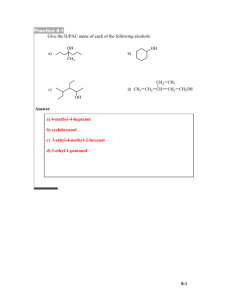
The shortened structural formula for 2,3
advertisement

CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT WAID ACADEMY CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND ESTERS The shortened structural formula for 2,3-dimethylpentanoic acid is. 20 1. A 0% 2. B 3. C 4. D A B C D Which of the reactions shown can be used to make 3-methylbutanoic acid? 1. 2. 3. 4. Catalytic hydration of 3-methylbut-1-ene. Oxidation of 3-methylbutan-2-ol. Dehydration of 3-methylbutan-1-ol. Oxidation of 3-methylbutanal. 20 0% Catalytic hydration of 3-methylbut-1-ene. Oxidation of 3-methylbutan-2-ol. Dehydration of 3-methylbutan-1-ol. Oxidation of 3-methylbutanal. Butanoic acid can be made by 1. 2. 3. 4. Warming a mixture of butan-2-ol and acidified potassium dichromate. Passing butan-1-ol vapour over hot aluminium oxide. Warming a mixture of butanal and Fehling's solution. Reacting but-1-ene with steam over a zinc oxide catalyst. 25 0% Warming a mixture of butan-2-ol and acidified potassium dichromate. Passing butan-1-ol vapour over hot aluminium oxide. Warming a mixture of butanal and Fehling's solution. Reacting but-1-ene with steam over a zinc oxide catalyst. Which of the compounds shown will neutralise sodium hydroxide? 20 1. A 2. B 0% 3. C 4. D A B C D Which structure shown represents the ester formed when propan-2-ol reacts with methanoic acid? 20 1. A 2. B 0% 3. C 4. D A B C D Which two compounds are formed when the ester shown below is hydrolysed? 20 1. 2. 3. 4. Propan-1-ol and ethanoic acid. Ethanol and butanoic acid. Butan-1-ol and ethanoic acid. Ethanol and propanoic acid. 0% Propan-1-ol and ethanoic acid. Ethanol and butanoic acid. Butan-1-ol and ethanoic acid. Ethanol and propanoic acid. Name the ester formed when the acid and alcohol shown below react together. 20 1. 2. 3. 4. Pentyl ethanoate. Ethyl propanoate. Propyl ethanoate. Ethyl butanoate. 0% Pentyl ethanoate. Ethyl propanoate. Propyl ethanoate. Ethyl butanoate. The shortened structural formula for methylbutanoate is. 20 1. A 2. B 0% 3. C 4. D A B C D Name the type of reaction which occurs when an ester is formed. 1. 2. 3. 4. 20 Dehydration. Dehydrogenation. Oxidation. Condensation. 0% Dehydration. Dehydrogenation. Oxidation. Condensation. Esters can be prepared in the laboratory by heating an alcohol and a carboxylic acid with a few drops of sulphuric acid in a water bath. After 5 minutes the reaction mixture is poured into a beaker containing sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. Which two observations show that an ester has been formed? 1. 2. 3. 4. 30 Bubbles of gas are given off and the product smells differently to the reactants. 0% An oily layer forms on the surface of the solution and the product smells differently to the reactants. An oily layer forms on the surface of the solution and bubbles of gas are given off. An oily layer forms on the surface of the solution and the product is coloured. Bubbles of gas are given off and the product smells differently to the reactants. An oily layer forms on the surface of the solution and the product smells differently to the reactants. An oily layer forms on the surface of the solution and bubbles of gas are given off. An oily layer forms on the surface of the solution and the product is coloured.