Document
advertisement

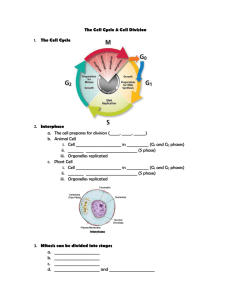
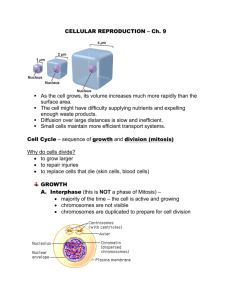
Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis Cells that make up the “body” of an organism 2 Chromosomes condense during cell division • DNA plus proteins is called chromatin. • When chromatin coils up it forms chromosomes. • One half of a duplicated chromosome is a chromatid. • Sister chromatids are held together at the centromere. Interphase – Longest phase of cell life cycle – G1 Phase: Cell Growth and Normal Functions – S Phase: DNA is replicated (copied) – G2 Phase: Additional Cell nucleus with Growth DNA Parent cell centrioles spindle fibers centrosome Nuclear Membrane breaking down Prophase – The nuclear membrane breaks down – Chromatin condense to chromosomes – Spindle fibers form – Centrioles move towards opposite ends of the cell Chromosomes condensed Spindle fibers appear Centrioles Metaphase – Chromosomes line up in the MIDDLE of the cell – Spindle fibers attach to the centromere of each chromosome Chromosomes Spindle fibers Centrioles Centromere Anaphase – Sister chromatids separate to opposite sides of the cell – Think AWAY Chromatid Centriole Spindle fibers Centromere Telophase – New nuclei form and chromosomes begin to uncoil into chromatin – The nuclear membrane reappears – Spindle fibers disappear – Cleavage furrow begins Cleavage Furrow Chromatin begins to uncoil Spindle fibers Centromere Centrioles Nuclear Membrane reappears Cytokinesis • Cytokinesis is the division of the rest of the cell contents. – In animal cells, the membrane pinches closed (Cleavage furrow). – In plant cells, a cell plate forms (forms new cell wall).