Frameshift mutation

HAPPY TUESDAY
Bellwork:
• Study the Central Dogma, Transcription, &
Translation.
• On Bellwork sheet write “Study for Quiz”.
Standard: identify and illustrate
changes in DNA (B.6E)
Essential Question: How can I identify changes in DNA?
Think about it:
What happens if our DNA gets messed up?
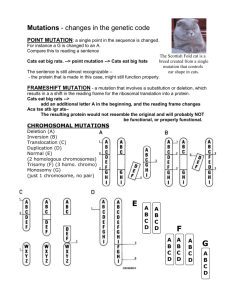
Mutations: changes in genetic material
• May be caused by:
• mistakes in DNA replication
• mistakes in transcription
• environmental factors (like radiation )
Point mutation: involves a change in a single base
• called substitution
• three types:
• silent: results in no change to the protein
• missense: results in one wrong amino acid
• nonsense: results in an early stop
Which type of point mutation is this?
Types of Mutations
Frameshift mutation: involves a change that affects the entire amino acid sequence
• three types:
• insertion: an extra base is added
• deletion: a base is subtracted
• duplication: an entire codon is repeated
Genetic Mutations: Your Name
1. Copy the chart below.
2. Write your name in the first box.
3. Put a box around each codon.
4. Fill in the rest of the start by doing the mutation.
5. Put a box around each codon after the mutation.
Name:
Point(add a base into the sequence)
E N R I Q U EGA R Z A
E N R I Q U EGA R Z K
Deletion (take a base away)
E N R I U E GA R Z K
Insertion(add a base) E X N R I U E GA R Z K
Think-Pair-Share
Which would more likely have a bigger effect on an organism, a point mutation or frameshift mutation?
Why?
frameshift point mutation protein mutation point frameshift protein
Quickwrite
• Answer the following question in your journal (29 words):
– If you have a mutation in a body cell
(skin, stomach, bone, etc.), can you pass that mutation on to your children? Why or why not?
Do you know of any diseases caused by genetic mutations?
Sickle Cell Anemia
These are the sickle-shaped blood cells of someone with sickle cell anemia.
Sickle cell anemia is the result of a point mutation, a change in just one nucleotide in the gene for hemoglobin. This mutation causes the hemoglobin in red blood cells to distort to a sickle shape when deoxygenated. The sickleshaped blood cells clog in the capillaries, cutting off circulation.
Having two copies of the mutated genes cause sickle cell anemia, but having just one copy does not, and can actually protect against malaria an example of how mutations are sometimes beneficial.
Color Blindness
• Most forms are caused by a point mutation on the X chromosome.
What number do you see? A color blind person won’t see anything. A color deficient person may see the number 35
Achondroplasia
• This is the most common form of dwarfism. It is caused by a substitution mutation for the gene that codes for bone growth.