Grain Products
advertisement

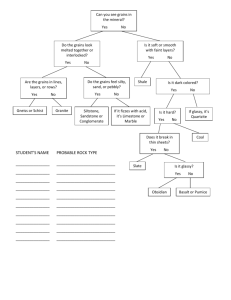
Grain Products Nutrition and Wellness Gold 5 Key Concepts Describe how food is made from Grains. Explain how the processing of grains can affect their nutritional value. Name and describe six grains. Main Idea Grains are a versatile, nutritious, and flavorful addition to meals and an economical way to stretch a food budget. Grains Grains are plants in the grass family cultivated for their fruits or seeds. Common grains include ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Wheat Oats Rye Barley Buckwheat Grains Kernels- separate dry fruits harvested and processed for food. Sometimes called wheat berries. Four parts to every grain kernel ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Bran Endosperm Germ Hull Kernel Make-up Bran- edible, outer layer of the kernel Endosperm- Largest part of the kernel made of proteins and starches. Supply the plant with food. Germ- the seed that grows the new plant. Hull- the edible outer shell that is removed after harvesting. Nutrients in Grains Bran Contains ◦ Dietary fiber ◦ B Vitamins ◦ Minerals Endosperm Contains ◦ Complex carbohydrates ◦ Proteins Nutrients in Grains Germ contains ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Protein Unsaturated Fats B Vitamins E Vitamins Iron Zinc Phytochemicals Nutrients in Grains All grains must be processed before consumption. The type of processing affects a grain’s nutrient value. A Grains’ bran and germ are often removed during processing, leaving only the endosperm. ◦ White flour and breakfast cereals Nutrients in Grains Removing the Bran and Germ removes most vitamins, minerals, phytochemicals, and dietary fiber. Enrichment- replacing lost nutrients using supplements and/or fortified nutrients. Nutrients in Grains Whole-Grain products- processed with the whole grain kernel. Include products like whole wheat flour, whole grain bread, and whole grain cereals. Maintains most of the natural nutritional value. Grains Texture Wheat Usages Wheat BerriesChewy Include the entire wheat kernel Used as cereals or in Grain dishes Buckwheat- seed of a non grass plant that is used like grain Nutlike & earthy flavor Flour and cereals Couscous- steamed, cracked endosperm or durum wheat. Pasta like flavor and texture Cereals, salads, and desserts. Quinoa- small ivory colored, rice-like grain that has more protein than any other grain Unique Used in South American mild flavor. cuisines. Used as a side dishes, soups, and puddings. Grains-Rice Starchy seed of plants grown in flooded fields in warm climates Grown mostly in Asia, but also in the United States. Rice is often identified by the length of the rice grain. Types of Rice Grains Long-Grain Rice ◦ Most popular rice in the U.S. ◦ Grains are fluffy and stay separated when cooked. ◦ Fine texture and a nutlike aroma and flavor. Medium-Grain Rice ◦ Plump, tender, and moist. ◦ Grains stick together. ◦ Works well for puddings and cold salads. Types of Rice Grains Short-Grain Rice ◦ Almost round ◦ Highest starch content of the 3 types of rice ◦ Used in creamy dishes and Asian cuisine Rice Processing Processed in several different ways yielding products with different colors, textures, and nutritional values. ◦ Enriched Rice- Bran and Germ removed losing nutrients. ◦ Brown Rice- Whole-grain form of rice. Takes considerably longer to cook. ◦ Converted- Steamed under pressure to remove hull and preserve nutrients ◦ Instant- Precooked and Dehydrated before packaging. Minute Rice Corn Most popular food plant in the world and the most widely grown crop in the United States. Used for many purposes including food, plastics, dyes, and ethanol fuel. Served in many different forms. Corn Hominy- dried kernel with the hull and germ removed, leaving only the endosperm. Grits- coarsely ground hominy used as breakfast cereals and side dishes. Cornmeal- ground, dried, corn kernels. Cornstarch- Used as a thickening agents for desserts. Made only from the endosperm of the corn kernel. Oats Pleasant, slightly sweet flavor. Used mostly to feed live-stock and for a hot breakfast cereal. Have a considerable amount s of nutrients and dietary fiber. Can be pre-cooked and dehydrated for instant uses. Other Grains Barley- contains large amounts of dietary fiber and has a mild flavor with a chewy texture. Used mostly in soups and stews. Rye- often used in crackers and bread, rye is a dark grain with a hearty flavor. Wild Rice- a seed of a water grass with a crisp texture and nutlike flavor. ◦ Not an actual form of rice. Pasta Pasta is an Italian word meaning “paste” that refers to dough made from flour and water. Macaroni- made from durum wheat flour and water. Noodles-which have egg solids added for tenderness. Pasta Durum wheat is grown only for pasta and is processes into semolina flour. Semolina flour gives pasta its yellow color and nutlike flavor. Products made from durum keep their shape and firm texture when cooked. Pasta Pasta is sold in both dry and fresh forms Dried tend to be less expensive, have a longer shelf life, and are a staple in many diets. Fresh pasta is perishable and is found in the refrigerated sections. Common Types of Pasta Egg Noodles- Egg soilds added for tenderness. Orzo- Small, rice-shaped pasta, good for salads and soups. Penne-Straight tube-shaped pasta cut diagonally on the ends. Common Types of Pasta Elbow macaroni- Small, curved tubeshaped pasta. Conchiglie- Seashell pasta Manicotti- Large tube-shaped pasta, usually stuffed Common Types of Pasta Linguine- Long, narrow, flat pasta. Holds sauces well. Lasagna-Wide, flat noodles, usually baked with sauce. Fettuccine-long, flat pasta, wider than linguine. Farfalle-Bowtie pasta Spaghetti- Long, thin round pasta.