertisement

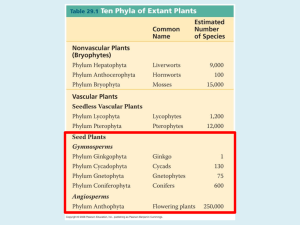
Conifers BIOL 1407 Seed Plants • Vascular Tissue • Produce seeds – Dispersal of offspring • Produce pollen • Sperm transfer without water Seed Plants • Sporophyte dominant • Gametophytes – Greatly reduced in size – Dependent on sporophyte Seed Plants • Heterosporous – Megaspore • Grows into female gametophyte eggs – Microspore • Grows into male gametophyte sperm – – Photo Credit for Ovulate Cone: Dr. Stephen Bostic, ACC Circled area: Ovule Pollen Production • Pollen cones have microsporophylls • Each microsporophyll has microsporangia • Photo Credit for Immature Male Pine Cones: Menchi, Wikimedia Commons Pollen Production • Meiosis occurs within microsporangia microspores • • • • Photo Credit for Staminate Cone: Dr. Stephen Bostic, ACC Microsporangium circled in red Microsporophyll at tip of yellow pointer Microspores circled in pink Pollen Production • Microspores grow into male gametophytes • Male gametophyte = pollen grain Pollination • Pollen is released • Travels from male to female • Pollination occurs when pollen grain lands on female • http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=Bwl4g48-uIE Pollen Germination • After landing pollen coat breaks open • 1 cell produces pollen tube • Photo Credit: Dr. David Byres, Florida Community College at Jacksonville Pollen Germination • A different cell produces 2 sperm cells by mitosis • They will move down pollen tube as it grows • Photo Credit: Dr. David Byres, Florida Community College at Jacksonville Pollen Germination • Pollen tube digests its way through female tissues to reach the egg Ovules • Ovulate cones have megasporophylls • Each megasporophyll has ovules containing megasporangia • Photo Credit for Immature Female Ponderosa Pine Cones: Susan McDougall @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database Ovules • Meiosis occurs within megasporangium forms 1 megaspore and 3 haploid nuclei (degenerate) • • • Photo Credit: Dr. Stephen Bostic, ACC Megasporangium circled in red Megasporophyll at tip of yellow pointer Ovules • Megaspore grows into female gametophyte • Female gametophyte makes 1-2 eggs by mitosis Ovules • Integuments surround female gametophyte • Micropyle lets pollen reach female gametophyte Ovules Seeds • Integuments seed coat • Female gametophyte food supply • Fertilized egg embryo Seeds • Dispersed by: – – – – • Wind Animals Water Mechanical Photo Credit for Pitch Pine Seeds: Steve Hurst @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database Types of Seed Plants • Gymnosperms – Naked Seeds – Not enclosed in ovaries – No fruits or flowers Types of Seed Plants • Angiosperms – Flowering Plants – Seeds enclosed in ovaries – Fruits and flowers Modern Gymnosperms • Conifers – Oldest living plants – Largest living plants – Widespread – Reproductive structure: Cones Modern Gymnosperms • Cycads – Wiry leaves – “Sago palms” • Ginkgos • Deciduous trees • One species • Herbal supplement Modern Gymnosperms • Gnetophytes – Ephedra (Mormon tea) – Welwitschia The End Unless otherwise specified, all images in this presentation came from: Campbell, et al. 2008. Biology, 8th ed. Pearson Benjamin Cummings.