Mutations
advertisement

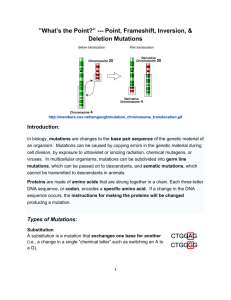
MUTATIONS What happens when we change DNA? MUTATIONS What do you think a mutation is? What happens to you during a mutation? MUTATIONS Mutations are ANY change in an organism’s DNA. Mutations usually happen during if a mistake is made during replication (S phase). MUTATIONS As we’ve discussed before, your cells have many ways to prevent mutations from happening. Cells use proofreading when duplicating DNA. If a cell detects a mistake is made in phase G2, it self-destructs (apoptosis). Your genetic code is degenerate. This means that there are multiple possibilities to make most of the amino acids. MUTATIONS Mutations will either change the individual DNA sequences, or an entire chromosome. We will look at DNA mutations first. There are four types: Substitution Deletion Insertion Inversion MUTATIONS A substitution switches one DNA letter for another. These are usually point mutations – mutations that only affect one letter! Example: Original sequence: THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT. Mutant sequence: THE FAT HAT ATE THE RAT. MUTATIONS Many point mutations are also silent mutations – they will NOT change the amino acids that are created. Original sequence: AUG CCA GGG UGU Amino acids: Met – Pro – Gly - Cys Mutant sequence: AUG CCC GGU UGU Amino acids: Met – Pro – Gly - Cys MUTATIONS A deletion removes one or more DNA letters at once. These are always frameshift mutations – mutations that change how codons are divided. Example: Original sequence: THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT. Mutant sequence: THE FAT ATA TET HER AT. MUTATIONS An insertion adds one or more DNA letters at once. These are also always frameshift mutations! Example: Original sequence: THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT. Mutant sequence: THE FAT WCA TAT ETH ERA T. MUTATIONS An inversion reverses a sequence of DNA letters. These usually happen during mitosis (M phase), as chromosomes line up in metaphase. Example: Original sequence: THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT. Mutant sequence: THE FAT HTE TAT ACE RAT. MUTATIONS Remember, point mutations leave the same number of nucleotides. In contrast, frameshift mutations either add or remove nucleotides. Point mutation: AUG CGA UUA → AUG CUA UUA Met – Arg – Leu → Met – Leu – Leu Frameshift mutation: AUG CGA UUA → AUG CGG AUU A Met – Arg – Leu → Met – Arg - Iso MUTATIONS Now we will look at chrmosomal mutations. Mutations that affect ONLY ONE chrmosome: 1. Deletion 2. Duplication 3. Inversion MUTATIONS Now we will look at chrmosomal mutations. Mutations that affect TWO chrmosomes: 1. Insertion 2. Translocation MUTATIONS: NON-DISJUNCTION EX: TRISOMY 21 (DOWN SYNDROME) Sometimes, there is an error when egg or sperm cells divide, resulting in too many or too few chromosomes. How do you think this type of change would impact an organism?