Cell Cycle & Mitosis Study Guide - High School Biology
advertisement

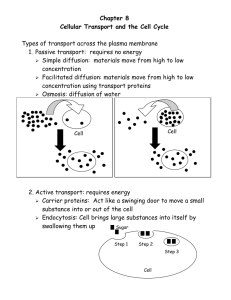
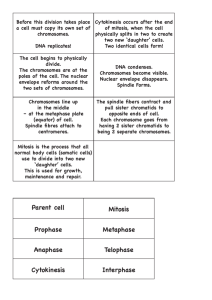
NAME __ANSWER KEY___________________________________ CH. 9 STUDY GUIDE 1. What are 2 reasons that a body cell will go through the cell cycle? GROWTH OF THE ORGANISM, REPLACE DAMAGED OR DEAD CELLS, TO KEEP CELL AT THE CORRECT SIZE. 2. CELL CYCLE: Draw & label all the phases of the cell cycle. a. Interphase: i. Describe what happens:_CELL GROWS & PREPARED FOR CELL DIVISION_______________ b. G1: i. Describe what happens:_ G1 – CELL GROWS, CARRIES OUT NORMAL FUNCTIONS, COPIES ORGANELLES __________________________________________________ c. S: i. Describe what happens:_ S PHASE – DNA DUPLICATED______________________________ d. G2: i. Describe what happens:_ G2 – CELLS GROW, CARRIES OUT NORMAL FUNCTIONS, CHECK POINTS TO MAKE SURE THAT ALL ORGANELLES & DNA COPIED & CELL IS LARGE ENOUGH FOR CELL DIVISION__________________________________________________ e. Prophase: i. Describe what happens:_NUCLEAR MEMBRANE BREAKS DOWN, NUCLEOLUS DISAPPEARS, CENTRIOLES START TO MIGRATE TO THE POLES OF THE CELL & SPINDLE FIBERS BEGIN TO FORM, CHROMATIN CONDENSES DOWN TO CROMATID, PAIRING UP WITH ITS COPY CREATING SISTER CHROMATIDS__________________________________________________ f. Metaphase: i. Describe what happens:_SPINDLE FIBERS ATACH TO THE CENTROMERES OF THE SISTER CHROMATIDS, SPINDLE FIBERS LINE UP THE SISTER CHROMATIDS DOWN THE EQUATOR OF THE CELL.__________________________________________________ g. Anaphase: i. Describe what happens:_SPINDLE FIBERS PULL THE SISTER CHROMATIDS APART, PULLING THE CHROMOSOMES TO OPPOSITE ENDS OF THE CELL. _____________________________________ h. Telophase: i. Describe what happens:_2 NEW NUCLEAR MEMBRANES BEGIN TO REFORM, SPINDLE FIBERS DISAPPEAR, CHROMATID IS RELAXING GOING BACK TO CHROMATIN, PLASMA MEMBRANE BEGINS TO PINCH IN__________________________________________________ i. Cytokinesis: i. Describe what happens:_PLASMA MEMBRANE PINCHES IN COMPLETELY DIVIDING THE CYTOPLASM CREATING 2 GENETICALLY IDENTICAL DAUGHTER CELLS. ___________________ 3. In a newly formed cell after mitosis, describes how the daughter cell would resemble the parent cell in regard to the number of chromosomes? A: THEY WOULD HAVE THE SAME # OF CHROMOSOMES. HUMAN CELL WOULD EQUAL 46 CHROMOSOMES. 4. If a cell with 30 chromosomes undergoes mitosis, how many chromosomes will each of the two new cells have? 30 CHROMOSOMES WOULD BE IN EACH CELL AFTER MITOSIS 5. What is a centromere? A: AREA ON THE CHROMOSOME WHERE A CHROMATID CAN ATTACH WITH ITS COPY. 6. Fill the boxes to the right with the correct labels: SISTER CHROMATIDS 7. Mitosis is the division of what? NUCLEUS OF THE CELL 8. Cytokinesis is the division of what? THE CYTOPLASM OF THE CELL. CENTROMERE 9. What is the role of cyclins in the cell cycle? TO REGULATE THE CELL CYCLE 10. Describe the relationship between surface area and volume and what ratio is most beneficial for the cell. SURFACE AREA OR PLASMA MEMBRANE NEEDS TO BE LARGER THAN THE VOLUME TO MAKE SURE THAT THINGS CAN BE TRANSPORTED IN & OUT OF THE CELL QUICKLY 11. What is cancer? UNCONTROLLED CELL GROWTH 12. What causes cancer? THE INABILITY OF THE CELL TO CONTROL THE CELL CYCLE 13. What is a carcinogen? GIVE AN EXAMPLE. A SUBSTANCE THAT IS HARMFUL AND CAN CAUSE CANCER, EX: TOBACCO 14. If cancer is present, explain why the cancer cells eventually cause the healthy cells to disappear. THEY CROWD OUT THE HEALTHY CELLS BY REPRODUCING RAPIDLY AND USING UP ALL OF TE RESOURCES. 15. What is apoptosis? PROGRAMMED DEATH OF THE CELL 16. Describe what stem cells are? CELLS THAT HAVE NOT BEEN GIVEN JOBS TO DO 17. What organelle provides the cell with energy to do the cell cycle? MITOCHONDRIA