Ch 15 Germany
advertisement
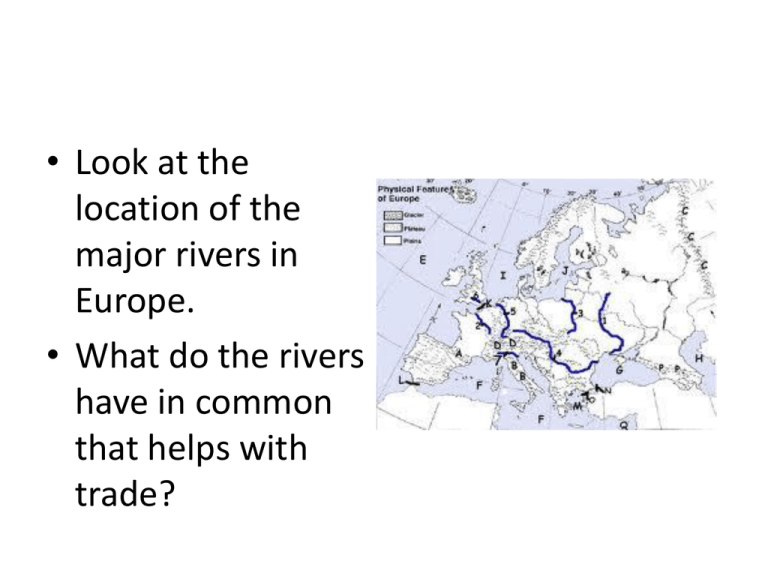
• Look at the location of the major rivers in Europe. • What do the rivers have in common that helps with trade? Welcome to Second Semester! Monday Jan. 6, 2014 Review of Procedure • Coming into class—must be seated by the bell and ready to work. • Bell Ringers count for 5 pts a day – Around 150 points per 9 weeks. Must be done in complete sentences. – Purpose is to get your mind working in Social Studies mode and review or introduce material or practice skills, NOT to waste time. Tests this 9 weeks • With rare exception will be done using Active Votes. • Most of the test will come from Chapter Notes but everything we talk about in class could be on a test. • Assessment at least once a week. • Some tests will get study guides but some will not. Tests once a week will be based on class notes. Seating Arrangement • Speak to me privately about seat changes. • Do not change your seat without permission. This semester we will be covering • • • • • • • • Central and Southern Europe Russia and surrounding countries MENA (Middle East and North Africa) Sub-Saharan Africa India and surrounding countries Southeast Asia Southwest Asia Australia Chapter Notes Model • Fill in the blank notes for the entire chapter. • Notes will be given along with videos, pictures, and music • Notes will cover the bulk of the test and serve as the study guide for once a week tests. Begin numbering at #1 •Chapter Ch. 15 Notes on Central Europe #1 Ch. 15 s. 1 • Use map and pg. book to locate the following countries. Locate: Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary Ch. 15 s. 1 Germany pg. 328 • GERMANY has had a large role in shaping Europe’s history. • World War I ended with a harsh peace agreement meant to punish Germany. Treaty of Versailles 1919 • • • • • • • • War Guilt clause - Germany to accept blame for starting the war. Financial Clauses Reparations - Germany was to pay for the damage caused by the war. The figure of £6,600 million was set some time after the signing of the treaty. Military Clauses Army - was to be reduced to 100,000 men and no tanks were allowed Navy - Germany was only allowed 6 ships and no submarines Air force - Germany was not allowed an air force Rhineland - The Rhineland area was to be kept free of German military personnel and weapons Territorial Clauses Anschluss - Germany was not allowed to unite with Austria. Land - Germany lost land to a number of other countries. Alsace-Lorraine was returned to France, Eupen and Malmedy were given to Belgium, North Schleswig was given to Denmark. Land was also taken from Germany and given to Czechoslovakia and Poland. The League of Nations took control of Germany's colonies http://www.historyonthenet.com/WW1/versailles.h tm • Yellow • The German economy collapsed in 1920. Food shortages, high inflation (prices), and high unemployment left many feeling hopeless. Inflation makes it hard to afford basic food stuffs. • Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party offered stability to a Germany in crisis. • Hitler takes power in 1933 and becomes Chancellor of Germany. Hitler was enthusiastic and gave some people pride and hope again. • Hitler rebuilt and allied with Italy and Japan. Hitler’s goal was to conquer Europe and take all the land and resources for the Deutschland. • WWII devastated Europe and divided Germany among the victorious Allied Forces, eventually Germany divided into East and West. • USSR’s (Russia) Communist Bloc ruled EAST Germany and other East European countries. WEST Germany became democratic and rebuilt through international aid. Don’t write this page • The USA spent billions on aid to rebuild and feed Europe after the war. Mainly to avoid more countries becoming communist. • Berlin is a symbol of the Cold War between democratic and communist forces. • East and West Germany reunited in 1990 when Communist USSR collapsed. • Guards try to prevent protesters from crossing at first. • Today Germany is a democracy and Berlin is the capital. • Berlin Today • It is an economic and political powerhouse. Germany has a diversified, free market economy with many different types of industries. • The Ruhr Valley is a major industrial region built around coal deposits. Germany is rich in coal, iron ore, and other minerals but imports most of its oil.











