Chapter
1
•Short-Term Finance and
Planning
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 1 – Index of Sample
Problems
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Slide # 02 - 03
Slide # 04 - 08
Slide # 09 - 10
Slide # 11 - 12
Slide # 13 - 14
Slide # 15 - 16
Slide # 17 - 18
Slide # 19 - 20
Slide # 21 - 22
Slide # 23 - 24
Slide # 25 - 28
Sources and uses of cash
Operating and cash cycles
Receivables schedule
Payables schedule
Disbursements schedule
Net cash inflow
Cumulative surplus
Short-term financial plan
Compensating balance
Cost of factoring
Collections
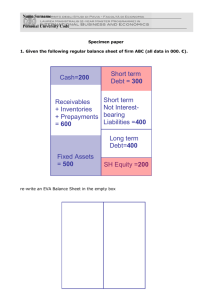
2: Sources and uses of cash
Account
Beginning
Balance
Ending
Balance
Cash
444
460
Accounts receivable
996
980
Inventory
1,387
1,405
Fixed assets
4,813
5,209
Accounts payable
1,042
1,234
250
500
Long-term debt
1,500
1,200
Common stock
2,900
3,000
Retained earnings
1,948
2,120
Note payable
Source
of Cash
Use
of Cash
U
S
3: Sources and uses of cash
Account
Beginning
Balance
Ending
Balance
Cash
444
460
Accounts receivable
996
980
Inventory
1,387
1,405
U
Fixed assets
4,813
5,209
U
Accounts payable
1,042
1,234
S
250
500
S
Long-term debt
1,500
1,200
Common stock
2,900
3,000
S
Retained earnings
1,948
2,120
S
Note payable
Source
of Cash
Use
of Cash
U
S
U
4: Operating and cash cycles
Average accounts receivable
$ 2,080
Average inventory
2,400
Average accounts payable
1,135
Sales
Cost of goods sold
15,600
9,761
Given the information in the table,
compute the operating and cash cycles.
5: Operating and cash cycles
Credit sales
Receivable s turnover
Average accounts receivable
$15,600
$2,080
7.5
365 days
Re ceivables period
Receivable s turnover
365 days
7.5
48.7 days
6: Operating and cash cycles
Cost of goods sold
Average inventory
$9,761
$2,400
4.0671
Inventory turnover
365 days
Inventory turnover
365
4.0671
89.7 days
Inventory period
7: Operating and cash cycles
Cost of goods sold
Average accounts payable
$9,761
$1,135
8.6
Payables turnover
365 days
Payables turnover
365 days
8.6
42.4 days
Payables period
8: Operating and cash cycles
Operating cycle Inventory period Receivable s period
89.7 48.7
138.4 days
Cash cycle Operating cycle - Payables period
138.4 - 42.4
96 days
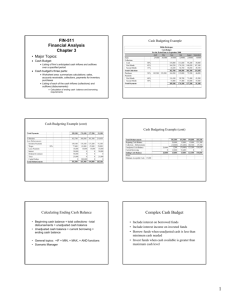
9: Receivables schedule
Q1
Beginning receivables
290
Sales
300
Q2
Q3
Q4
270
360
420
Cash collections
Ending receivables
The receivables period is 60 days.
Assume that each month has 30 days.
Can you complete this table?
10: Receivables schedule
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Beginning receivables
290
200
180
240
Sales
300
270
360
420
Cash collections
390
290
300
380
Ending receivables
200
180
240
280
Q1 collection s $290 30/90(300) $390
Q2 collection s 60/90($300 ) 30/90($270 ) $290
Q3 collection s 60/90($270 ) 30/90($360 ) $300
Q4 collection s 60/90($360 ) 30/90($420 ) $380
Q4 ending receivable s 60/90($420 ) $280
11: Payables schedule
Sales
Beginning payables
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
300
270
360
420
90
Purchases
Payments
171
Ending payables
Sales for Q1 of the following year are $310.
Purchases are equal to 60% of the next quarter sales.
The payables period is 45 days.
Assume that each month has 30 days.
