Sensory Lab
advertisement
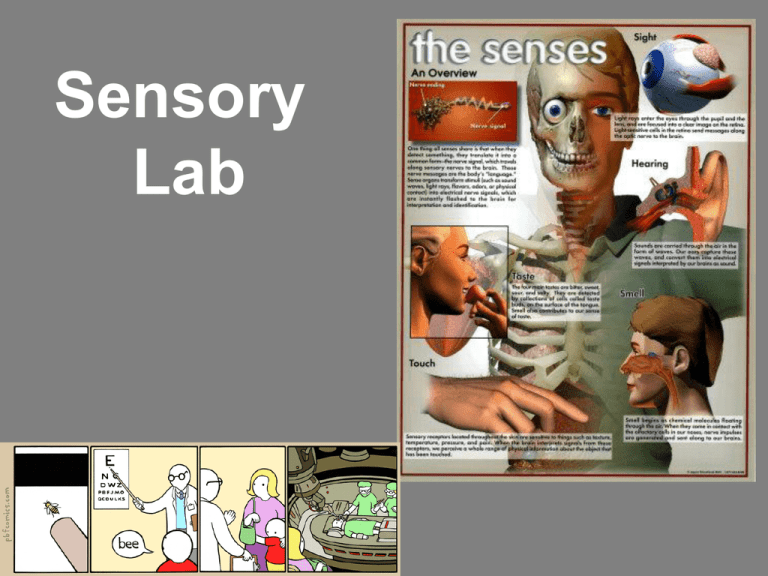
Sensory Lab Nonhuman Senses • Infrared imaging • Electrosense • Vomerolfaction • Ultrasound detection • Infrasound detection • Magnetoreception • Cutaneous chemosense Sensory Pathway 1. Stimulus is detected by a sensory neuron or specialized receptor cells. The receptor cell converts stimuli into an electrical signal. 2. This action potential is now sent to the CNS for integration. 3. A signal is then sent to the effectors (specific muscle groups). Reflexes Functions that should happen while you are free to think about other matters!! Best known Tendon Reflex: Patellar Reflex Other Reflexes to test today: Blink Reflex Light Reflex Grasp reflex in infants Patellar Reflex The tendinous attachments of muscles have special sensory receptors: • Attachment receptors respond to stretch stimuli • Receptors relay info to the CNS • Nerve impulses pass up to the spinal cord and through a synapse to the a motor neuron and then to a nearby muscle—reflexive response impulses never reach the brain!! You will quantify the strength of the patellar reflex in response to different stimuli. Specific Reflexes Blink Reflex: As an object comes near the eye the eyelids rapidly close to protect the eye. You will observe this reflex reaction. Light Reflex: The iris contracts and relaxes controlling the amount of light allowed through the pupil. You will measure the dilation of the irises under various light conditions. Chemosense: Taste EXPERIMENT: 1) Locate the various types of taste receptors 2) Diagram the surface of the tongue and identify the regions where the taste sensations are most strongly experienced. 3) Determine your threshold for salt and sugar using concentrations of varying intensities. Umami Fattiness Calcium Sour Bitter Piquance 4) Record your observations and compare your threshold with other members of the class Salty & Sweet RINSE YOUR MOUTH BETWEEN TASTES!! Chemosense: Smell Smell receptors are located in upper portion of nasal cavity Characteristics: 1. Sense of smell shows high degree of adaptation 2. Certain odors mask others Experiment: 1. Close your eyes and distinguish the odors 2. Smell the camphor until the odor can no longer be detected and then try to distinguish between oil of cloves and oil of peppermint. (Repeat with alcohol as masking agent, and compare the ability of the two substances to affect your ability to distinguish.) Cutaneous Sensations: Touch Just a touch of information: A given neuron can have a small or large receptor field over which a stimulus can affect it “Sensitive areas” (ex. fingers) contain the highest density of touch receptors Finger Back of Neck DON’T WATCH!!! Experiments: Distribution of receptors: 1. Mark your: palm, back of hand, back of arm and back of neck 2. Using an aesthesiometer, stimulate each ink spot with a minimal and CONSISTENT stimulus. Locate those areas with the highest concentration of sensitivity (touch receptors) and try to quantify the differences between body parts. • With a pithing needle locate the distribution of pain receptors in the same area you did with the touch receptors • Also locate the distribution of temperature receptors using one each of cold and warm glass rods. Cutaneous Sensations Experiment: Warning!! 1. Make sure the intensity isn’t too strong (no one should feel too much pain!) 2. Use consistent intensity throughout the entire experiment Cutaneous Sensations: Touch Experiments: Tactile Discrimination: 1. Determine a person’s ability to distinguish two distinct stimuli using a compass. 2. Make sure the two areas are applied simultaneously. 3. Quantify the differences in tactile ability among different parts of the body. DON’T WATCH!!! Finger Back of Neck Cutaneous Sensations: Temperature, intensity, and thermal adaptations Experiments: 1. Survey areas on the ventral and dorsal surfaces of forearm with a cold glass rod --Determine whether there are differences in intensity of cold in different areas. 2. Set up three beakers: Hot water, room temperature water, cold water. Place one index finger in the hot and one in the cold water, then place both in the room temperature water. Compare the sensations. Mechanoreception - Hearing Sound waves enter ear through auditory meatus Tympanic membrane moves back and forth Movement of tympanic membrane is transmitted to ossicles Ossicles vibrate against membrane (oval window) Oval window sets fluid of the cochlea into motion Ion channels open and cause a receptor potential along auditory nerve 0 Specific portions of the basilar membrane (in the cochlea) move in response to the movement of the cochlear fluid Deafness Conduction Deafness: Due to abnormalities of the auditory canal, tympanic membrane, or ossicles Nerve deafness: Due to abnormalities of the cochlea and neural mechanisms Mechanoreception - Hearing Experiments: Webber’s Conduction - Deafness test: Place the handle of a vibrating tuning fork on the mastoid process. When sound can no longer be heard move the fork to the front of the ear. Localization of Sound: Attempt to locate the position of a time clock held in different positions Repeat with one ear closed; record the position of the clock when you could and could not locate it. Cochlear Implant Mechanoreception - Balance Balance is determined by the movement of fluid, the endolymph, in the labyrinth (a complex set of tubing in the inner ear) Movement of the endolymph causes nerve impulses which are signals to the brain indicating motion, direction of motion, etc. Mechanoreception - Balance Experiment: 1. 2. 3. Whirl until dizzy Attempt to quickly strike the outstretched finger of partner with your finger Record the direction in which you over-corrected your attempt to make contact Vision Blind Spot + ● Visual Acuity Myopia and Hypermetropia Myopia: Occurs when the lens is too convex or the eyeball is too long Hypermetropia: Occurs when the eyeball is too short, the lens is too flat, or there is a corneal imperfection, Astigmatism Other Vision Experiments • Accommodation • Eye Dominance • Afterimages In your lab report: • • • • Abstract Experimental (brief, but include all) Results/Observations Discussion w/ study questions • Next week: Muscles