ESCh3.4-Metamorphic Rocks.ppt
advertisement

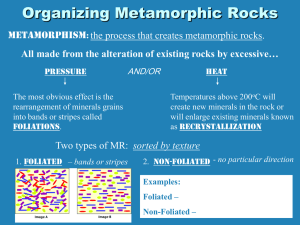
Metamorphic Rocks Earth Science Chapter 3 Section 3 BELLWORK: Explain how igneous rocks and sedimentary rocks are related. ● TODAY’S OBJECTIVES: Describe the agents of metamorphism. List the criteria used to classify metamorphic rocks. List the names, textures, and environments of formation for the most common metamorphic rocks. METAMORPHIC ROCKS ● Definitions “Meta” = change ●“Morph” = shape ●A rock that has been changed from its original form by heat, pressure, and fluid activity into a new rock ● Original form = “parent” ●New form = “daughter” ● METAMORPHIC ROCKS Rocks that have changed form ●Produced from preexisting ● Igneous rocks ●Sedimentary rocks ●Other Metamorphic rocks ● METAMORPHISM Takes place where preexisting rock is subjected to temperatures and pressures unlike those in which it formed ●Degrees of metamorphism ● Exhibited in the rock’s texture and mineralogy ●Types ● Low-grade (eg. Shale becomes slate) ●High-grade (causes the original features to be obliterated) ● HEAT ● Sources include… Magma ● Temperature of magma ●Composition of magma ● Geothermal Gradient ● Temperature increases with depth of burial ●Core of Earth is warmer than outer crust ● **METAMORPHIC SETTINGS ● 1. Contact, or thermal metamorphism Near a mass of magma ●Change is driven by a rise in temperature ● Vein of magma Contact Metamorphism ● 2. Regional metamorphism Result of directed pressures and high temperatures during mountain building ●Produces the greatest volume of metamorphic rock ● Regional metamorphism occurs here The tremendous pressure heat and pressure may cause rocks to buckle and fold. Pressure Pressure METAMORPHIC AGENTS Heat ●Pressure (stress) ● From burial (confining pressure) ●From differential stress during mountain building (best place to find meta. rock) ● ● Chemically active fluids Mainly water and other volatiles ●Promote recrystallization by enhancing ion migration ● METAMORPHIC TEXTURES ● Foliated texture Minerals in a parallel alignment ●Minerals perpendicular to the compressional force ● ● Non-foliated texture Contains equi-dimensional crystals ●Resembles coarse-grained igneous rock ● COMMON METAMORPHIC ROCKS Foliated rocks ● ● Slate fine-grained ●splits easily ● ● Schists strongly foliated ●“Platy” ●Types based on composition (eg, mica schist) ● ● Gneiss Strong segregation of silicate minerals ●“Banded” texture ● COMMON METAMORPHIC ROCKS ● Non-foliated rocks Marble ● Parent rock – limestone ●Large, interlocking calcite crystals ●Used as a building stone ●Variety of colors ● Quartzite ● Parent rock – quartz sandstone ●Quartz grains are fused ●