12: Payables schedule
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
300
270
360
420
90
81
108
126
Purchases
162
216
252
186
Payments
171
189
234
219
81
108
126
93
Sales
Beginning payables
Ending payables
Sales for Q1 next year = $310
Q1 purchases = .6($270) = $162
Q2 purchases = .6($360) = $216
Q3 purchases = .6($420) = $252
Q4 purchases = .6($310) = $186
Q1 payments = $90 + 45/90($162)
= $171
Q2 payments = 45/90($162)+ 45/90($216) = $189
Q3 payments = 45/90($216) + 45/90($252) = $234
Q4 payments = 45/90($252) + 45/90($186) = $219
13: Disbursements schedule
Payment of accounts
Wages, taxes, other expenses
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
171
189
234
219
70
85
90
110
80
35
12
12
Capital expenditures
Long-term financing expenses
Total cash disbursements
12
12
14: Disbursements schedule
Payment of accounts
Wages, taxes, other expenses
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
171
189
234
219
70
85
90
110
80
35
12
12
12
12
253
366
371
341
Capital expenditures
Long-term financing expenses
Total cash disbursements
15: Net cash inflow
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Collections
390
290
300
380
Disbursements
253
366
371
341
Net cash inflow
What is the net cash inflow for each quarter?
16: Net cash inflow
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Collections
390
290
300
380
Disbursements
253
366
371
341
Net cash inflow
137
-76
-71
39
17: Cumulative surplus
Q1
Beginning cash balance
Net cash inflow
Cumulative surplus (deficit)
Can you complete this table?
Q3
Q4
-76
-71
39
20
137
Ending cash balance
Minimum cash balance
Q2
-20
18: Cumulative surplus
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
20
157
81
10
Net cash inflow
137
-76
-71
39
Ending cash balance
157
81
10
49
Minimum cash balance
-20
-20
-20
-20
Cumulative surplus (deficit)
137
61
-10
29
Beginning cash balance
In which quarters does the firm have surplus funds?
In which quarter does the firm need to borrow funds?
19: Short-term financial plan
Assume amounts are in thousands
Beginning cash balance
Net cash inflow
Q1
New short-term borrowing
---
Interest
-.9
Short-term borrowing repaid
Q3
Q4
-76.0
-71.0
39.0
-20.0
-20.0
-20.0
20.0
137.0
12% annual rate
Q2
-30.0
Ending cash balance
Minimum cash balance
-20.0
Cumulative surplus (deficit)
Beginning short-term borrowing
Change in short-term debt
Ending short-term debt
30.0
20: Short-term financial plan
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
20.0
126.1
50.1
20.0
137.0
-76.0
-71.0
39.0
New short-term borrowing
---
---
40.9
---
Interest on short-term borrowing
-.9
---
---
-1.2
Short-term borrowing repaid
-30.0
---
---
-37.8
Ending cash balance
126.1
50.1
20.0
20.0
Minimum cash balance
-20.0
-20.0
-20.0
-20.0
Cumulative surplus (deficit)
106.1
30.1
0.0
0.0
30.0
0.0
0.0
40.9
-30.0
0.0
40.9
-37.8
0.0
0.0
40.9
3.1
Beginning cash balance
Net cash inflow
Beginning short-term borrowing
Change in short-term debt
Ending short-term debt
21: Compensating balance
You have a $50,000 line of credit with your local bank to cover your
quarterly cash needs. The loan terms have a 5% compensating
balance requirement.
How much will you have to borrow if you need to net $20,900?
What is the effective interest rate of the loan if the stated rate is 8%
and the loan is for one year?
22: Compensating balance
Net proceeds (1 compensati ng balance requiremen t ) Amount borrowed
$20,900 (1 - .05) Amount borrowed
$20,900
.95
Amount borrowed $22,000
Amount borrowed
Interest paid
Amount borrowed
$1,760
$20,900
Effective interest rate
Interest .08 $22,000
$1,760
.0842
8.42%
23: Cost of factoring
Your firm has average receivables of $990 and a 60 day receivables
period. You factor your receivables at a rate of 2.5%.
What is the effective annual rate of your factoring program?
24: Cost of factoring
.025
Interest rate for 60 days
1 - .025
.025641
Annual percentage rate R N
365
60
.025641 6.08333
.15598
.025641
15.60%
Effective annual rate (1 R) N 1
(1 .025641) 6.08333 1
1.16651 1
.16651
16.65%
25: Collections
Your projected sales are:
Jan
$800
Feb
$720
Mar
$940
You collect 50% in the month of sale, 40% in the month following
the month of sale and 8% in the second month following the month
of sale.
What is the amount of your March collections?
26: Collections
March collections:
50% of March sales:
40% of February sales:
8% of January sales:
.50 $940 = $470
.40 $720 = $288
.08 $800 = $ 64
Total: $822
27: Collections
Your projected sales are:
Q1
$900
Q2
$880
Q3
$970
Your receivables period is 38 days.
Assume every quarter has 90 days.
Assume sales occur evenly throughout the quarter.
What is the amount of your Q2 collections?
28: Collections
Q2 collections:
From prior quarter:
From current quarter:
(38/90) $900
= $380
(90 - 38)/90 $880
= $508
Total: $888