Follow Along Sheet Week 8 Lifeline
advertisement

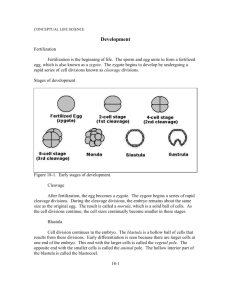
Week 8: Animal Evolution & Development Follow Along Sheet Final Concept Maps Due this week on: For Monday & Tuesday Lifelines: Friday, October 17th, 2014 at 11:59 p.m. For Wednesday – Friday Lifelines: Saturday, October 18th, 2014 at 11:59 p.m. Don’t wait until the last minute to submit them! Final date to withdraw (with a W) is Friday, October 10, 2014 by 5pm. Week 8 Lifeline Points for this Week: 2 Points PPP and 1 Extra Credit HW Remember To Print The EC Homework!! What is an Animal? Members of Kingdom Animalia are: • Eukaryotic and mostly multicellular • ______________ • Mostly ________ Two unique types of tissues are found only in animals: ______ Tissue ______ Tissue Most animals reproduce sexually. The _______ stage usually dominant in the life cycle Reproduction and Development Fertilization occurs when a small flagellated sperm (n) fertilizes a larger, non-motile egg (n), forming a diploid ________ (2n). Cleavage A series of rapid cell divisions by _______ and __________. The number of cells increases while the total surface area of the embryo remains the same. The blastula stage is usually comprised of about _____ cells and occurs roughly one week after fertilization. Cleavage Development Radial vs. Spiral Cleavage Most Deuterostomes: _________ e.g. Humans Most Protostomes: ___________ e.g. Mollusks Gastrulation The process in which the invagination of the blastula creates the ________ The opening of the newly formed cavity is called the ___________ The germ layers, now present in the gastrula, develop into ____________ Zygote to Gastrula Process of cell division: ___________ -> Eight-cell stage -> ___________ -> Blastula -> Gastrula Animal Diversity Animals are classified by four main attributes of their body plans: 1. ______________ 2. Symmetry 3. ______________ 4. Fate of __________ Tissues Groups of cells that have a __________, specialized function Parazoa Lack true tissues (No Endoderm, Mesoderm, or Ectoderm) Most are _____________ Example: Phylum Porifera (Sponges) Eumetazoa Have _______ tissues (Have Endoderm,Mesoderm, and/or Ectoderm) Symmetry Imaginary planes create __________ images. “Bilateria” Exhibits bilateral symmetry Triploblastic - 3 germ layers: • Endoderm • ___________ • Ectoderm “Radiata” Exhibits radial symmetry Diploblastic - two germ layers: • ___________ • Ectoderm Body Cavity _________________ - lack a body cavity altogether Platyhelminth (flatworm) is an example of this. _________________ - body cavity partially derived from mesoderm Nematode is an example of this. __________________ - those with a true coelom derived completely from mesoderm Crayfish is an example of this. Mesoderm Development - When a coelom is formed by introducing a gap surrounded by mesodermal cells at the base of the _____________, between the ectoderm and the endoderm, it is said to exhibit _____________ development. - When a coelom is formed by “pinching off” a portion of the endoderm that develops into mesoderm, it is said to exhibit _______________________ development. Fate of the Blastopore Protostome- __________ Develops from blastopore Deuterostome- __________ Develops from blastopore