Science-9-LFS
advertisement

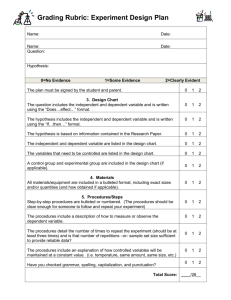
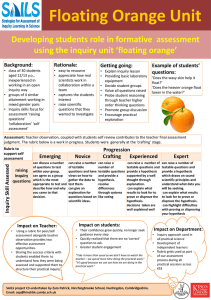
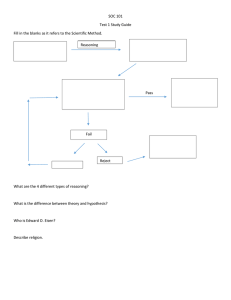
Unit 1: Nature of Science Unit Essential Question: Why is Science an ongoing and continuous process that is open for change? Lesson Essential Question 1 Why is the use of scientific inquiry a sensible approach to the study of science? SC.912.N.1.2, SC.912.N.1.3, SC.912.N.2.2, SC.912.N.2.4, Lesson 1 Vocabulary Experiment, science, scientific inquiry, hypothesis, variables, control, data Lesson Essential Question 2 Why is it important for scientific investigations to be replicable? SC.912.N.1.1, SC.912.N.1.4, SC.912.N.1.5, SC.912N.1.6, Lesson 2 Vocabulary Replication, repetition, Lesson Essential Question 3 How would you explain the difference between a scientific theory and a scientific law? SC.912.N.3.1, SC.912.N.3.2, SC.912.N.3.3, SC.912.N.3.4, Lesson Essential Question 4 How can you describe the benefits and limits to models and other fields of science? SC.912.N.3.5 Lesson Essential Question 5 Lesson 3 Vocabulary Scientific Law, Scientific theory, Lesson 4 Vocabulary Scientific model Lesson 5 Vocabulary How is science different from other fields of study? SC.912.N.1.7, SC.912.N.2.2, SC.912.N.2.5, Lesson Essential Question 6 How does science affect our lives? SC.912.N.4.1, SC.912.N.4.2, Lesson 6 Vocabulary Lesson Essential Question 7 Lesson 7 Vocabulary What is the difference between science and pseudoscience? SC.9.12.N.2.1, SC.912.N.2.2, SC.912.N.2.3, pseudoscience Major Unit Assignment Students will demonstrate their understanding of the nature of science by completing the steps of a scientific experiment. Students will use the Sumter County Schools Experimental Design to answer a question or solve a problem with a clear purpose for investigation. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Identify a question or problem concerning life science. Explain the purpose of investigating this question or problem. Conduct background research on the topic, listing your findings in a bibliography. Develop a testable hypothesis in an “If, then, because” statement. Create a specific bulleted list of materials needed for the experiment. Write out detailed procedures for how to do the experiment and how to analyze the data. Include any safety concerns. 7. Records all observations and data from the experiment in charts, graphs or tables. 8. Evaluate the results of the experiment. 9. Construct an argument using the evidence to explain if the results support or do not support the hypothesis and write a conclusion statement. 10. Share the project in the school science fair or in the class.