Electrons - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

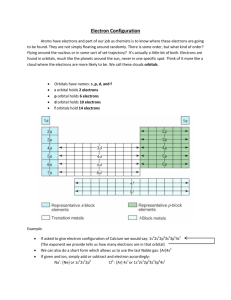
Valence Electrons and Electron Configuration Explaining the arrangement of electrons 08/27 & 08/28 Catalyst • Take out your HW to be stamped. • On your Daily Work Organizer, fill in your goal for the week. • Catalyst: Describe the pictured substances. Video Clip: Review http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1PSzSTilu_s&feature=bf_prev&list=PL6 5159266CFC74682 Homework Baseball Answer the questions on a blank sheet of paper. Use your homework. 1. Why are the noble gases the least reactive elements? 2. In the electron configuration 1s2, the 1 represents the: (a) number of protons (b) number of electrons (c) the energy level Homework Baseball: Answers 1. Why are the noble gases the least reactive elements? They have a full shell of valence electrons. 2. In the electron configuration 1s2, the 1 represents the: (a) number of protons (b) number of electrons (c) the energy level Objectives • SWBAT draw Lewis dot diagrams. • SWBAT write electron configurations. • SWBAT explain the octet rule and use it to predict ion formation. Agenda • • • • Catalyst Electrons and Intro to Ions Mystery Elements Puzzle Exit Ticket Properties of the atom • Protons determine the physical properties – The number of protons makes the element • Electrons determine the chemical properties – Only the electrons react!!! Electron Energy Levels •In the electron cloud, electrons are arranged in energy levels (aka orbitals or shells). •Electrons fill the levels from the inside out. •Electrons in the outer shell form chemical bonds (react) with other atoms. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Write: periods tell us energy levels What are valence electrons?? • Valence electrons are electrons on the outer shell of an atom that are available for bonding. – Valence Electrons are VERY IMPORTANT, they determine an element’s reactivity and general characteristics 3 45678 12 Write: groups tell us # valence electrons Practice: Draw the Bohr model and Lewis Dot Structure for N, O, F, Ne, Na, and Mg. Note: 1st orbital has 2 e, 2nd and 3rd orbitals have up to 8 e. • Bohr models show • Lewis Dot symbols us all the electrons, show us how many separated by valence electrons energy level are in an atom. (orbital). Li Ions! • Octet Rule: When forming ions, atoms give or take electrons in order to have a full outer orbital (or shell). – They end up with the same number of electrons as the closest noble gas. This is usually 8. (Exception: Helium with 2.) Think, pair, share. • How many electrons would N, O, F, Na, & Mg lose or gain to have the same number of electrons as Ne? • What ions are formed? • Example: Lithium loses 1 e to form Li+ (same # e as He) (Work with the person next to you and write your answers under your Lewis Dot structures in your notes.) Ions! Cations and Anions • Ion = an atom that has gained or lost electrons – Ions have a negative or positive charge. • Anion = ion with a negative charge. – Usually nonmetals • Ex: Cl- S2- • Cation = ion with a positive charge. – Usually metals • Ex: Be2+ Al3+ Think, Pair, Share • Are the ions of N, O, F, Na, and Mg cations or anions? – Label them in your notes. – Then share with your partner. • Does Ne form an ion? Why not? Electron Configuration • A way to keep track of all those electrons! • Write this down: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vb6kAxwSWgU Within the Energy Levels, electrons are arranged in 1 or more orbitals. Label the orbitals on your periodic table. S orbital 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 P orbital D orbital 6 7 F orbital © 1998 by Harcourt Brace & Company Orbitals Each orbital within a level has: • different energies • different shapes • Different orientation in space S p d f Periodic Table & Electron Configuration • Example - Hydrogen 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 1s 1st Period # e- in sublevel s-block Periodic Table & Electron Configuration • Example - Carbon 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 X XX X XX 2 2 2 1s 2s 2p 2nd Period 2 e- in p sublevel p-block Short Hand Configuration • Example - Carbon 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 X X XX XX 2 2 [He]2s 2p 2nd Period p-block Notation • Longhand Configuration S 16e- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 Core Electrons (Inner orbitals) Valence Electrons (Outer shell) • 1s2 2s2 Let’s 2p6 3s2Try 3p6 It! 4s2 3d10 4p6 Practice! Write the electron configuration for the following elements: N, O, F, Ne, Na, Mg Write your answers under your Bohr models and Lewis Dot Structures for these elements. Agenda • • • • Catalyst Electrons and Intro to Ions Mystery Elements Puzzle Exit Ticket Mystery Elements Puzzle • Work in a group of 4 at your table • Use the clues and your periodic table to match each symbol with an element. • Write down your answers on a sheet of paper. • Raise your hand when you think you have solved the puzzle. Exit Ticket 1. Draw the Bohr model and Lewis Dot Structure for Phosphorus (P). 2. Write the electron configuration of P. 3. How many electrons will P lose or gain to form an ion? How do you know? 4. What ion does P form? Is it an anion or cation? If you are done, work on HW packet.