Animal Diversity
advertisement

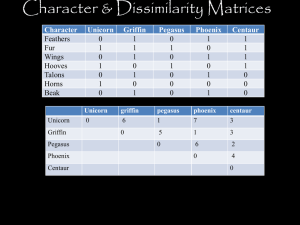
D I V E R S I T Y ANIMAL Where are We? What makes an Animal? • • • • • Eukaryotic Heterotrophic Multicellular Diploid Are motile at some stage of the Life Cycle Evolutionary History in Development Why is embryonic development important in our understanding of evolution? • Evolutionary Developmental Biology (“Evo-Devo”) – Comparisons of developmental characters in different organisms can often reveal ancestral relationships – Excellent characters for use in building phylogenies Ernst Haeckel 1892 Development Videos • Development of the Blastula • Gastrulation Blastopore Mouth: protostomes Anus: deuterostomes Triploblastic Development Protostomes (“mouth first”) Blastopore= mouth Deuterostomes (“mouth second”) Blastopore= anus Body Plan: Symmetry Symmetry Radial Symmetry Bilateral Symmetry Symmetry Practice Tissues • Parazoa - group of organisms without true tissues • Eumetazoa - group of animals with true tissues Germ Layers • Diploblastic – Endoderm + ectoderm • Triploblastic – Endoderm + mesoderm + ectoderm Triploblastic Animals - Body Cavities Red = ectoderm Yellow = endoderm Blue = mesoderm Lophotrochozoa Lophotrochozoa Trochophore larvae Lophophore •Used for filter feeding Ecdysozoa Today’s Lab • Work through all stations (use flowchart!) • Identify unknowns in tank • Show me your tree! True Tissues? Flow Chart yes no Parazoa Eumetazoa Number of Germ Layers? Asymmetry two three Triploblastic Diploblastic Bilateral symmetry Fate of blastopore? Radial symmetry mouth Protostome Acoelomate, Pseudocoelem, or Coelem Which clade? Lophotrochozoa Trochophore larvae or lochophore (or neither) ? Ecdysozoa anus Deuterostome Coelom