Chapter 14 Reading Assignment #1
advertisement

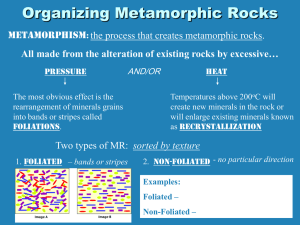
Chapter 3 Guided Reading Assignment #4 1. Read: 80-85 2. Define the following terms: a) b) c) d) Metamorphism Contact Metamorphism Regional Metamorphism Hydrothermal Metamorphism e) Foliated Metamorphic Rock f) Nonfoliated Metamorphic Rock 3. List the five key concepts for this section. 4. How do metamorphic rocks form? 5. According to the drawing of the rock cycle on page 67, which rocks can turn into metamorphic rocks? 6. Looking at figure 14, how do we know these are metamorphic rocks? 7. How do most metamorphic changes occur? 8. In the graphic organizer provided, compare and contrast contact and regional metamorphism. 9. Describe the process of contact metamorphism. 10. How does marble form? 11. In the table below, list at least 4 features or characteristics each of the 3 agents of metamorphism. HEAT PRESSURE HYDROTHERMAL 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 3. 3. 3. 4. 4. 4. CPHS Physical Geology Mr. G. Edelman 12. What is the most important agent of metamorphism? Explain 13. How hot is it deep in the rock? 14. Explain how pressure increases with depth? 15. Explain how pressure causes metamorphism in rocks. 16. Examine figure 16B on page 82. Explain how some areas became deformed and others didn’t. 17. Describe how water solutions cause metamorphism. 18. Explain how hydrothermal solutions cause metamorphism. 19. In the table least a number of features and characteristics of foliated and nonfoliated metamorphic rocks. Clastic Sedimentary Rocks Chemical Sedimentary Rocks 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 5. Questions 20-24 relate to Table 3 on page 84. 20. What is the parent rock of marble? 21. Which metamorphic rock is made of fused quartz crystals? 22. Which tow metamorphic rocks have medium to coarse grain size? 23. How is slate different from anthracite? 24. How is schist identified? CPHS Physical Geology Mr. G. Edelman