8th Review pictures
advertisement
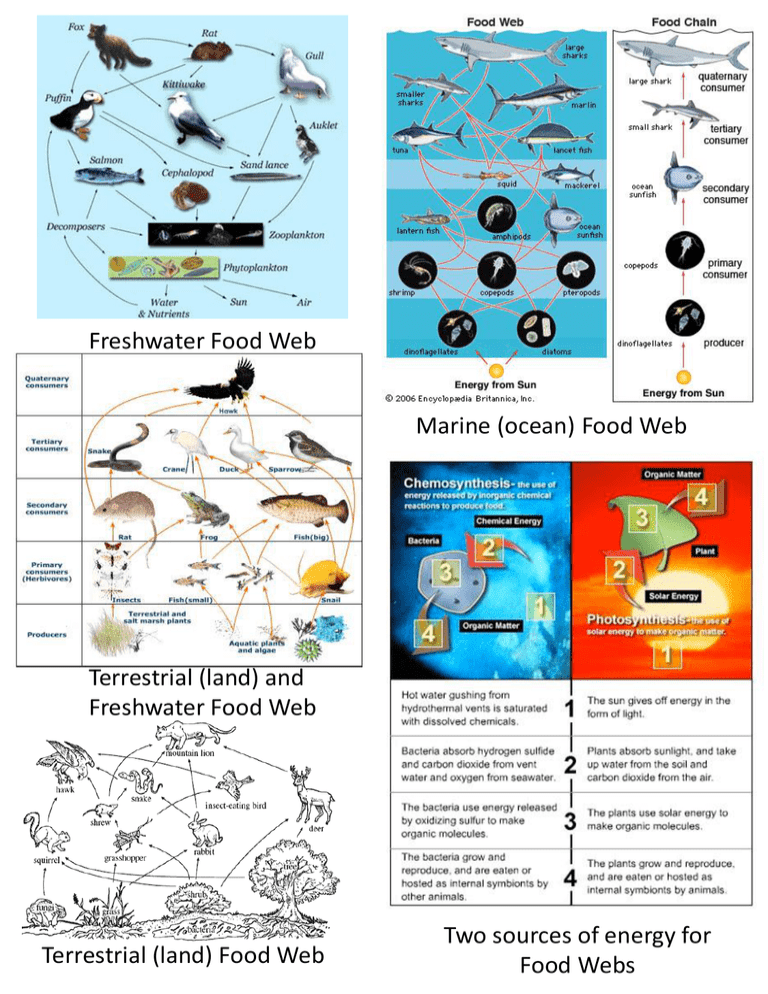
Freshwater Food Web Marine (ocean) Food Web Terrestrial (land) and Freshwater Food Web Terrestrial (land) Food Web Two sources of energy for Food Webs Photosynthesis uses light energy from the sun Chemosynthesis uses chemical energy from volcanic vents The greatest amount of energy is always at the bottom and starts with the sun or with chemicals in hydrothermal vents. 10% of the energy from one level passes on to the next level. Not much energy left at the top—not many organisms can be there. Plants will compete for light and bacteria will compete for chemicals. Limiting factors are biotic and abiotic factors that organisms have to compete for. Biomass is the mass of living things at each trophic level needed to support the individuals at the level above them in the pyramid. The greatest mass is always at the bottom A pyramid of numbers shows how many individuals are needed at each level to support the level above. The greatest numbers are always at the bottom Remember that Noble Gasses are in group 8A and don’t react. Remember that H is a non-metal. Metals: lose valence electrons, are malleable and ductile, conduct electricity and have metallic luster. Nonmetals: gain valence electrons, are brittle, and do not conduct electricity. Velocity is speed in a direction Acceleration is changing speed or velocity. (faster, slower, or direction) Always read the labels on your graphs! Unbalanced forces cause movement. Balanced forces mean no movement. Work is done when something is moved Wheel and inclined plane make the job of lowering material much easier. By increasing the distance something is moved, simple machines reduce the force needed to move them. The long string on a pulley increases the distance. Potential and Kinetic Energy A long lever makes it easier to life a heavier load. Folded mountains, thrust fault, trenches, volcanoes Volcanoes, mid-ocean ridges, rift valley Major Earthquakes Earthquakes can occur along any boundary—both recent tsunamis were caused by convergent boundary quakes Hurricanes form over warm ocean water Bright Hot Sun Cool Dim Blue Convection currents in the mantle drive the plates Red Hotter is on the left Brighter is on the top Red Away Spiral galaxy Blue toward Blue Milkyway Galaxy with Sun Red Vernal = Spring Summer Solstice June 21 or 22 The amount of sunlight is always the same at the equatorequal day/night & no seasons Autumn =Fall H = high pressure (fair) L = low pressure (clouds/rain) Winds generally blow from west to east Half circles and cones point where the front is going The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus— that is the atomic number. Valence Level Energy Levels Lithium has 1 valence electron • in group 1: highly reactive metal • will lose the outside electron when bonding • 2 electrons in the first energy level are stable when the valence electron is gone Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus and have all the mass. Together they are the atomic mass number. At. Mass – atomic #= neutrons MAN Beryllium has one more proton than Lithium—it is a different element. 1 more proton means 1 more electron also. APE •2 valence electrons •In group 2: very reactive •Will lose both outside electrons when bonding •2 electrons in the first energy level are stable when the valence electrons are gone. Electrons have almost no mass, are in energy levels, but move all the time, so we say they are in the electron cloud. Low energy electrons are in level 1. Na-Mass 23 Add p & n for mass 7 + 1 = 8 valence 23 – 11 = 12 Na—Sodium F—Flourine •Will lose 1 valence electron when bonding •In group 1: highly reactive metal •8 electrons in the second energy level is stable when the valence electron is gone •Has 7 valence electrons •Will gain 1 electron when bonding—non-metal to metal •Could share 1 electron when bonding with another non-metal •8 valence electrons is the most stable valence Topographic Maps show changes in elevation Contour lines are connected points of equal elevation Contour interval is the change in elevation between the lines Global Positioning System: Uses information relayed to satellites to identify locations on Earth and changes to locations on Earth. Satellite images and topographic maps can show changes in north and east directions on Earth, as well as changes in elevation.




