cell division study questions
advertisement

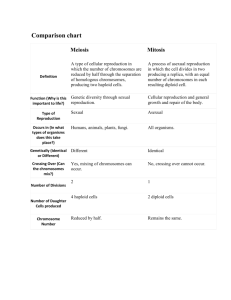
UNIT 8 – CELL DIVISION STUDY QUESTIONS U8P1 Define: a) interphase b) cytokinesis c) daughter cells d) spindle fibers e) diploid f) centriole g) haploid h) gamete i) somatic cells k) chromatin l) centromere 1. Which increases faster as a cell grows, its volume or surface area? 2. List 3 reasons why cells divide. 3. Draw & label a chromosome. 4. List the phases of the cell cycle in order. 5. If your diploid number is 20, what is your haploid number? 6. What is the diploid number for humans? 7. Are somatic cells diploid or haploid? 8. Are gametes diploid or haploid? U8P2 Define: a) prophase b) metaphase c) anaphase d) telophase e) cytokinesis f) sister chromatid 1. List the phases of mitosis in order. 2. What are some differences between plant & animal cell division? 3. In mitosis, if the parent cell has 8 chromosomes, how many will the daughter cells have? 4. List & briefly describe the stages of interphase. U8P3 Define: a) homologous chromosomes b) crossing over 1. In meiosis, if the parent cell has 8 chromosomes, how many will the daughter cells have? 2. What happens when cells come into contact with each other? 3. How are gametes produced? 4. What is crossing over? 5. Why is crossing over important? 6. When does crossing over occur? 7. When during meiosis does reductive division take place? 8. How many sperm cells result from meiosis? 9. How many egg cells result from meiosis? U8P4 1. What are the benefits of asexual reproduction? 2. What are the disadvantages of asexual reproduction? 3. What are the benefits of sexual reproduction? 4. What are the disadvantages of sexual reproduction? 5. List 3 methods of asexual reproduction. 6. List 2 methods of sexual reproduction. Complete the chart below. Mitosis Meiosis Types of cells that undergo it Number of daughter cells produced Genetic makeup of daughter cells Are daughter cells haploid or diploid? U8P5 Define: a) carcinogen b) apoptosis c) cancer 1) What is a tumor? 2. Describe what causes cancer on a cellular level. 3. Draw & describe the steps of cancer development. 4. What are stem cells? 5. What can stem cells be used for? 6. How do internal & external cell regulators work? 7. Name 4 carcinogens. UNIT 8 – CELL DIVISION STUDY QUESTIONS U8P1 Define: a) interphase b) cytokinesis c) daughter cells d) spindle fibers e) diploid f) centriole g) haploid h) gamete i) somatic cells k) chromatin l) centromere 1. Which increases faster as a cell grows, its volume or surface area? 2. List 3 reasons why cells divide. 3. Draw & label a chromosome. 4. List the phases of the cell cycle in order. 5. If your diploid number is 20, what is your haploid number? 6. What is the diploid number for humans? 7. Are somatic cells diploid or haploid? 8. Are gametes diploid or haploid? U8P2 Define: a) prophase b) metaphase c) anaphase d) telophase e) cytokinesis f) sister chromatid 1. List the phases of mitosis in order. 2. What are some differences between plant & animal cell division? 3. In mitosis, if the parent cell has 8 chromosomes, how many will the daughter cells have? 4. List & briefly describe the stages of interphase. U8P3 Define: a) homologous chromosomes b) crossing over 1. In meiosis, if the parent cell has 8 chromosomes, how many will the daughter cells have? 2. What happens when cells come into contact with each other? 3. How are gametes produced? 4. What is crossing over? 5. Why is crossing over important? 6. When does crossing over occur? 7. When during meiosis does reductive division take place? 8. How many sperm cells result from meiosis? 9. How many egg cells result from meiosis? U8P4 1. What are the benefits of asexual reproduction? 2. What are the disadvantages of asexual reproduction? 3. What are the benefits of sexual reproduction? 4. What are the disadvantages of sexual reproduction? 5. List 3 methods of asexual reproduction. 6. List 2 methods of sexual reproduction. Complete the chart below. Mitosis Meiosis Types of cells that undergo it Number of daughter cells produced Genetic makeup of daughter cells Are daughter cells haploid or diploid? U8P5 Define: a) carcinogen b) apoptosis c) cancer 1) What is a tumor? 2. Describe what causes cancer on a cellular level. 3. Draw & describe the steps of cancer development. 4. What are stem cells? 5. What can stem cells be used for? 6. How do internal & external cell regulators work? 7. Name 4 carcinogens.