Accuplacer Reading Comprehension Test
advertisement
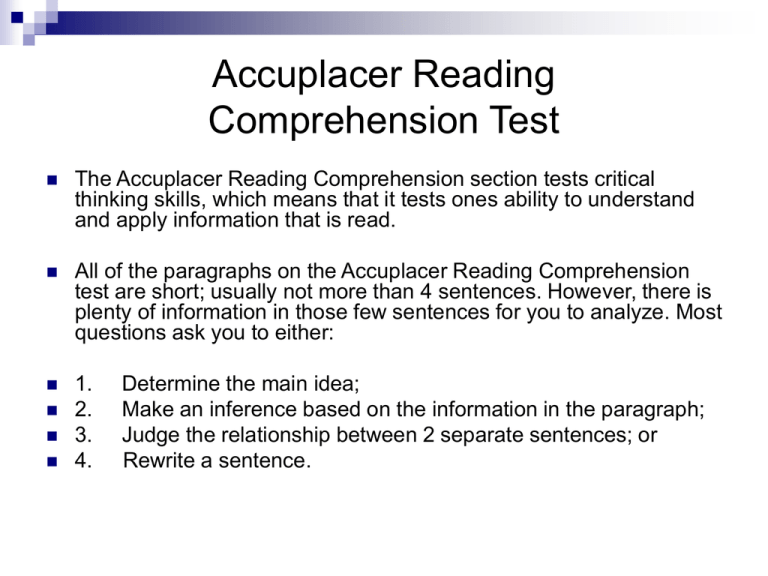
Accuplacer Reading Comprehension Test The Accuplacer Reading Comprehension section tests critical thinking skills, which means that it tests ones ability to understand and apply information that is read. All of the paragraphs on the Accuplacer Reading Comprehension test are short; usually not more than 4 sentences. However, there is plenty of information in those few sentences for you to analyze. Most questions ask you to either: 1. 2. 3. 4. Determine the main idea; Make an inference based on the information in the paragraph; Judge the relationship between 2 separate sentences; or Rewrite a sentence. Accuplacer Reading is a CAT Test The Accuplacer Reading Comprehension test is computer adaptive. This means that you must answer each question in order to move on and once you have moved on, you cannot go back to previous questions. There is no time limit. You can take as long as you need. The Accuplacer Reading Comprehension Test is comprised of 20 questions. If you have time, a good way to prepare for the Accuplacer Reading Comprehension test is to read as much as possible and quiz yourself upon finishing individual paragraphs. You can read newspaper and magazine articles, or books. After reading a paragraph, ask yourself what point the author was making. If you do not know or did not understand what was being discussed, then try to examine the paragraph more closely in order to uncover the big picture. From information you read, try to make conclusions. For example, if it was cold when someone shoveled his driveway, there was probably snow on the ground. There are also some very good web sites to help you prepare. We will review these later in the workshop. Tips for taking the test Take your time. Read slowly and repeat as necessary. Look for details as you read. When reading passages you can following along with your mouse. Reread a passage before making your answer choice. For some questions, you will have to locate one specific sentence that answers the question. The rest of the paragraph will be related or even discuss an opposing idea, but will not answer the question. When an answer is based on an implied idea, one of the answer choices may be a restatement of a sentence in the passage. More Tips for Taking the Test An answer can be the counterpoint in a passage. For example, one idea in a passage may be that viral infections cause short term inner ear imbalance, while another idea posed in the same passage is that arteriosclerosis restricts blood supply causing long term inner ear imbalance. Even though the passage may seem to be focused on one of the ideas and not the other, be careful when choosing your answer. By reading the passage carefully and more than one time, you can avoid making the wrong choice. More Tips for Taking the Test Reread a passage before confirming your answer choice and moving on to the next question. Remember, you cannot go back. Since all of the passages are short (approximately 4 sentences), you can reread to be sure you have not chosen a red herring. For example, if a passage discusses two positions that a person held, such as lawyer and judge, both options may be given as answer choices. You will need to be sure of which position the question is targeting. Sentence Completions Two underlined sentences are followed by a question or a statement. You must read the sentences and choose the best answer to a question or choose the best completion for a statement. When you are asked to choose the best completion for a statement, you are actually being asked to rewrite the original sentence. When you are asked to rewrite a sentence using a different beginning phrase, the new sentence must have essentially the same meaning as the original. Be sure to read all of the choices. It is best to rewrite the whole sentence in your head or on scratch paper in order to be sure you are choosing the right answer option. Run through the entire sentence with each of your options. Sentence Completions Your options will be a few words (a phrase). Sometimes it will be specified that the phrase will directly follow the new beginning and sometimes it will be specified that the phrase will be included in the new sentence. This is a reason why it is important to run through entire sentences with new wording inserted to be sure you are choosing the right option. Sentence Completions In order to construct a new sentence when the answer choices are to be included, not directly follow the beginning phrase, look for a part of the original sentence that will complete the beginning thought and then look at the answer choices to continue the sentence. For example, “She thought that advertising should have an immediate, powerful impact and, as a result of this notion of hers, she made commercials with a strong emotional content.” You are asked to rewrite this sentence, beginning with, “Her new commercials had…” Sentence Completions The choices that your new sentence will include are they resulted from the result was that caused by thinking because she thought You can reconstruct the new sentence as follows: “Her new commercials had a strong emotional content because she thought that advertising should have an immediate, powerful impact. Sentence Completions When you have to rewrite a portion of a sentence or a whole sentence, never make a choice without reading all of the options. A sentence with a mechanical error will often sound okay until you have read the other choices. Finally, since there are two types of sentence completions, be very careful to note how you are being asked to rewrite a sentence. The phrasing will be: The next words are OR The sentence will include Sample question in which you must infer information: 1. Cheating is the ultimate trick a student plays on him or herself. Aside from the primary point of making an absolute mockery of the purpose of a college education, there is also the fact that there is no way a student can avoid being found out - there is at least one person who will always know about it. With which of the following statements would the author agree? a. Students should not cheat because someone will find out and report it. b. Cheating really hurts the cheater. c. Professors should expect students to cheat. Sample question about the main idea: 2. Many college students do not want to take a math class. When they learn that math is requirement, these students hope for a way to avoid it. These students may be suffering from math anxiety, an overwhelming fear of the subject, rather than an intellectual impairment. The main idea of this passage is: a. Many students are bad at math b. Students who are bad at math can avoid taking it. c. Students who hope to avoid math may have math anxiety. Do not get discouraged by unfamiliar words. You can often figure out what the answer is even if you do not know the definitions of all of the words in a paragraph. Also, you can often figure out the definition of a word by its context. 3. The protagonist of a popular children’s tale has an aversion to colored poultry products and smoked meat. His pursuer took increasingly creative measures to ensure that the protagonist would consume these victuals here, there or anywhere. The author states that: a. The pursuer took increasingly creative measures. b. The victuals were virtually real. c. The protagonist consumed the pursuer. Sample Question in which you Compare Two Sentences The Midwest is experiencing its worst drought in fifteen years. Corn and soybean prices are expected to be very high this year. 5. What does the second sentence do? a. It restates the idea found in the first sentence. b. It states an effect. c. It gives an example. Answer Key for Reading Comprehension Test Sample Questions Answers: 1.b ; 2.c ; 3.a ; 4.a; 5.b Reading Placements based on Accuplacer Reading Comprehension Test Scores Score 20 – 30 31-77 78-120 UTEP Placement BASK 0323 (at EPCC) ENGL 0310 (remedial reading course) Eligible to take reading intensive courses (HIST 1301, 1302, SOCI 1301, PSYC 1301, POLS 2310, 2311) Score 20-45 46-55 56-77 78-120 EPCC Placement BASK 0323 READ 0308 READ 0309 Developmental Reading Course not required